45+ Sample Annual Budgets
-

Annual Church Budget Template
download now -
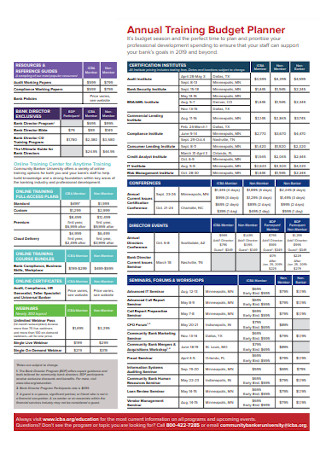
Annual Training Budget Template
download now -

Sample Annual Budget Checklist
download now -
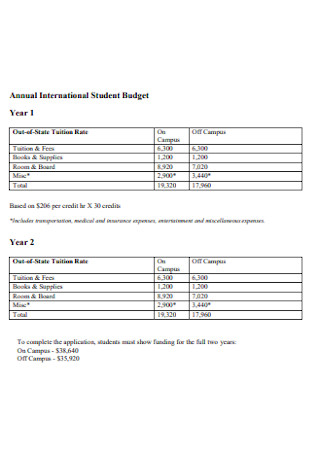
Annual Student Budget Template
download now -

University Annual Budget Template
download now -

Annual Capital Budget Template
download now -

Annual Operating Budget Examples
download now -

Annual Business Plan Budget
download now -

Simple Annual Operating Budget
download now -

Annual Research Budget Template
download now -
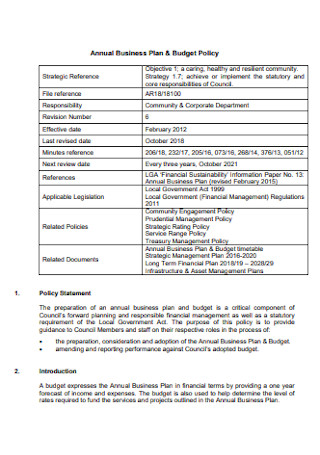
Sample Annual Business Budget
download now -

College Annual Budget Template
download now -

Annual Budget Form
download now -
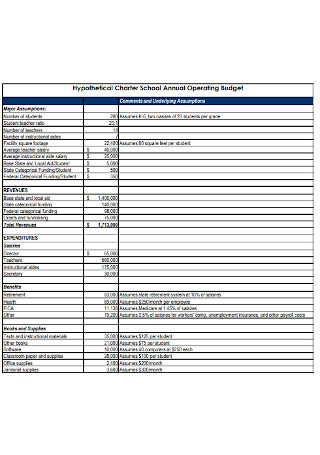
School Annual Operating Budget
download now -

Monthly and Annual Budget
download now -

Annual Event Budget
download now -
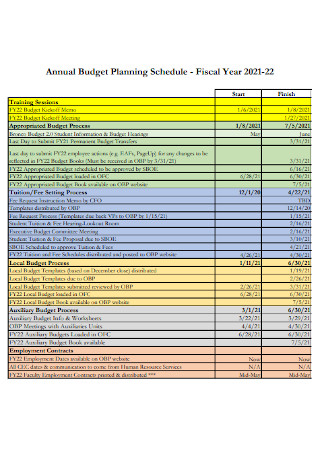
Annual Budget Planning Schedule
download now -
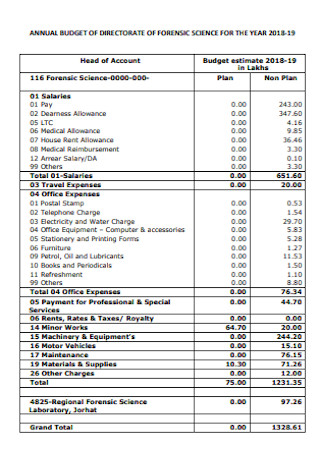
Annual Science Budget Template
download now -
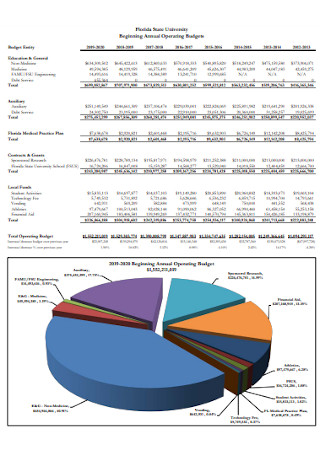
Beginning Annual Operating Budget
download now -
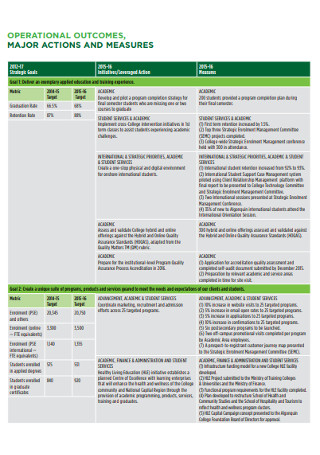
Annual Business Budget Template
download now -
Marketing Annual Budget
download now -

State Annual Budget Template
download now -
Annual Budget Receipt Template
download now -

Annual Budget Report Template
download now -

Project Annual Budget Template
download now -
Town of Webstar Annual Budget
download now -
General Annual Budget Template
download now -

Annual Budget Preparation Template
download now -

Simple Annual Budget Template
download now -

Annual Year Budget Template
download now -
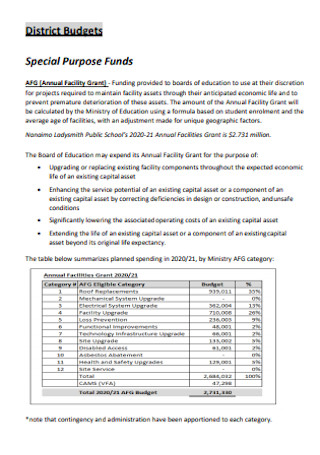
Preliminary Annual Budget
download now -
Annual Budget Proposal Template
download now -
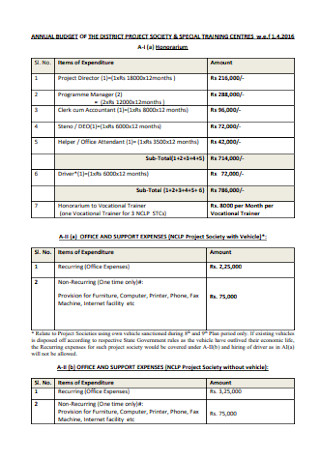
Project Annual Budget Format
download now -

Minutes of Meeting Annual Budget
download now -

Associated Student Annual Budget
download now -

Annual Financial Budget Template
download now -

Sample Annual Analyst Budget
download now -
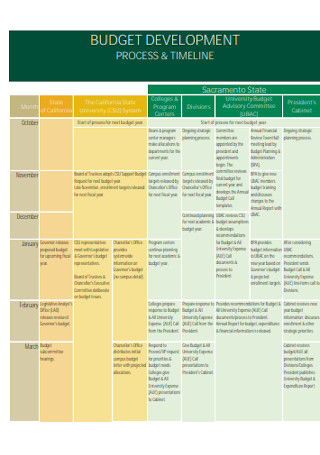
Annual Development Budget Template
download now -

Anniual Monitoring Budget Template
download now -
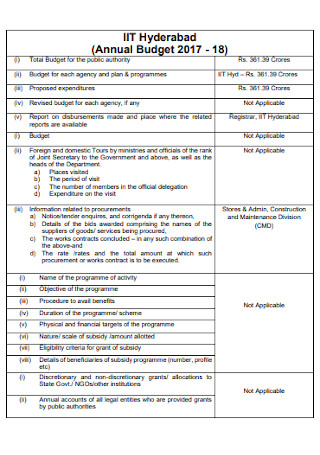
University Annual Budget Template
download now -

Annual Making Budget Template
download now -

Final Annual Budget Template
download now -
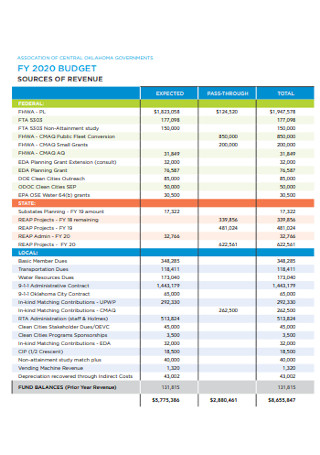
Annual Work Plan Budget
download now -
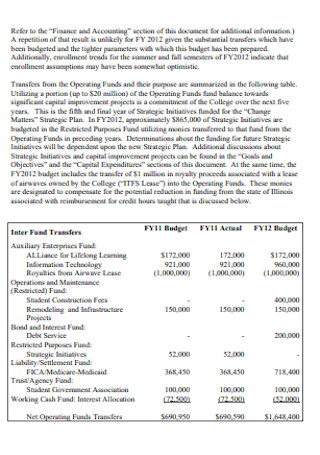
Board of Trustees Annual Budget
download now -
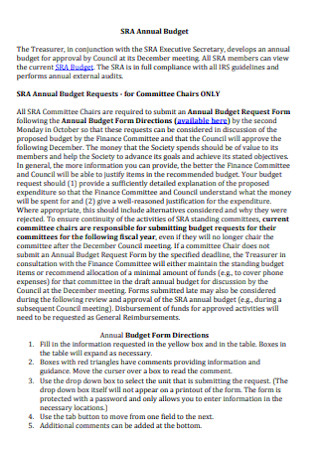
Standard Annual Budget Template
download now -
Annual Revenue Budget Template
download now
What Is an Annual Budget?
An annual budget details an organization’s projected income and expenses for the coming year. The process of developing an annual budget entails balancing a company’s sources of revenue against its expenditures. In many cases, especially for non-individuals, an annual budget comes with a balance sheet and cash flow statement. Individuals, companies, agencies, governments, and other kinds of organizations that need to manage and track their financial activity use annual budgets. Annual budgets are balanced when projected expenses equate to projected revenues. There is a gap if the costs exceed its revenues, and it is in surplus if its earnings exceed its expenses. Annual budgets cover either a fiscal or a calendar year. These budgets aid organizations and businesses in planning for the coming year and making the required modifications to achieve financial objectives. Annual budgets support individuals in managing their finances better. Annual budgets are critical and frequently mandated for effective planning for corporations, governments, and other organizations in terms of sources of revenue and financial needs, liabilities, and equity to support operations over one year; and cash flows used for reinvestment, financial planning, or contingent purposes.
According to the United States Census Burea’s Annual Capital Expenditures Survey, between the years 2011 to 2020, the total spending of United States nonfarm organizations amounts to $463.5 billion or 37.3 percent from $1243 billion in 2011 to $1706.4 billion in 2020.
Components of an Annual Budget
An annual budget is a vital planning tool and document for different industries and organizations to guarantee their operations, projects, and activities for the fiscal year. As such, businesses must construct an annual budget that contains all the relevant information to process and implement the following year’s activities and company projects. When an organization understands its obligations and opportunities, it sets itself up for better objectives and priorities for long-term relationships with stakeholders, clients, and consumers while making better hiring and onboarding decisions. The contents of the annual budget depend on how large the allocated budget is and the number of programs and activities the business lines up. The section below covers the different components of an annual budget and a brief description of each.
How To Prepare an Annual Budget for an Organization
When working on a company’s annual budget, there are various things to consider, including the company’s priorities for the following fiscal year and what benefits the company for specific stages of the organization’s growth and development. It takes an organization-wide budget planning procedure to incorporate the projected income and expenses for an organization to plan for its annual budget. Develop an annual budget for the company by following the steps below.
1. Review the Company’s Profit and Loss Statement in a Useful Format
Begin the annual budget planning process by examining the profit and loss statements from the past two years, removing all unusual and unexpected expenses, including one-time revenue. Average the numbers from the previous two years’ profit and loss statements, then modify them for increasing expenses during the year. Make any changes necessary to take into account variances in operating profits, one-time investments, market trends, and revenue the company foresees in the coming year. Consider how changes in one area impact others. Construct a spreadsheet detailing all the information to make it easier for the organization to list all the funding sources and expense categories. Using Excel spreadsheets enables companies and individuals to assign funds to their proper categories to see how much money is available for an expense category.
2. Take a Closer Look at Company Expenses
After gaining a general idea of the company’s revenue and expenses for the year, consider looking at the company expenses further. Several of the company’s expenses are fixed costs, including business insurance, rent, leases, and other services and facilities that the company uses daily. Take a closer look into the current rates the company disposes of to check if the company can negotiate more favorable terms and conditions on insurance or other services. The organization must also consider employee compensation, which must be equivalent to the company’s revenue and profitability. Take into consideration whether the company still requires the need to hire and how hiring affects and influences other areas of the budget. An organization also accounts for the level of experience the company requires an applicant to have to optimize their roles and functions.
3. Examine and Derive All the Company’s Capital Expenditures
The organization must also account for capital expenditures such as new computers, machinery, furniture, and other items for the company. If the company is in the process of hiring new employees, for example, they require resources and other equipment to fulfill their jobs properly and efficiently. Consider the list of equipment and supplies the company needs to buy for new hires. Take into account any facilities the company needs to acquire or update in to produce a specific product or service. Consider how the company investment affects the company output. While it is tempting to postpone major investments, the decision affects delivery timing, product quality, and output, all of which have a significant impact on revenue over time.
4. Calculate the Business’ Cash Flow for the Year
Cash flow refers to the amount of cash that goes in and out of a company. Businesses earn money from sales and spend cash on expenses. They also receive revenue from interest, investments, royalties, and licensing agreements, including selling products on credit with the expectation of receiving the money owed in the future. Financial reporting seeks to evaluate the sums, timeframe, and uncertainty of cash flows, as well as where they arise and where they go. It is critical for determining a bank’s profitability, adaptability, and overall financial performance. Positive cash flow indicates that a company’s liquid assets continue to rise, allowing it to cover liabilities, reinvest in its company, return money to shareholders, cover expenses, and provide a buffer for future financial problems.
5. Input and Store the Budget in the Finance System
Businesses can evaluate their monthly revenue and expenditures by dividing the annual budget to represent the 12 months of a year. When the company reviews its monthly financial statements, make a comparison with the funding to acquire a better sense of the differences in the projections. It helps the company to keep expenses under control while also creating a more precise annual budget in the future.
FAQs
Why are annual budgets important?
Businesses must construct their annual budgets to encourage and allow them to set their priorities, objectives, and spending limits, enabling the business to track their finances for long-term planning.
Who sets an annual budget?
When talking about the budget for the United States of America, the entity responsible for setting the annual budget is Congress through spending and tax decisions using various legislative actions.
What is the purpose of constructing a budget?
A budget plan enables an organization to plan how it can spend its money monthly, to guarantee that it does not run out of funds to continue daily business operations and processes while keeping money stored for emergencies.
An annual budget is an essential planning tool for different organizations, especially those that are planning to expand their operations or are starting to make a name for themselves in the industry. Annual budgets require a company to look back on their previous years’ spending to make an accurate representation of an annual budget for the following fiscal year. Organizations must consider constructing the annual budget with the help of different department heads to guarantee each division gets the necessary funding. Craft an annual budget for the organization by browsing through our collection of annual budget samples to help construct an efficient document, only from Sample.net.
