13+ Sample Project Plan Budget
-
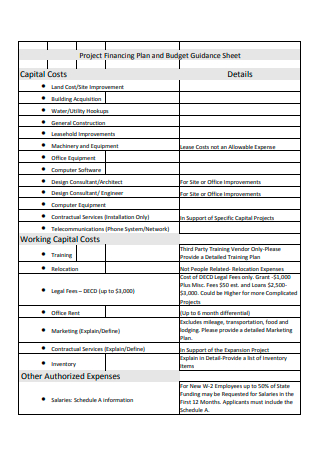
Project Financing Plan and Budget Sheet
download now -

Project Work Plan Budget
download now -

Project Capital Improvement Plan Budget
download now -

Project Plan Budget in PDF
download now -

Basic Project Plan Budget
download now -

Capital Project Improvement Plan Budget
download now -
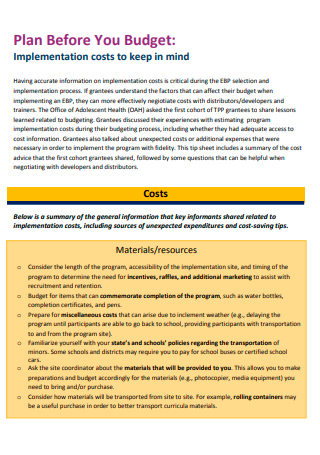
Project Plan Budget Example
download now -

Standard Project Plan Budget
download now -

Project Plan Budget For Community Education
download now -

Printable Project Plan Budget
download now -

Sample Project Plan Budget
download now -

Business Project Plan Budget
download now -

Project Plan Legislative Budget Commission
download now -

Capital Project Fund Plan Budget
download now
What Is a Project Plan Budget?
The budget plan for a project is a technique that project managers use to estimate the project’s entire cost. A budget template for a task comprises a detailed assessment of all costs expected to be incurred before completing the project. Budgets for large commercial projects might be many pages long. These projects frequently incur a high amount of fees, including labor, material procurement, and running expenses. The budget plan for the project is a dynamic document in and of itself. It is updated constantly during the duration of the project. According to statistics, 54% of small firms with a budget predict an increase in their budget in 2021, indicating that enterprises anticipate a prosperous business environment as the COVID-19 pandemic subsides. Fifty-four percent of small firms have established an official budget for 2021, suggesting that most enterprises recognize the benefits of budgeting.
Benefits of Project Plan Budget
Budgeting is critical when developing any significant business endeavor. Without a well-planned budget, initiatives might disintegrate and remain unfinished. On the other hand, budgeting is not a straightforward procedure, as budgets might be fixed, depending on the industry in which the project is being performed and the availability of different revenue sources. Nevertheless, budgeting has a variety of benefits that a project manager should consider.
Tips for Smart Budgeting in a Business
Unsurprisingly, launching a business involves a significant financial investment, but expenses do not stop after the company is up and operating. As a small business owner, you’ll desire to establish and adhere to a dependable budget to keep your finances under control. Create a sustainable yet reasonable budget for your firm before you begin your journey in the business world. We compiled a list of professional suggestions for small company owners wishing to stay on top of their money.
1. Make your staff a part of the process.
Simply because you own a company does not mean that all of the pressure is on you. Because your budget affects everyone in your organization, each employee should be informed of its fundamentals and contribute any insights or recommendations they consider relevant. Additionally, employees should be informed of any changes they make that may affect them or your business, so they understand what is expected of them in the future.
2. Make sure you are not underpaying yourself.
Many business owners, particularly initially, are tempted to save every penny they earn for their budget. And, while having backup funds is critical, your budget should provide ample room for you to be paid. Specific individuals feel terrible about compensating themselves when the funds could be better spent elsewhere. However, the proprietor is still an employee at the end of the day. You must indemnify yourself appropriately and find alternate means of paying off other debts.
3. Bear in mind that time is money.
One of the most common errors small firms make is failing to budget for time. This reminds business owners that time is money, so working with individuals who are compensated for their time. Timing miscalculation raises expenses directly, and not only do you begin to lose time on the delivery schedule, but your team also loses momentum as their collective mind switches to another project.
4. Maintain a constant eye on your finances.
Budgets are never static or consistent; they vary and evolve along with your firm, and you’ll need to adapt them to reflect your growth and profit trends. Regularly revising your budget enables you to exercise greater control over financial decisions, as you will know exactly how much you can provide to spend against how much you anticipate earning. Also, it would help to analyze historical market trends to assist you in preparing for the coming year. From there, you can account for contingencies and unforeseen expenses.
How To Create a Project Plan Budget
Budgeting for a project should be done with the utmost precision. Accuracy is critical because the funding for the project is not self-contained. It affects other aspects of the project, such as the schedule. If the budget for the project is incorrect, your team may be unable to execute deliverables on time. A precise budget for a project plan also accounts for anticipated and unforeseen costs, avoiding cost overruns. The steps that follow serve as a guide and are relevant to the majority of project budgeting circumstances.
Step 1: Analyze cost data from previous projects.
When developing a project budget, reviewing past projects and historical data is one of the most incredible places to start. Attempt to discover comparable projects or projects that contain similar activities. Consider the initial budget projections for those projects and the final expenditures on those projects. Actual last cost data from comparable projects is beneficial because it includes incidental charges. The insights gained from this data will enable you to develop more accurate budget estimations for all future similar projects. Keep this information ready as you progress through the budget creation process. If you lack access to previous data or if this particular project lacks precedents, you may be forced to start from scratch. Maintain accurate records of your calculations and include notes about the project’s actual final expenditures so that the project can serve as a reference for future initiatives. ?
Step 2: Reduce the scope of your project by breaking it down into smaller components. ?
By dissecting your project into its constituent elements, you may more precisely determine the expenses associated with each. While developing a work breakdown structure is one option, there are others more. Numerous project managers discover that effective project management software can assist them in this process. As an example, suppose the project at hand entails the development of a new software application. When breaking down this project, you’ll need to determine which team members will be required, which tools and technology will need to be provisioned during the development process, whether any training will be required and what the testing and deployment processes will entail. Note the work hours necessary for each project increment, the cost limitations, job dependencies, and other pertinent facts. Make a note, if applicable, of historical data for equal increments from past projects. ?
Step 3: Costs connected with each milestone should be estimated. ?
After segmenting your project into milestones and accumulating notes on the resources required for each, it’s time to begin estimating expenditures for each. Begin by determining the project’s primary milestones and then matching each project increment to the milestone it supports. If you have actual data, you can use it to develop cost estimates. If you lack historical data, seek assistance from project stakeholders or competent team members in calculating pricing. Estimate project expenses for both the best and worst-case scenarios wherever possible to provide a range of estimates to work with. While you should record an average estimate for each milestone, knowing the content of probable expenses can assist you in subsequently setting a contingency budget. ?
Step 4: Calculate the total cost of the project. ?
When you break a project down into component sections and estimate its costs separately, you may ignore expenditures related to the entire project. This could include overhead, hiring fees, and so forth. Discuss with the others of the project team and make an effort to identify all other project-related expenses and produce precise estimates for each. Throughout this procedure, you may find it beneficial to consult a budget template. Such templates are easily accessible online or may be incorporated with your preferred project management software. ?
Step 5: Add up your component estimates to arrive at a budget total. ?
After dissecting your project into its component pieces, estimating the cost of each component, aggregating these estimates by milestone, and determining whether any additional project-wide expenses exist, you may compile all of your data into a total budget estimate. Contrast your assessment with previous projects of comparable size and scope; if there are significant variations between your estimate and the final cost of similar previous projects, set aside some time to rectify the inconsistencies. Because each project is unique, your level of confidence in the accuracy of your estimate may vary. It’s worthwhile to keep track of various causes of mistake, such as whether you believe specific figures are under-or over-estimated and by how much. This will guarantee that you are prepared for budget changes as the project proceeds and that the project is a success. ?
Step 6: Allow for contingencies and unforeseeable dangers. ?
Budgeting errors can be accounted for by allowing for contingencies and unplanned expenses. Utilize your budget notes to determine how much additional funds you should set aside for this project to reasonably ensure you will have all you need. ?
FAQs
Why is budgeting critical for planning? ?
Budgeting establishes a spending plan for your money and can assist in ensuring that you always have enough money to cover meals, bills, and other obligations. A budget is an effective strategy for avoiding credit card debt and promoting savings. It is critical to establish an emergency reserve that is three to six months’ worth of costs. ?
What does a budget entail? ?
A budget’s key components are income, fixed costs, variable costs, and profit. Estimating income enables you to determine the maximum amount of fees that your organization can sustain. Then it’s a matter of making the difficult choice of which costs to cut to earn a reasonable profit. ?
What is a PDF budget? ?
A budget is a management tool that any institution can use to ensure the financial component of its objectives, revenues, expenses. It results at the management center level and evaluates economic efficiency by comparing actual results to budgeted results. ?
Budgeting is a critical skill for everybody in the business. Bear in mind that the most challenging budget you’ll ever create is for your first endeavor. Once you’ve mastered this method, your planning efforts will become more efficient, and your projects will consistently stay within budget constraints.
