23+ Sample Sample Audience Analysis Templates
-

Sample Audience Analysis Template
download now -

School Audience Analysis Template
download now -
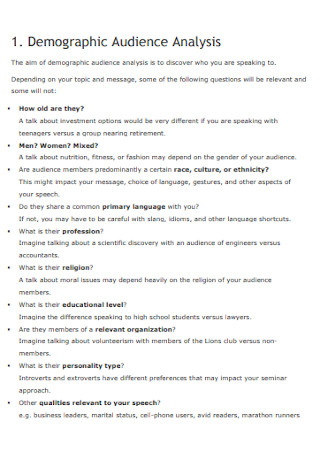
Demographic Audience Analysis
download now -

Audience Analysis Worksheet Template
download now -

Audience Analysis and Segmentation Template
download now -

Purpose and Audience Analysis
download now -

Audience Analysis of Major
download now -
Audience Speaking Analysis
download now -

College of Business Audience Analysis
download now -
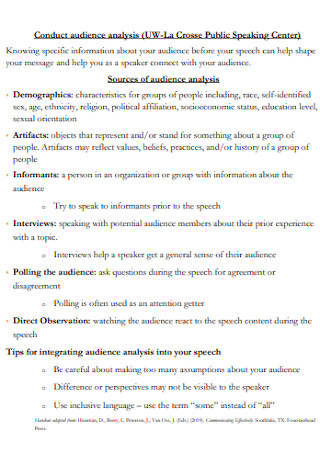
Public Audience Analysis Template
download now -

Basic Audience Analysis Template
download now -

Simple Audience Analysis Template
download now -

Audience Analysis for Memes in Social Media
download now -

Feedback-Driven Audience Analysis
download now -

Teaching Audience Analysis Template
download now -

Audience Analysis in Cyberspace Template
download now -

Audience Analysis Activity Template
download now -

Ten Audience Analysis Exercises
download now -

Target Audience Analysis
download now -

Marketing Audience Analysis
download now -
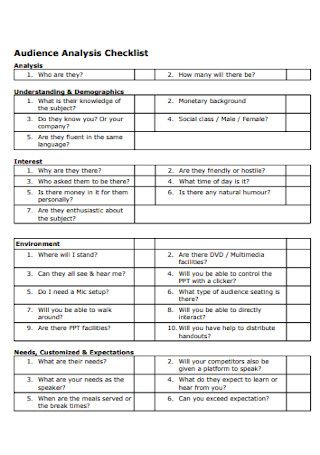
Audience Analysis Checklist
download now -

Audience Analysis Memo Rubric Template
download now -

Standard Audience Analysis Template
download now -

Audience Analysis Evaluation Form
download now
What Is Audience Analysis?
There is no doubt that every person is different from their attitude, interests, beliefs, or levels of understanding. But as a speaker, writer, or reporter, your presentation’s effectiveness might not work out as intended because of failing to observe an audience-driven approach. And in any means of communication, whether it is visual, written, or oral, don’t forget to provide the appropriate level of information and approach to your listeners. And you do that with audience analysis—the process of knowing and examining your audiences.
According to CommBox, a 2005 study reported that out of 80% of businesses that believed they displayed superb customer service, only 8% of their customers actually believed so.
Moreover, another study concluded that 75% of clients agreed that quick response time is the most important customer experience element.
On another note, Statista’s 2020 survey stated that there were around 13.9% of women between 18 and 24 years old who are active on Instagram worldwide.
Why Use Audience Analysis?
We communicate every day. For example, you spread the good news that you won from a lottery by conversing with your family, talking with your coworkers, or responding to your friends’ messages on social media. But in delivering the same message, your audience may react differently. Your family might be delighted. Meanwhile, your colleagues and friends may see it that you’re showing off. And this example is why examining your audience from the demographics, preferences, language, and other metrics is vital to know how to adjust to each audience.
Aside from your everyday communication, audience analysis also helps in marketing, analytics, or serious business. You outline your consumers’ interests, for example, to form strategies in making them want to purchase from your store. Also, audience analysis plays a significant role in technical writing during the initial stages of a project. And in marketing, you would need a more detailed picture of your audience to resonate according to their behavior and preferences. Thus, you reach your target. Nonetheless, these examples are only a few applications of audience analysis, and you can come up with your own too.
Who Prepares the Audience Analysis?
Audience analysis is often done by a small group of researchers whose task is to have an in-depth look at particular recipients or audiences. Whether they belong in marketing, health, social services, communication, or any other business, they can prepare the analysis for research purposes. Also, stakeholders can take part in the process as there are results in the analyses that may intrigue them. An example is the research survey mentioned by CommBox about how out of 80% of companies that believed they observed excellent customer service, only 8% of clients agreed to it. Therefore, what the audience thinks also portrays a lot about a company.
Common Factors that Affect Audience Analysis
It takes a lot of factors to know someone. And how much more when you are expected to analyze a whole audience? But in audience analysis, there are around eight typical factors that help you scrutinize your audience. What are they? Here are the common factors that affect audience analysis:
How to Process an Audience Analysis
Now for the main course, how do you conduct audience analysis? Approaches may differ, but there are common denominators in processing it. And without further ado, here are the easy steps you must follow on how to process an audience analysis effectively:
Step 1: Determine Your Potential Audience
First, address your main objectives and questions for your introductory statement. Are you going to analyze the audience from a published article, speech, or any other example? Be specific with your objectives since those will be your basis in brainstorming and listing your potential audiences. An example is to solve the problem of why Alaska has a high rate of people infected with sexually transmitted diseases. You can think of men and women in Alaska for your potential audience.
Step 2: Note Your Priority Audience
Next, specify your audience further by figuring out your priority audience. Instead of just generalizing the men and women in Alaska, you can prioritize down from a specific age range, gender, and other demographics. A tip is to focus on the group that must change to improve a situation. A common example is teenagers as they are often more curious and active in terms of sex. This step helps you determine who is most affected and how many they are.
Step 3: Identify the Audience Analysis Factors
Remember those factors that affect audience analysis discussed earlier? Don’t forget to write those down in your analysis sheet. And there are plenty of tools you can use to determine the factors like surveys, researches, and questionnaires. Just remember to write each element correctly. Bear in mind that gathering the wrong demographics already assures you in reaching the wrong conclusions at the end.
Step 4: Analyze and Interpret the Data
The real challenge is when you finally have the data to analyze and interpret according to the objectives. Find out the barriers or challenges that let you fail in reaching your audience. Or perhaps, learn the key influencers or the aspects that affected the audience’s behavior, decision, and so forth. Be critical in analyzing by preventing biases and opinions until you can interpret the results accurately.
Step 5: Create Solutions and Strategies
Your conclusion follows after the data interpretation. And your conclusion should answer the problems and questions from the start where you made the objectives. However, don’t simply stop there. It is a big deal to come up with solutions and strategic plans after. Thus, analyzing is not for naught because you can form strategies that can help you next time. Ensure that every strategy created enables you to improve in communicating with your audience. And you have your analysis results to guide you in formulating such solutions.
FAQs
What are the types of audience analysis?
Before you create a speech, report, or presentation, there are three main approaches to how to analyze your audience. You can use demographic, attitudinal, environmental analysis, or a hybrid of all. And these examples are also known as the types of audience analysis.
What is demographic analysis?
Aristotle taught us that a person is more than his or her age. And that statement leads us to why demographic analysis exists?—which aims to understand someone’s gender, age, culture, educational level, race, and more. If you plan to determine your audience in marketing via Instagram, then the common demographic would be women. Specifically, 13.9% of women between 18 and 24 years old are often active on Instagram globally. Hence, aim to market on the platform that appeals mostly to these women, so your target reach is effective.
What is attitudinal analysis?
Attitudinal analysis teaches us to discover more about audiences according to attitude, beliefs, or values. A notable take refers to what audiences like or dislike. For example, do you wonder what consumers prefer the most in terms of customer experience? According to CommBox, 75% of consumers agreed that quick response time is the most crucial element for customer experience. Thus, you focus on responding to clients as it is their preference.
How long does it take to know someone? The answer varies, but one thing’s sure—it takes time to know people. And just like audience analysis, it takes some time to get the best results. In addition, identifying audiences via extensive research can be complicated. Aside from learning their identities, you delve further by understanding how they receive information from you. So in the audience adaptation, you must rely on your wisdom, creativity, and analytic skills. And you can apply such skills using audience analysis.
