28+ Sample Business Models
-

Start up Business Model Template
download now -

Analysis of Business Models
download now -
Multi Business Model Approach
download now -

Company Business Model Template
download now -

Business Marketing Model
download now -

Business Models for Connected Car Services
download now -

Study of Business Model
download now -

Business Model in Context of Strategy
download now -

New Business Model Template
download now -
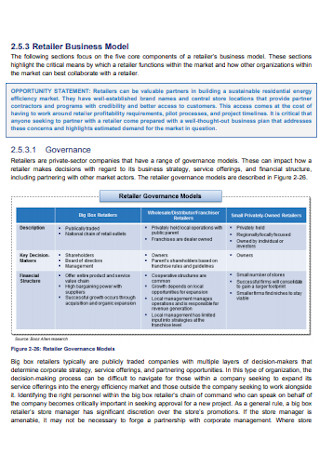
Retailer Business Model
download now -
Market and Business Model
download now -
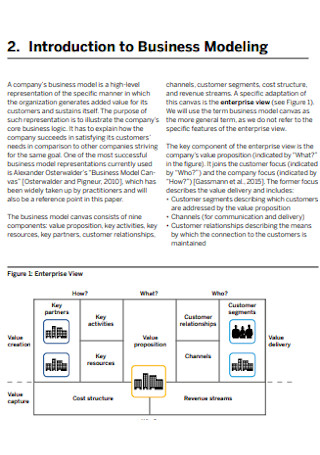
Digital Business Model
download now -

Power of Business Model
download now -

Conceptualizing Business Model
download now -
Business Model for Electronic Market
download now -

Business Model Innovation Example
download now -

Business Models and Strategy Template
download now -

Business Model Analysis Template
download now -

Business Model Design
download now -

Importance of Business Models
download now -

Business Models of Social Enterprise
download now -

Identifying e-Business Models
download now -

Sustainable Business Models
download now -

Business Model Format
download now -

Business Model as an Institution
download now -

Constructs of a Business Model
download now -

Bank Business Model
download now -

Business Model Generation
download now
FREE Business Models s to Download
28+ Sample Business Models
What Is a Business Model?
Common Types of Business Models
Components of a Business Model
How to Create a Business Model
FAQs
What are the 4 types of business models?
What is a good business model?
How do you create a business model?
What are the 9 parts of a business model?
What business model should I choose?
What is the purpose of a business model?
What Is a Business Model?
A business model is a business’ plan for making profit. However, nowadays, companies incorporate much more into their model than just its expenses and income. It examines the interconnectedness of the business in relation to its customers, strategies, resources, and value proposition.
According to Harvard Business Review, in a post-pandemic era, companies may need to rethink their present business model. Organizations can no longer assume that what worked in previous years will continue to do so. It is important for them to acknowledge the changes brought about by the pandemic. It’s business as usual, but modified to survive in a new post-pandemic world.
Common Types of Business Models
Regardless if you are an internet startup or global conglomerate, you need to have a solid business model to serve as your guide. Although relative to each company, there are dozens of business models that have been proven to work. The following are just a few examples of popular models that have been tried and tested.
Components of a Business Model
The business model canvas is a famous and widely used format that helps businesses create a good model. Identifying these key components will lead to a holistic understanding of what your business can do for you and for the people you want to serve.
How to Create a Business Model
Starting a business is a goal many people have but few actually have the stomach for. It’s easy to run a business when things are going great. But when things start to take a turn for the worse or everything seems to fall apart, that’s when the commitment starts to falter; because the dream is being ripped apart. Having a business model in place cannot guarantee perpetual success. But it can guide you when you find yourself questioning your commitments. Follow these practical steps:
Step 1: Establish an Objective
Why do you want to start a business? Or perhaps your company is planning to reorganize and needs a business model facelift. Always start by asking what drives you to believe that your business is a worthwhile endeavor. It needs to be your reason for doing; because with a shaky objective, it’s much easier to fall off the wagon and doubt yourself. Establishing a clear goal will make it easier to create a business plan.
Step 2: Create a Plan
Know your resources, assess your strengths, but also don’t hide your weaknesses. Being transparent and aware of all of these will help you develop your business model with more ease. It will allow you to craft a more realistic and realizable business plan. Your plan should also consist of a feasible assessment of the competition. You need to have some idea of the situation on the ground. Who are the leading companies in your industry? What businesses started out promising but then ultimately failed? What were the reasons behind theses failures?
Step 3: Develop Your Business Model
After going through an internal examination of yourself and of your business, it is time to put it into writing. Using the nine parts mentioned above, brainstorm with your organization or trusted team members and fill in the key details. Make sure to document every step meticulously. Having a business model does not mean it is enshrined like a constitution. Although just like a government’s constitution, a model can be amended and modified when the need arises. This is applicable to centuries old companies where there is a need to be able to constantly adapt to changing times and attitudes. If a policy or practice is outdated and no longer serves the company, then it might be best to throw it out. Business development is always an evolving process. You will most often find that the truly successful ones are those bold enough to change the face of the industry and those committed to lifelong learning.
Step 4: Launch Your Model
Starting a business is not easy. If you are not careful, you may fall prey to survivorship bias where you selectively focus only on the exceptional (i.e., success stories). And inevitably leave out the failure and constant struggle from the bigger picture. This could give you the impression that your business can also become an overnight success, without the necessary toil and sacrifice. It is easy to get carried away sometimes by our ideas, but once difficulty settles in, some abandon their commitments because they were not prepared for the struggle. Be prepared to launch your business model with an optimistic and ambitious attitude, but one that is grounded in reality.
FAQs
What are the 4 types of business models?
There are dozens of existing business models. Many companies have pioneered some distinct ones and have paved the way for other businesses to duplicate or refine their business model. Common examples include the razor and blade model, franchise model, consulting business model, and the direct sales model.
What is a good business model?
A good business model contains a comprehensive understanding of the business in relation to its stakeholders, revenue, resources, and overall value. An effective model incorporates all these to provide a sense of direction for a company. It normally serves as a guide for the organization and is subject to amendments.
How do you create a business model?
The best way to start is by having an objective in mind. Once you have established your goal for putting up a business, you can begin creating your plan. There are hundreds of existing business model templates, so you don’t have to worry about starting from scratch. The best part of it is you can customize and tailor fit it to meet your company’s goals. A business model is not a permanent sentence; but more of a guide that makes it easier for businesses to navigate the highs and lows of a competitive economy.
What are the 9 parts of a business model?
The nine parts of a business model canvas are the key partners, key activities, key resources, value proposition, customer relationships, customer segments, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams.
What business model should I choose?
To answer that question, you would need to thoroughly examine your objectives and motives. A little research wouldn’t hurt as well. What companies pique your interest? Or as a consumer, ask yourself why you like a particular brand. What companies emulate the same values and practices as yours? You can do research on well-known business models and choose to either adopt it totally, or tweak it to suit your needs. Choosing the best model for your business is highly dependent on the objectives and priorities of the company.
What is the purpose of a business model?
The purpose of a business model is to help a company or business strategize and understand its place and value in the market. Companies create business plans not only to identify profit-generating strategies, but to find ways to improve their brand and maximize its resources.
The business model of a small town restaurant may be different from the business model of a multinational ecommerce corporation. The key is in understanding the different facets of your business and finding ways of making it work. Your business model should aim to generate, replicate, and deliver your desired results. Making a business plan is not a walk in the park. And remaining fully committed to it is an even harder task. However, its use and benefits far outweigh the challenges. Browse any of the samples above to create your business model today!
