39+ SAMPLE Corporate Budget
-
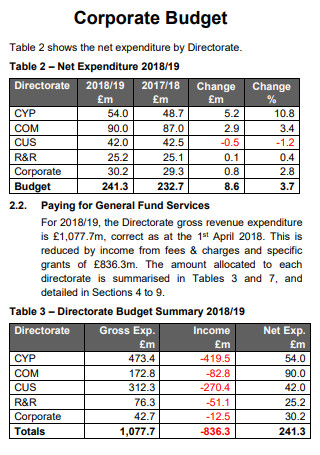
Corporate Budget
download now -

Corporate Budget Impacts
download now -
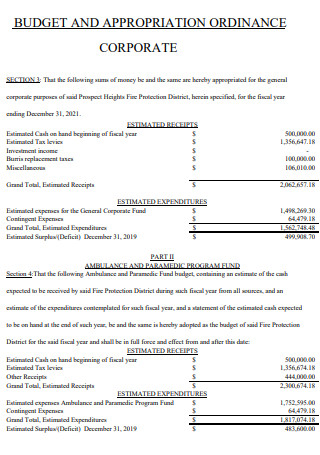
Appropriation Ordinance Corporate Budget
download now -
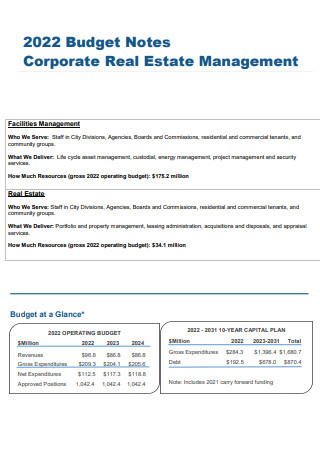
Budget Notes Corporate Real Estate
download now -
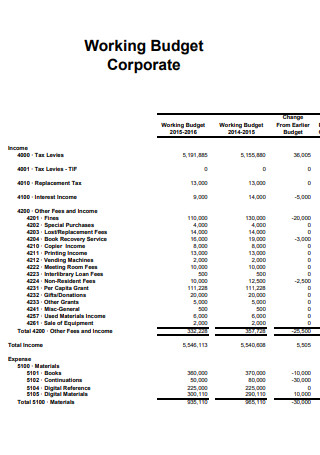
Working Budget Corporate
download now -
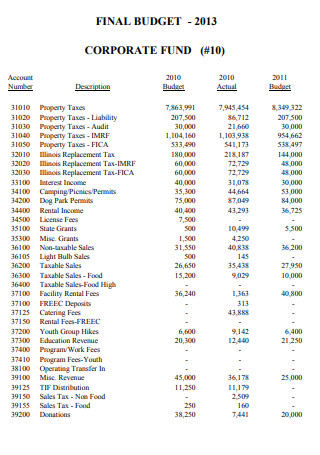
Final Budget Corporate Fund
download now -

Effective Corporate Budgeting
download now -

Corporate Budget Planning
download now -

State Corporate Budget
download now -
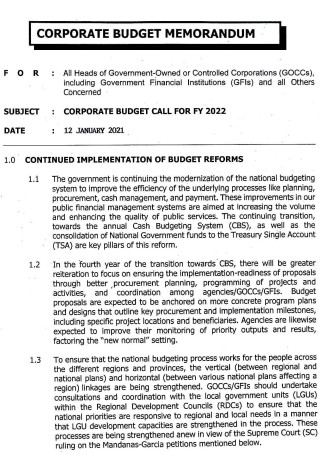
Corporate Budget Memorandum
download now -
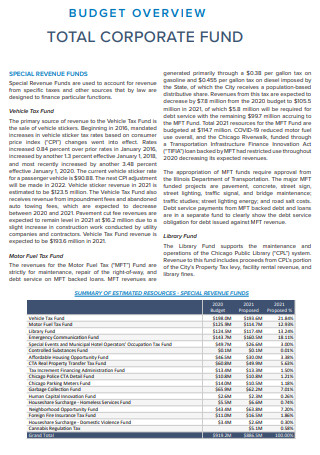
Corporate Budget Overview
download now -

Proposed Corporate Budget
download now -

Corporate Budget Director
download now -

Corporate Budget Monitoring Policy
download now -
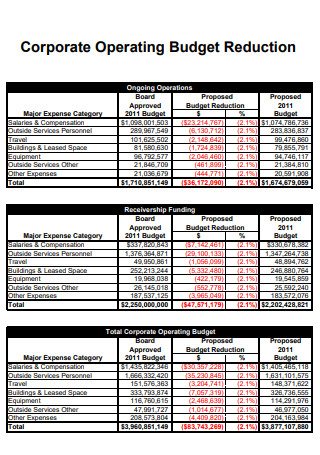
Corporate Operating Budget Reduction
download now -

Corporate Budget Setting
download now -
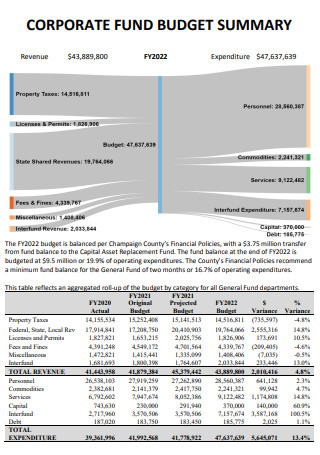
Corporate Fund Budget Summary
download now -

Increased Corporate Budget
download now -

Corporate Services Operating & Capital Budget
download now -
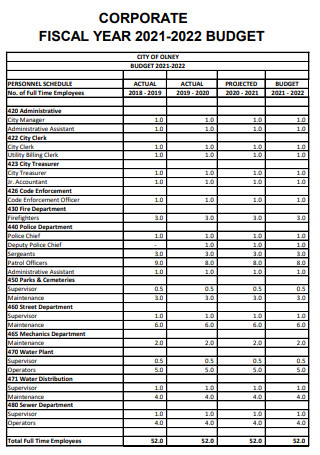
Corporate Budget Fiscal Year
download now -
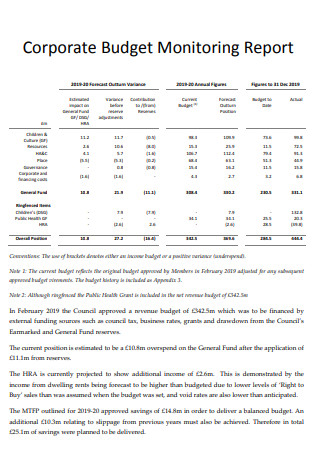
Corporate Budget Monitoring Report
download now -

Corporate Budget Committee
download now -

Corporate Operating Budget Variance
download now -
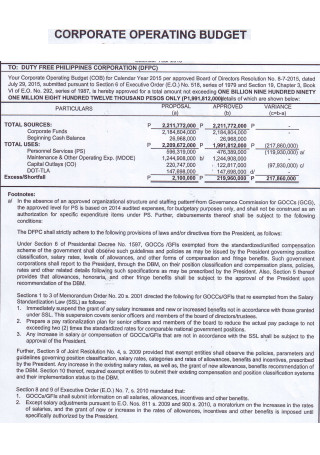
Corporate Operating Budget
download now -

Corporate Plan and Budget
download now -

Corporate Workplan Budget
download now -

Corporate Services Budget Overview
download now -

Corporate Welfare Budget
download now -

Corporate Travel Budget
download now -

Corporate Budget Five-Year Plan
download now -

Corporate Budget Agreement
download now -
Corporate Budget Officer
download now -
Policy Concerning Corporate Budget
download now -
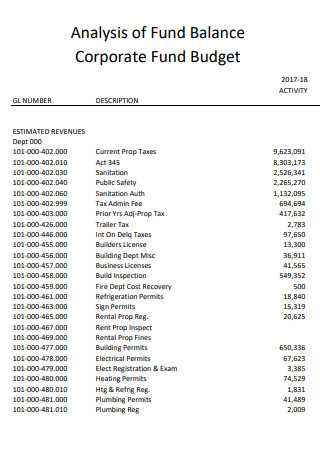
Corporate Fund Budget
download now -

Corporate Budget Instructions
download now -
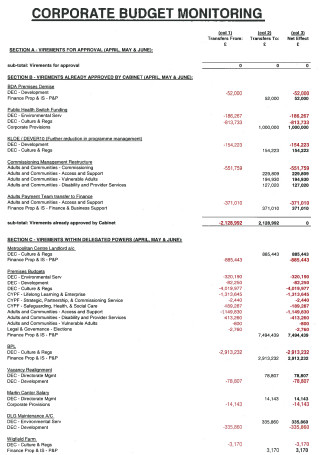
Corporate Budget Monitoring
download now -
Health Corporate Budget
download now -
Basic Corporate Budget
download now -
Corporate Budget Example
download now -
Corporate Budget Template
download now
What Is a Corporate Budget?
A corporate budget is a document that details a comprehensive estimation of the possible business expenses and revenues within a particular fiscal period. Each corporate budget deals with and includes income guidance and expense estimations. The information comes from previous corporate budgets dealing with revenue and expenditure with necessary adjustments for the future. Constructing any budget plan for a company is a top priority for the finance department since every business needs a budget to manage daily operations. In the present setup, business or corporate budgeting is in the hands of the corporate performance management (CPM) team. CPM is a business approach that deals with planning, budgeting, and forecasting different business activities and functions, linking it to organizational strategies and techniques to its business plans. Afterward, the CPM also monitors the execution of these plans. Modern developments in software allow CPM teams to develop corporate budgets with great accuracy and confidence. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems use the applications to integrate budget plans complete with real-time performance monitoring that allows the company to forecast budgets with greater accuracy and visibility, following the flow of money coming in and out of the organization.
According to a statistical study from Clutch, out of the 335 small businesses in the study, half of these companies did not create an official and formally documented record of the company budget in 2020. It speaks volumes as many businesses do not see the significant impact of writing a business budget for their operations.
Components of a Corporate Budget
When creating a corporate budget, there are different things to consider. Remember that the principal goal of the corporate budget is to indicate business expenses and profit for an entire fiscal period, and it must show accuracy as much as possible. A company that has a corporate budget sets itself up to align monetary needs to events or projects that the business needs to achieve its short and long-term goals. The following section identifies the necessary components that a corporate budget must have to ensure the continuity of business operations towards success.
How To Write a Corporate Budget
Working on corporate budgets or budgets, in general, require companies to look back on previous budget statements and records about income and expenses. Many businesses find it easier to create these budgets if they have been serving for a long time as they have accurate information to look back on in creating a more accurate budget. For startup businesses, market research on the typical costs in the industry and or area to gather budget estimates is the way to go. The section below helps you create a corporate budget for your company.
-
1. Examine the Company’s Revenue
The first step to any budgeting process is to look back on previous years and identify all income sources. Combine all of the revenue data you have to discover where the money comes from every month. For an accurate representation of the company income, calculate for revenue and not profit. After identifying all the possible income supplies for the company, compute the monthly income by using the information you have from the previous fiscal year. Through analyzing the monthly income, you can determine the peak seasons when the company performs. Knowing about the seasonal changes allows the company to make the necessary preparations in terms of the corporate budget.
-
2. Deduct the Fixed Costs
The next step to creating the corporate budget is to add all the fixed costs. Fixed costs are the expenses that are recurring to ensure that the daily operation remains uncompromised. These costs occur daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, or annually, and knowing what they are can become advantageous to writing the budget. Fixed costs include rent payments, debt repayments, employee payroll, asset depreciation, taxes, and insurance. Different businesses have various fixed costs, so it is critical to take note of all of them.
-
3. Identify the Variable Expenses
Variable expenses are changing costs depending on the goods and services that the company offers its customers. Many of these expenses guarantee that the company continues its daily tasks and business operations. Variable costs also include those that are unrelated to business functionality. Discretionary expenses, like seminars and training programs, increase business profitability. Other examples of variable costs include office supplies, marketing costs, and utilities. During dry seasons, companies must be wary of their variable expenses and take advantage of discretionary activities during peak seasons.
-
4. Prepare Contingency Funds For Unexpected Expenses
Whether you own a business for a long or short period, one-time expenses always come at the most inconvenient times. Prevent the worry of incurring unexpected expenses when you incorporate and assign extra cash in the budgeting process along with contingency planning within the budget. It is convenient to have emergency funding, making the company ready to replace or issue newer equipment and other office necessities whenever necessary. Writing for these unexpected expenses helps the company save time and money worrying about where to get funding.
-
5. Create a Profit and Loss Statement
After collecting the necessary information and completing the steps above, you can create a profit and loss statement. The profit and loss statement just asks you to add and subtract the income and expenses for a specific period. If the results return positive, then the company has a profitable month. If not, there is a loss that the company needs to get back in the following months to come. Losses are not something to lose hope over. There are times when months are just unprofitable. As such, you can make the necessary adjustments for the next month to recover.
-
6. Develop an Outline for the Corporate Budget in a Positive Light
Projecting what happens in the following years comes from experience, and the more experienced an individual is, the more accurate these predictions happen. The business can create a future-focused corporate budget by using the profit and loss statement. Through the statement, you can better understand and predict the seasonal peaks and troughs of the business. Examining the profit and loss document provides sufficient explanations and information to the fluctuations happening in business profitability.
FAQs
What are the three kinds of budgets?
There are three kinds of budgets in different sectors and industries. These include balanced budgets, deficit budgets, and surplus budgets.
Why is corporate budgeting necessary for companies?
Through realistic and accurate budgets, the business can strive to reach its short-term and long-term goals. The budget provides essential information to operate the business according to the means of the company while managing unexpected challenges and gaining profit.
How to manage a corporate budget?
There are different ways that an organization can manage its corporate budget. It includes:
- Setting the budget information appropriately and accurately
- Delegating expenses effectively
- Collaborating with different departments
- Standardizing budget reports
- Collecting complete and accurate monetary values
- Choosing an easily navigable budgeting software
- Updating budgets on schedule
- Keep looking onwards
Writing a corporate budget for a starting company is always a daunting task. However, with practice, experience, and research, the company can create an accurate and valuable document that ensures continuous operations with minimal hiccups along the way. Building a budget helps a company track its income and expenses, ensuring that there is a positive indication in terms of profit. Write a corporate budget for the company by using previous budget analysis and documents, and select and download from the 39+ SAMPLE Corporate Budget in PDF above. Get yours today, only at Sample.net.
