20+ SAMPLE Non Profit Budget
-
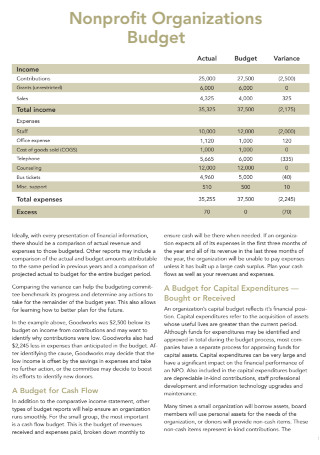
Non Profit Organizations Budget
download now -

Non Profit Budget Process
download now -
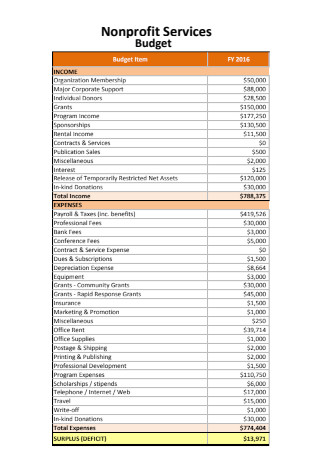
Non Profit Services Budget
download now -

Non Profit Annual Budget Checklist
download now -
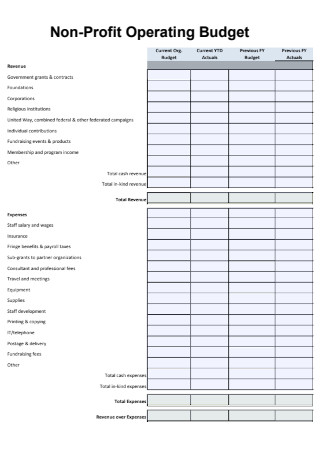
Non Profit Operating Budget
download now -
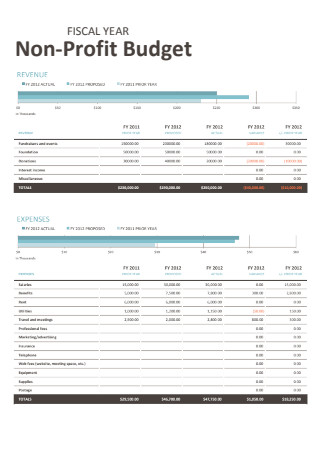
Non Profit Fiscal Year Budget
download now -
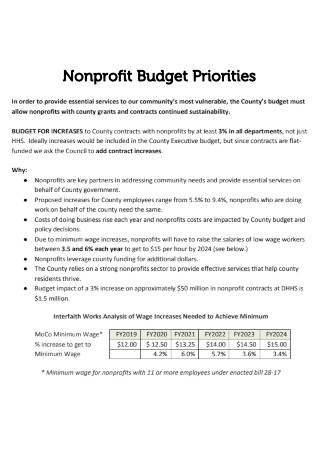
Non Profit Budget Priorities
download now -

Non Profit Budget and Credit Counseling Agency Bond
download now -

Budget Non Profit Request Form
download now -

Non Profit Agency Supplement Budget & Evaluation
download now -
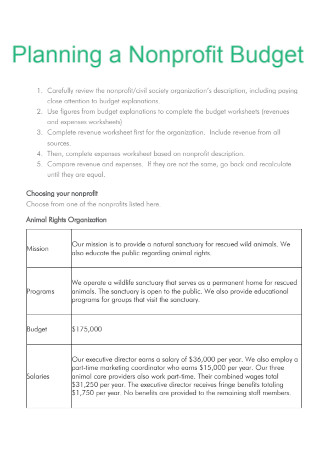
Planning a Nonprofit Budget
download now -

Application for Approval of Nonprofit Budget
download now -
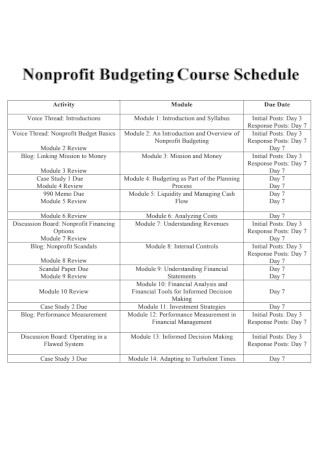
Nonprofit Budgeting Course Schedule
download now -

Nonprofit Pay Equity & Sustainability Budget Analysis Report
download now -

Simple Non Profit Budget
download now -

Basic Non Profit Budget
download now -
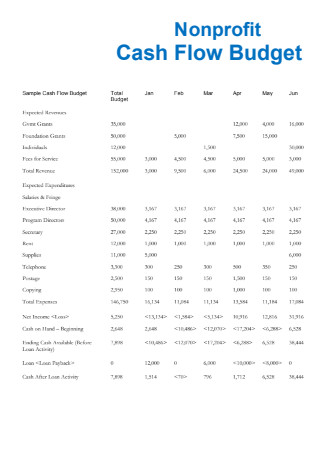
Non Profit Cash Flow Budget
download now -

Nonprofit Budgets Income and Expenses
download now -
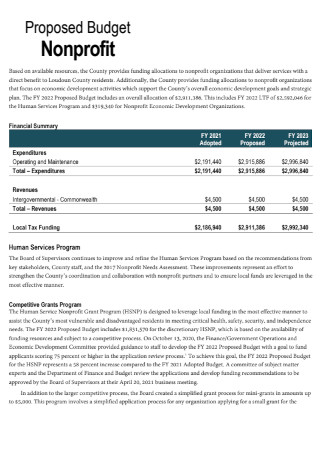
Non Profit Proposed Budget
download now -
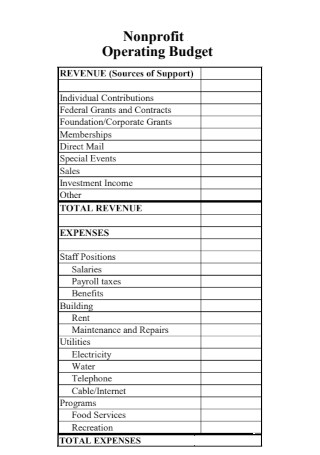
Sample Non Profit Budget
download now -
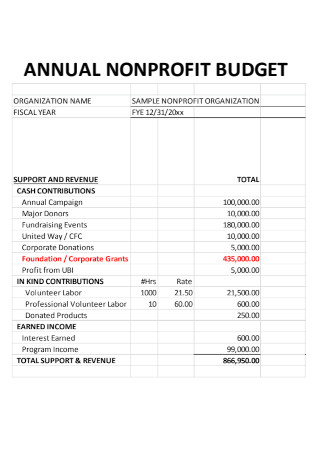
Annual Non Profit Budget
download now
FREE Non Profit Budget s to Download
20+ SAMPLE Non Profit Budget
What Is a Non Profit Budget?
Components of a Non Profit Budget
How To Develop a Non Profit Budget for a Nonprofit Organization
FAQs
What is included in a nonprofit operating budget?
Why does a nonprofit need a budget?
What is the significance of a nonprofit budget?
What Is a Non Profit Budget?
A non profit budget is a planning document that nonprofit organizations use to predict probable expenses and allocate the necessary resources for the organization. It details the cost that the nonprofit organization incurs and the revenue that the organization expects to generate throughout the implementation of the project or program. Nonprofits can create a budget for a fiscal year, a fundraising event, or their next capital campaign that can span over the years. A nonprofit organization can craft two primary budgets for specific purposes, including the operating budget and the capital budget. The nonprofit operating budget details the breakdown of annual projected revenues and expenses for the organization. It identifies the nonprofit revenue and its funding sources as well as the operating expenses of a program with its overhead costs. Meanwhile, a capital budget represents the possible expenditures and income that come from multi-year, long-term projects and programs. The budget covers the capital campaigns and other large-scale expense campaigns that a nonprofit organization implements. Throughout the year, the non profit budgets must undergo regular reviews to monitor the progress of different programs and projects, fundraising successes, and financial standing. It means that the budget is not a final document. Rather, it is a living document that must be the foundation of all financial activities of the organization.
According to The 2019 Nonprofit Employment Report, the data shows that nonprofit organizations have more than 12.3 million jobs, equating to 10.2 percent of the United States private sector employment. As such, nonprofit employees are the third-largest workforce among the US industries, following after the retail and food industries.
Components of a Non Profit Budget
Whether the non profit organization is writing the budget for the first time on their own or if they are writing with the help of an expert accountant, the organization must make sure to have a complete and comprehensive document by indicating the expected revenue and expenses in the budget. As such, there are two main components that every non profit budget must comprise, and the section below provides a more descriptive detail of each element.
How To Develop a Non Profit Budget for a Nonprofit Organization
As a nonprofit accountant or as a member of the accounting team for the nonprofit organization, it is your responsibility and duty to make comparisons between the budget and the actual income and expenses the organization incurs for a period. In doing so, the accounting department can help refine the budget and develop more accurate and realistic estimates for the budget in the future. Budgeting is a process that helps prevent the prevalence of unsolicited and unnecessary expenses. Instead of straining the financial capabilities of the nonprofit organization by limiting expenditures, make sure that the items in the budget are realistic and manageable for the organization. The section below provides a guide to help you develop a non profit budget for the organization.
-
1. Set a Standard for Bookkeeping Activities and Procedures
A budget requires an organization to make realistic decisions about past financial information. It is vital to prioritize standardized bookkeeping procedures, to create an effective and accurate non profit budget. Bookkeeping involves keeping financial records and documents, in contrast to accounting, which utilizes these records for strategic financial decisions. For bookkeeping, time is of the essence. If the records are not up to date, it results in a slow process of budgeting that leads to misinformed decisions. To save time, utilize an organized and easily understandable ledger, record all transactions promptly, and allocate all expenses appropriately. Bookkeeping serves as the foundation of effective accounting and proper budgeting for the nonprofit.
-
2. Examine All Funding Sources for the Nonprofit
It is necessary to identify the income sources for the organization. It includes fundraising activities, nonprofit grants, and all other funding that stems from philanthropic activities. The revenue defines the funds that a nonprofit needs to spend on different activities according to the received donations. Past funding campaigns and grant proposals are a good indicator of what future fundraising programs and projects look like. At present, it is difficult to predict the state of a nonprofit’s revenue with the state of the economy. For nonprofits that have been striving for many years, look at possible measures to counter a similar situation in the past and implement them for the present and future. For newer organizations, research studies and other methods can help you cope with the present situation. In times of difficulty, nonprofits must send out grant letters and reach out to the major donors of the organization. Make sure to continue the implementation of raising funds for the nonprofit, especially during an economic crisis. Provide alternative ways to donate, raise money, and keep donors involved in activities.
-
3. Consider the Fixed Expenses
When creating the non profit budget, the first thing to consider and incorporate into the plan is the fixed expenses. Fixed expenses are consistent monthly expenses that the organization incurs. It includes payments for office rent, utility bills, employee payroll, continuous programs, and software investments. These make up the majority of the operational budget of the nonprofit. While these expenses are predictable from month to month, there are consequences for missing due dates. That is why it is crucial to allocate funds for these expenses first.
-
4. Put Consideration on Variable Expenses
After calculating the fixed expenses for the budget, the next step is to look into variable expenses. These expenses fluctuate over time and are still necessary to analyze. Variable expenses include fundraising expenses that fluctuate according to the fundraising strategy and the type of campaign. It also covers marketing costs to spread the mission statement and campaign events. Event expenses are costs that are dependent on the type of event, venue, and activities. Variable expenses are difficult to estimate as they vary for each event, and it is advisable to use records of variable expenses from before to estimate the budget.
-
5. Analyze the Budget for Each Year
Budgeting is a continuous activity. For starting nonprofits, the first budget you create is crucial to the success of activities and programs year-round, making sure it is well-researched and accurate. Over the years, it becomes easier to estimate budgets as there is already an understanding of the yearly income and expenses of an organization. Despite this, it is still advisable to involve the accounting team when creating the non profit budget. Annual budget analysis is vital to ensure better and more accurate predictions, especially for variable expenses, and see if there is room for additional fixed costs.
FAQs
What is included in a nonprofit operating budget?
A nonprofit operating budget consists of the planned financial activities a nonprofit is planning to implement for the following year, visualizing the expected revenue of these activities, and the expenses it incurs to implement them.
Why does a nonprofit need a budget?
Similar to other organizations, nonprofits need an accurate budget. It enables them to achieve their organizational goals, mission, and vision statement for success and manage their cash flows efficiently to guarantee they have sound financial health and organizational stability.
What is the significance of a nonprofit budget?
The nonprofit budget serves as a guide for an organization to achieve financial sustainability. It helps track the revenue and expenses, limiting the chances of stopping activities or programs due to money shortages. It also gives the organization to operate for the long term, and gives the organization financial control, knowing the cash flow of the nonprofit.
A non profit budget is a document that helps a company to gain financial sustainability by creating an accurate representation of the foreseeable revenue and expenses the organization encounters in a year. A nonprofit organization needs to have a clear view of its expenses for the following year to guarantee the implementation of its programs, projects, and activities with little to no issue. Write a non profit budget that is comprehensive and accurate by consulting with the accounting team. Construct the document by downloading from the 20+ Sample Non Profit Budget in PDF, only from Sample.net.
