29+ Sample BMI Charts
-
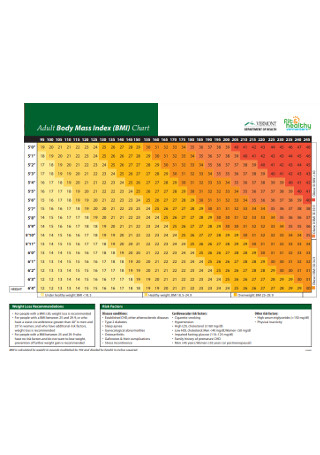
Adult Body Mass Index Chart
download now -
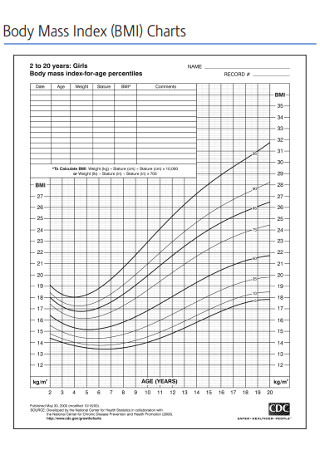
Girls Body Mass Index Charts
download now -
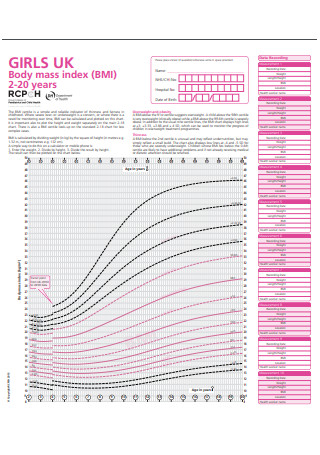
BMI Chart for Boys and Girls
download now -
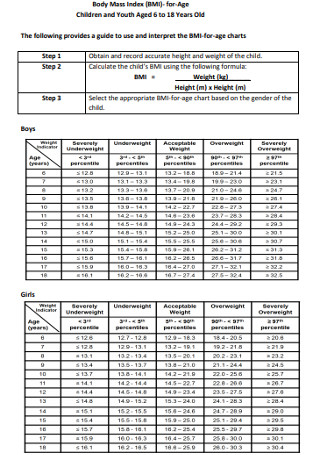
Children Body Mass Index Chart
download now -
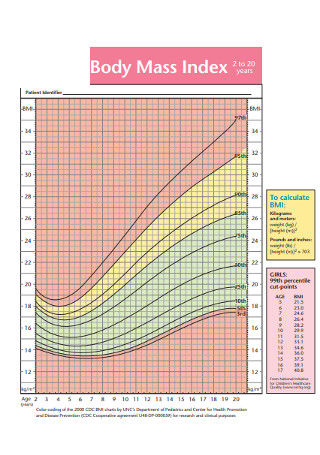
Sample Girls Body Mass Index Chart
download now -
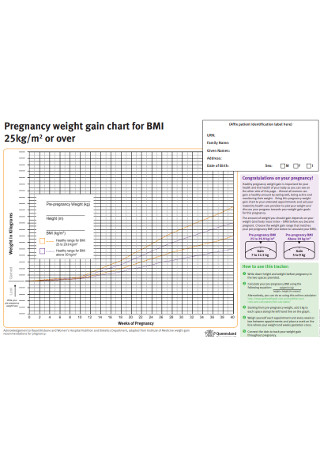
Pregnancy Weight BMI Chart
download now -
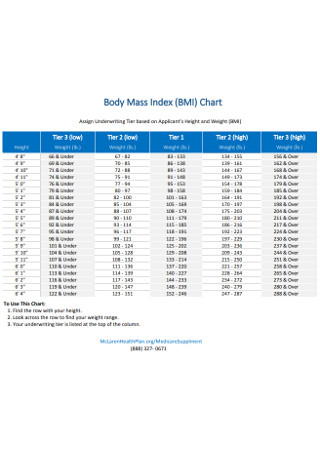
Applicant Body Mass Index Chart
download now -
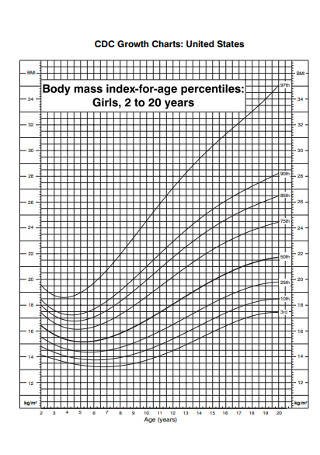
Sample BMI Growth Charts
download now -
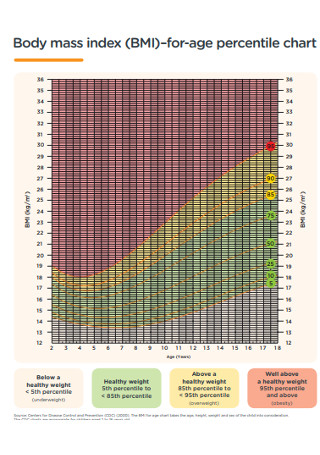
Body Mass Index (BMI) for-Age Percentile Chart
download now -
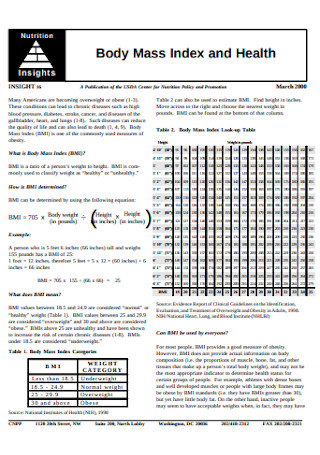
Body Mass Index and Health Table
download now -
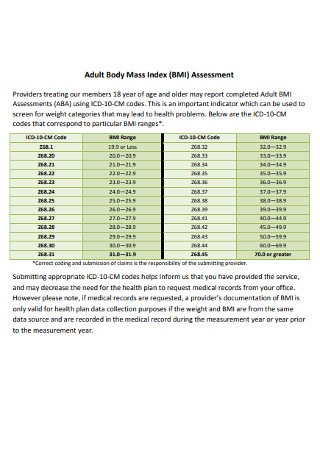
Adult Body Mass Index Assessment Chart
download now -
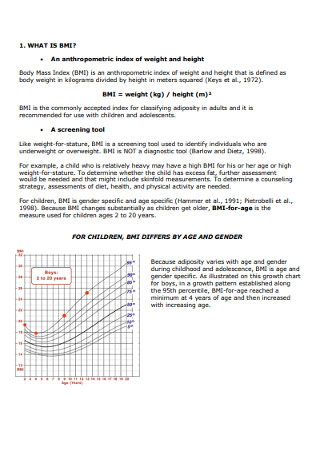
BMI-for Age Growth Charts
download now -
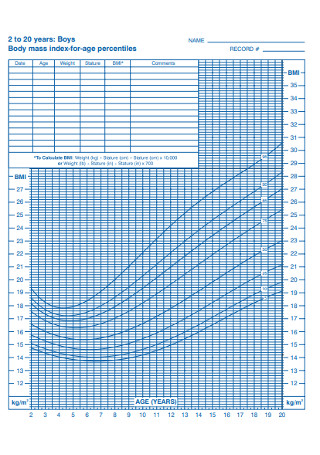
Boys BMI for-age Percentiles Chart Template
download now -
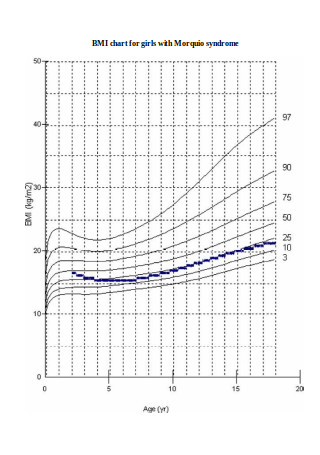
Morquio Syndrome Chart for Womens
download now -
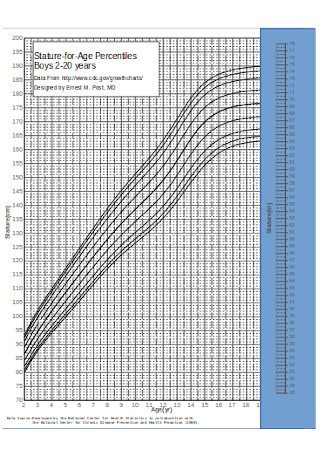
BMI Growth Chart for Ages
download now -
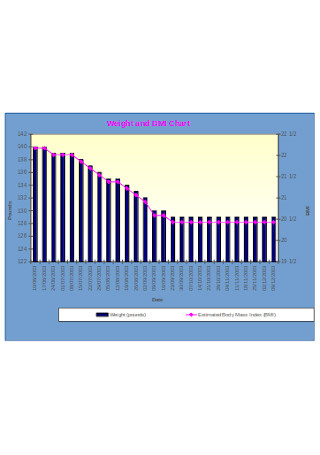
Weight and BMI Chart
download now -
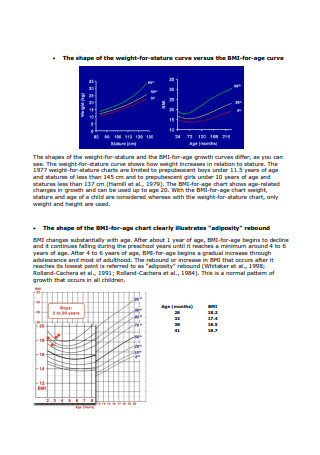
BMI for Age Growth Chart
download now -
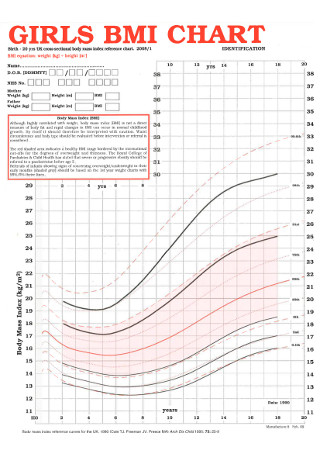
Basic Girls BMI Chart Template
download now -
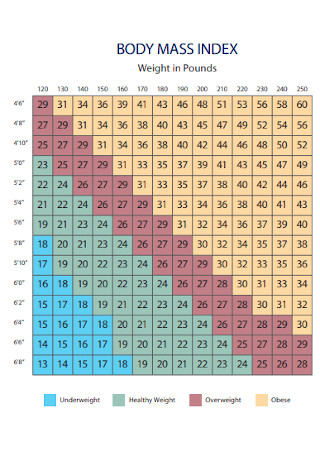
Sample Weight BMI Chart
download now -
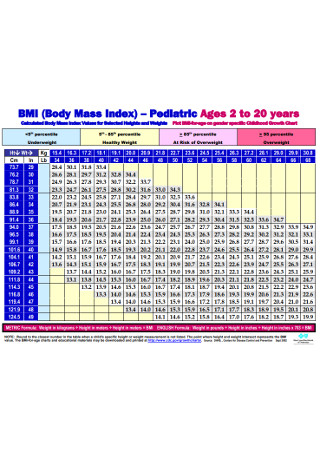
Pediatric Body Mass Index Template
download now -
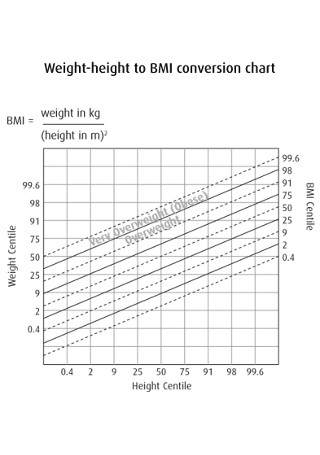
Weight-height BMI Conversion Chart
download now -
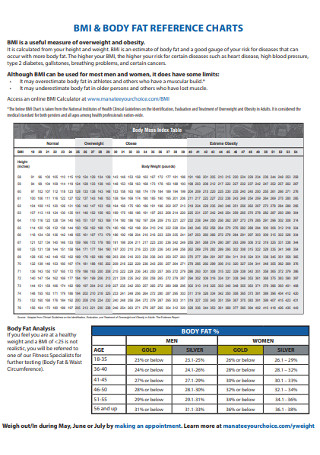
BMI and Body Fat Reference Charts
download now -
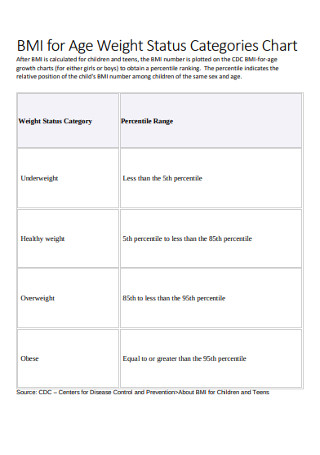
BMI for Age Weight Status Categories Chart
download now -
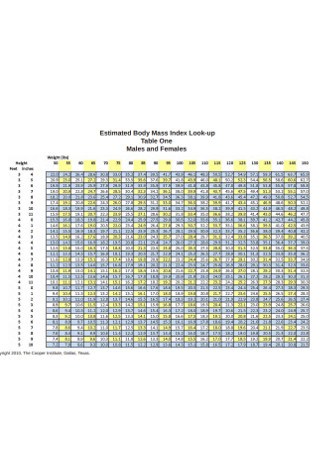
Males and Females BMI Chart
download now -
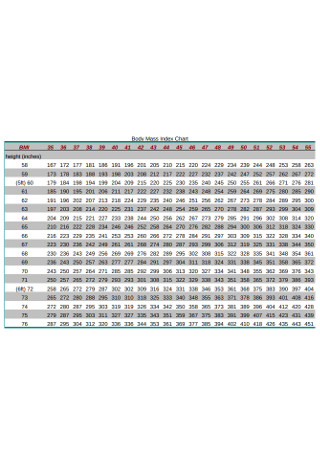
Standard Body Mass Index Chart
download now -
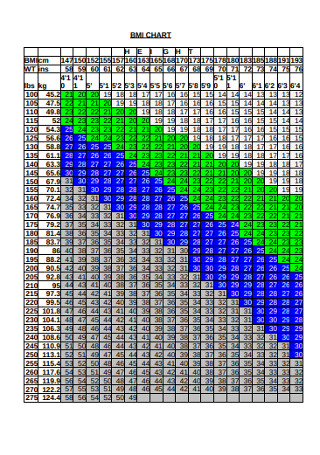
Formal BMI Chart Example
download now -
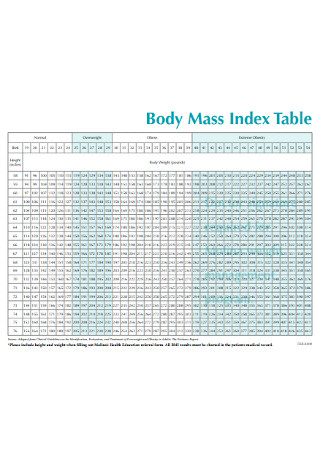
Sample Body Mass Index Table Template
download now -
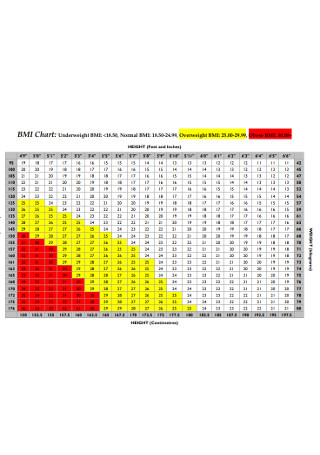
BMI Height Chart
download now -
BMI Chart for Adults
download now -

BMI Growth Chart for Ages
download now
FREE BMI Chart s to Download
29+ Sample BMI Charts
What Is a BMI Chart?
Common Health Risk Associated with Obesity
What Are the Benefits of a BMI Chart?
How To Calculate BMI
FAQs
How do I calculate my BMI?
What is the ideal body weight of a person?
Does BMI actually matter?
How can you tell if you are fat?
Are there any inaccuracies with BMI?
What Is a BMI Chart?
A BMI Chart (Body Mass Index Chart) is a tool used to calculate and scale a person’s weight in kilograms (kg) divided by the square of the person’s height in meters (m). Invented by Lambert Adolphe Jacques Quetelet by deriving the BMI from a simple mathematical formula in the 1830s, this chart details the weight and height category of a person. For more than a hundred years, it’s aim is to check and estimate whether an individual falls under the category of being underweight, healthy, overweight, obese, and extremely obese.
Common Health Risk Associated with Obesity
For years, doctors and other medical experts have been measuring the body mass index of people, scaling their health based from their body weight. Over the years, being overweight and obesity is an increasing problem globally and has become a severe medical condition that causes complications in a person’s body. According to National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), obesity causes high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, diabetes, sleep disorders, cancers, and other heart diseases that are lethal when left untreated. Listed below are some common health risks that are associated with obesity.
What Are the Benefits of a BMI Chart?
BMI charts are tools that simplify and hasten the calculation and measurement of one’s obesity level based on the ratio of its height and weight without the aid of additional and expensive clinical tools and equipment to get reliable medical results. Although BMI has its limitations, it still provides numerous benefits in the field of healthcare and medicine.
- For one, BMI charts provide researchers a good idea of the various overweight and obesity rates between populations through time, allowing experts to prevent and treat diseases related to obesity.
- It helps physicians estimate and calculate the risks of obesity-related diseases as well as to look through the health of their patients thoroughly.
- At the same time, these charts help researchers gather data in the fastest and most convenient way to investigate the obesity epidemic and check the dietary patterns of an individual.
- And it is cheap since it doesn’t need expensive clinical tools and equipment to gather the necessary data.
How To Calculate BMI
Technology such as computers and scientific calculators were not yet available when Quetelet invented the BMI chart in the 1830s. However, even until now, the BMI chart remains a handy tool in determining the bodyweight of a person. Although Trefethen, according to Medical News Today argued, “that Quetelet’s formula might lead to confusion and misinformation,” most people still rely on the BMI chart to gather data about weight ranges and obesity differences over time. Learn more on how to calculate a person’s body mass index and read these steps below:
Step 1: Identify Whether the Person is an Adult or a Child
BMI works the same for both children and adults since it doesn’t consider age, body fat distribution, nor does it distinguish muscles between fat. However, measurement is used differently. For children, their BMI range can gradually increase through adolescents and most during adulthood since they are still growing. The BMI ranges for adults, on the other hand, almost remains the same throughout their life.
Step 2: Indicate the Person’s Weight and Height Measurements
Determine a person’s BMI by allowing their height and weight measurement to intersect in the chart. Indicate the person’s height in meters and weight in kilograms. The ideal BMI for most adults ranges from 18.5 to 24.9, while children and young adults aging from 2 to 18 must take into account their age and gender to get their ideal BMI.
Step 3: Follow the BMI Formula
As stated earlier, the BMI of a person follows a specific formula (divide their weight by their height to the power of two) to get accurate results. The results of the BMI shall then be used for public health statistics purposes, weight range analysis, as well as a screening tool for weight problems in the community.
Step 4: Check the Person’s Weight Classification
Lastly, classify the person’s weight range based on the results of the calculation. A person may be considered as underweight, normal weight, overweight, obese, and extremely obese. From there, medical and health experts may find ways to reduce the obesity rate of the community as well as to prevent and treat diseases and other high-risk factors that are associated with obesity.
FAQs
How do I calculate my BMI?
The standard Body Mass Index uses a simple calculation based on a person’s height and weight. With the formula of BMI = kg/m², a person can check his/her weight category. However, since the formula does not distinguish muscle and fat, this may lead to inaccuracies in the results. This leads to the creation of the new BMI calculator, which has the formula of BMI = 1.3 x kg/m2.5 that may provide a closer approximation to the reality of human shape and size.
What is the ideal body weight of a person?
The ideal weight may differ from one person to another as different factors are affecting an individual’s weight, such as age, muscle-fat ratio, sex, and body shape. Nevertheless, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), a person is:
- Underweight when his/her standard BMI is less than 18.5
- Ideal when his/her standard BMI is between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight when his/her standard BMI is between 25 and 29.9
- Obese when his/her standard BMI is more than 30
Does BMI actually matter?
Defining the ideal body weight of a person for it to be considered as healthy requires consideration of other factors. One type of measurement does not fit all, according to some research. Despite the BMI’s inability to take into account a person’s body fat, his/her body fat distribution, as well as race, gender, and age, why is BMI still widely used nowadays? It’s simply because BMI still provides a “reasonable measure” of body fat, which gives an individual a rough estimate of whether he or she is healthy or not.
How can you tell if you are fat?
Besides using the BMI chart to calculate an individual’s weight, there are other ways to identify whether a person is obese or overweight. These includes:
- Waist measurement – a person is considered overweight once the waist circumference, for women, measures more than 35 inches, while man measures more than 40 inches.
- Snoring – a person is considered fat when it experiences shallow and short pauses in breathing during sleep, due to the fat accumulation around its neck area.
- Frequent heartburn – a person is overweight when it experiences acid reflux due to its slight changes in its body weight.
- Achy joints – osteoarthritis is not limited to older people. The extra weight carried by a person’s joints adds pressure to the area, which causes it to ache.
- Chronic fatigue – overweight adds extra pressure on a person’s organs, which leads to fatigue and shortness of breath.
Are there any inaccuracies with BMI?
BMI does not take into account whether a person’s weight is carried as muscle or fat. Muscle builders and athletes who exercise more often and have a higher muscle mass will be considered as “overweight” compared to a regular person who does not exercise at all. Furthermore, a pregnant woman’s body composition changes during pregnancy and lactation, making BMI inappropriate. Lastly, the BMI chart may lead to inaccuracies when determining children’s and elderly’s weight since children have yet to complete their growth while the elderly tend to lose their muscle mass as time passes by.
Obesity is a health hazard that remains to be the main problem in society nowadays. Millions of people are experiencing obesity, and their age is slowly reaching as early as childhood and adolescence. What’s worse, obesity is closely associated with various heart diseases and other health risk factors. Over the years, BMI remains to be one of the most reliable tools used by doctors and other health experts to measure and understand the overall weight and health of both men and women. Lastly, regardless of the BMI’s limitations, it is beneficial in gathering public health statistics, weight range analysis, and as a screening tool for other weight problems.
