25+ Sample Budget
-
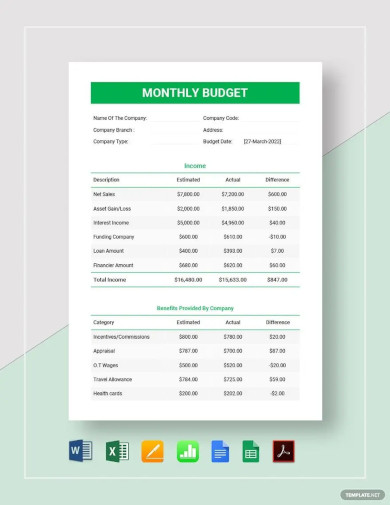
Monthly Budget
download now -
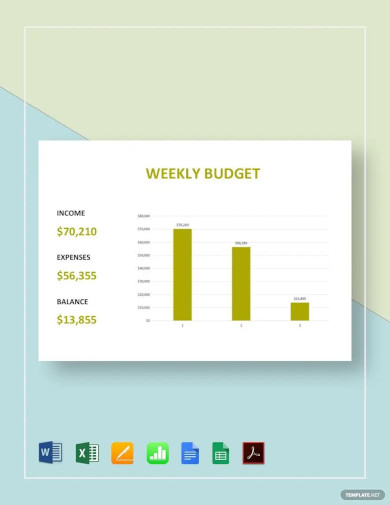
Weekly Budget
download now -

Sample Budget Calendar
download now -

Personal Budget
download now -

Bi-weekly Budget
download now -
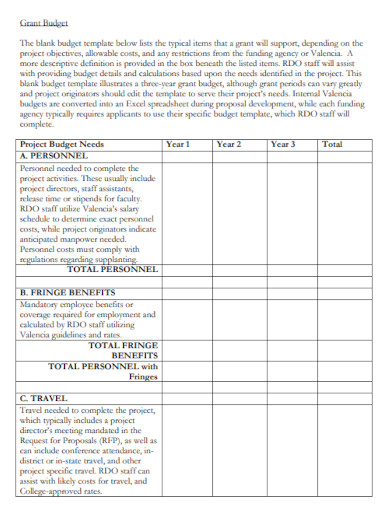
Blank Budget
download now -
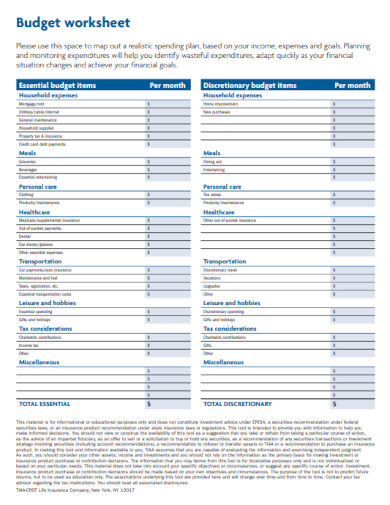
Budget Worksheet
download now -
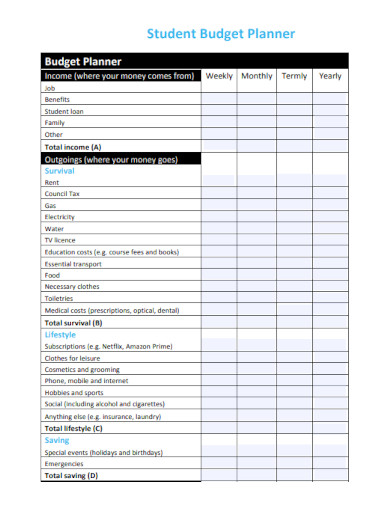
Student Budget Planner
download now -
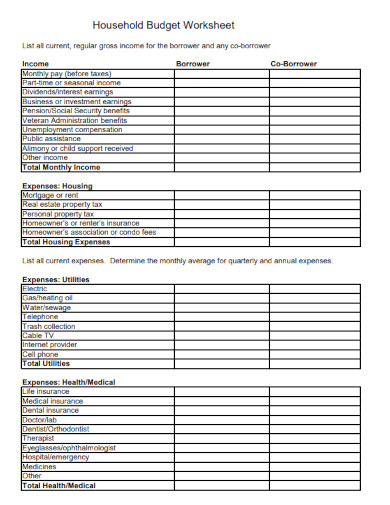
Household Budget Worksheet
download now -

University Budget Tracker
download now -
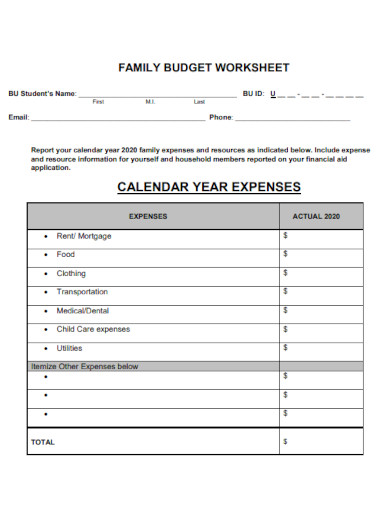
Family Budget
download now -

Sample College Budget
download now -
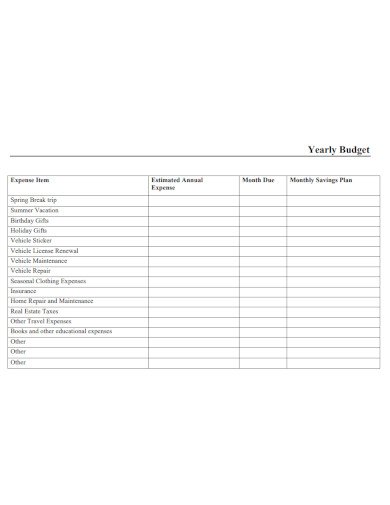
Yearly Budget
download now -

Expense Budget
download now -
Summary Budget Format
download now -

Printable Budget Detail Worksheet
download now -
College Student Budget
download now -

Sample Budget Example
download now -
Editable Budget Narrative
download now -
Relocation Budget
download now -

Library Budget
download now -
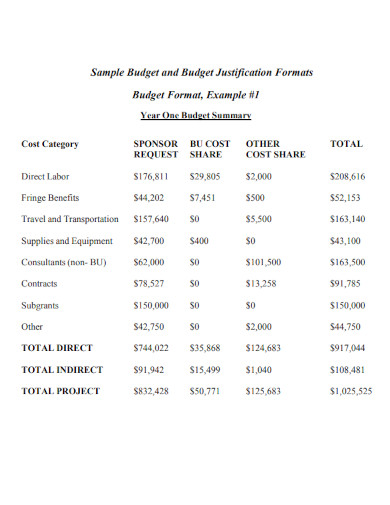
Sample Budget Format
download now -
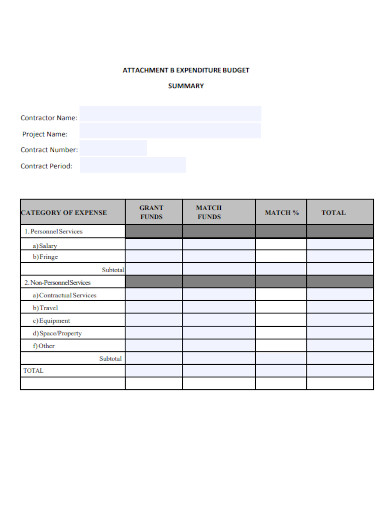
Expenditure Budget
download now -

Sample Budget Memo
download now -
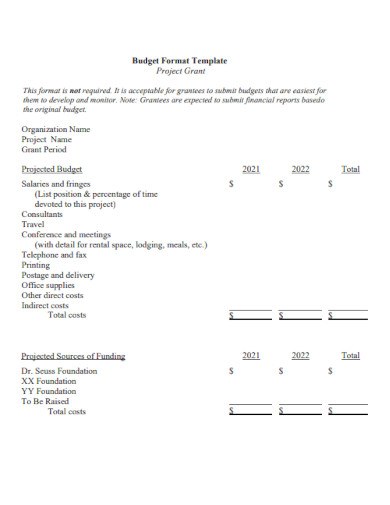
Printable Project Budget
download now -
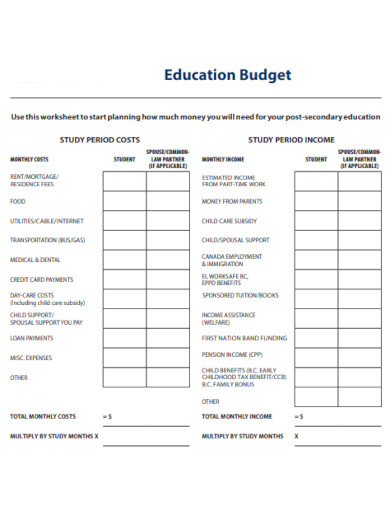
Education Budget
download now
What Is a Budget?
The term budget refers to an estimate of income and expenditures for a future period and is typically compiled and reevaluated regularly. Budgets can be created for any entity that wishes to spend money, including governments, businesses, individuals, and families of any income level. Budgeting is essential for managing monthly expenses, preparing for unforeseeable life events, and being able to afford expensive items without incurring debt letters. Keeping track of your income and costs can be a smooth process, does not require math skills, and does not preclude you from purchasing the desired items. It means you will know where your money goes and have greater financial control.
Benefits of Budgeting
An adequate budget should allow a business to monitor the company’s financial status to plan for both short- and long-term expenses, such as hiring new employees and expanding operations. In addition, it can enable a company to share its process and budget with a regulating body, such as a committee of directors, and provide essential status updates to current and prospective investors. Here are several explanations why budgeting is crucial for the success of an organization:
Components of a Budget
Creating a budget allows you to determine how much money you have, how much you’ve spent, and how much you will require in the future. A budget can guide crucial business decisions such as reducing unnecessary expenses, hiring more employees, and purchasing new equipment lists. If you need more funds, the budget can help you modify your business plan or prioritize your expenditures. The first budget you create for a new business may be complex, but it is a good learning experience and a method to determine what works best for your business. Introducing yourself to your budget’s components is the finest place to begin. To initiate a budget, you may need to make several initial assumptions.
1. Master Budget
A master budget is the sum of the budgets created by the various functional divisions of an organization. It utilizes financial statements, the cash flow forecast, and the financial plan as inputs. Management teams plan the activities required to attain their organization’s objectives using master budgets. In larger organizations, senior management is accountable for developing multiple versions of the master budget before its finalization. When the final evaluation is complete, funds can be allocated to specific business activities. Spreadsheets are frequently used by smaller businesses to construct their master budgets. However, replacing spreadsheets with efficient budgeting software can reduce errors.
2. Operating Budget
A budget for operations is a comprehensive estimate of an organization, corporation, or institution’s income and expenditures over a specified time. This budget is typically prepared as a target or forecast for the reporting period. Operating budgets assist businesses and organizations in achieving their financial objectives. As an HR manager, you can use it to evaluate the efficacy of your department by comparing actual results to the operating budget.
3. Cash Budget
A cash flow budget estimates the money that enters and leaves a business during a specific period. Cash budgets are developed by organizations using inferences from sales forecasts and production, as well as estimates of payables and receivables. The information in this budget can assist you in determining whether you have sufficient operating cash, whether your money is being used productively, and whether you are on course to generate a profit.
4. Financial Budget
Businesses create this budget to decide how much and when they will need capital to meet their short- and long-term requirements. It considers assets, liabilities, and stakeholders’ equity, the critical components of a balance sheet that give you an overall picture of the viability of your business.
5. Labor Budget
A labor budget will be essential for any organization that hires employees to attain its objectives. It helps you determine the number of employees you need to achieve your objectives, allowing you to plan your payroll accordingly. In addition to arranging regular staffing, it helps allocate costs for seasonal employees.
How to Prepare a Budget for Your Organization
Most organizations also produce an “actual budget” or “actual report” to compare budget estimates to actual results following the budget period. This enables a company to determine where it went wrong during the budgeting process and alter future estimates accordingly. Follow the steps below when creating a budget for a project, initiative, department, or organization.
1. Comprehend Your Organization’s Objectives
Before creating a budget, it is essential to have a thorough grasp of the objectives your organization will pursue during the budget period. By grasping these objectives, you can create a budget that supports and aligns with them. Consider, for instance, a company whose consistent year-over-year revenue growth is mitigated by rising expenses. This organization could benefit from a greater emphasis on expense management during the budgeting process. Consider an organization that is introducing a new product or assistance. The company may support the nascent business division more heavily to foster growth. To achieve this objective, the company may need to reduce expenses or growth initiatives in other areas of its budget.
2. Estimate Your Income Throughout the Budget Period
It would help if you first selected your income and cash flow accurately for the time to allocate funds for business expenses. Depending on the structure of your firm, this process may be straightforward or challenging. For instance, a company that sells goods or offers services to established customers bound by contracts will probably find it simpler to estimate income than a company that depends on active sales activity. In the second scenario, it would be crucial to consult prior sales and marketing data to determine whether the industry is changing in a way that could cause you to fall short of or outperform the latest trends. You should also include income from other sources, such as returns on investments, asset sales, bond or share issues, and income from quarterly sales activity reports.
3. Identify Your Expenses
After determining your anticipated income for the period, you must estimate your expenses. This procedure entails three primary categories: fixed costs, variable expenses, and one-time expenses. Fees that remain constant over time and do not fluctuate significantly from week to week or month to month are fixed prices. In many instances, these costs are set by a contract, making them simple to anticipate and account for. This category typically consists of expenses associated with overhead, such as rent and utilities. In addition to debt payments, phone, data, and software subscriptions can also fall under this category. Include all recurring and anticipated expenditures.
4. Determine the Surplus or Deficit of Your Budget
After accounting for your income and expenses statements, you can incorporate them into your budget. Here, you determine whether your projected income is sufficient to cover your costs. You have a budget surplus if your income exceeds your expenditures. Having this knowledge, you should determine how to utilize additional funds best. You may transfer the funds to an emergency fund that you can access if your existing revenue falls short of projections. You could also use the funds to expand your enterprise. Also, a budget deficit exists when expenses exceed income. You must now determine the optimal course of action to close the disparity. Can you increase revenue by selling more aggressively? Can you reduce your variable or fixed expenses? Would you contemplate selling bonds or shares of company stock to inject additional capital into the business?
FAQs
What is budget control?
Budget constraints are required to ensure that a government only spends what its governing body has legally appropriated. By establishing explicit spending limits, budget controls promote accountability and bolster organizational trust.
Why budgets are an important part of the planning process?
Budgeting facilitates formulating the company’s activities, allowing for a better understanding of priorities, resource allocation, and areas requiring reevaluation. The ability to establish attainable objectives is another aspect of the planning process that contributes to its significance.
How often should you create a budget?
While your budget shouldn’t vary significantly from month to month, the reality is that no two months are identical. This is why you establish a new budget every month before the beginning of the month.
That is all! This is how to create a budget and why you should. Now is the moment to act! It is time to gain financial confidence. But what about budgeting with confidence? You will have access to budget reports that outline your income and expenditure tendencies. Then you can determine if your spending behaviors align with your financial objectives. Also included is our personally favored feature: bank connectivity. You will not have to enter every transaction manually. They will enter in great numbers. Check out some budget templates! You can confidently budget every single month.
