64+ Sample Commission Agreements
-

Commission Agreement Template
download now -

Commission Agreement Letter Template
download now -

Exclusive Solicitation Sales Commission Agreement Template
download now -

Independent Contractor Sales Commission Agreement Template
download now -

Affiliate Commission Agreement Template
download now -
Agency Commission Agreement Template
download now -

Free Independent Contractor Commission Agreement Template
download now -

One Page Construction Commission Agreement Template
download now -

Free Real Estate Agent Commission Agreement Template
download now -

Commission Sharing Agreement Template
download now -

Commission Compensation Agreement Template
download now -

Corporation Commission Operating Agreement Template
download now -

Commission Sales Agent Agreement Template
download now -

Standard Exclusive Solicitation Sales Commission Agreement Template
download now -

Commission Agreement
download now -

Independent Contractor Commission Plan
download now -

Artwork Commission Agreement
download now -

Sample Commission Agreement
download now -

Sample Sales Payment Agency Agreement
download now -

Sample Sales Employee Agreement
download now -

Commercial Lease Commission Agreement
download now -

Sales Representative Property Agreement
download now -

Land Protection Commission Agreement
download now -

Rental Commission Master Agreement
download now -

Finance Project Introduction Agreement
download now -

Consultant Commission Agreement
download now -

Broker’s Construction Commission Agreement
download now -

Group Fee Commission Agreement
download now -

Sales Client Agency Agreement
download now -

Introducer Employment Commission Agreement
download now -

Trade Vendor Commission Contract
download now -

Commercial Hotel Agency Agreement
download now -

Standard Commission Agreement
download now -

Leasing Commission Agreement
download now -

Exclusive Agency Agreement
download now -

Commission Agreement Addendum
download now -

Business Referral Agreement
download now -

Standard Agency Agreement
download now -
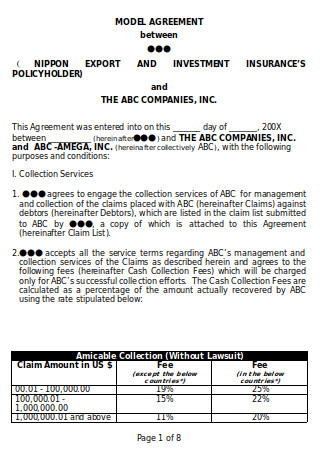
Collection Service Agreement
download now -

Aircraft Acquisition Agent Agreement
download now -

Salesperson Contract Percentage Contract
download now -

Salary and Commission Plan Agreement
download now -

Contract to Commission Artwork
download now -

Financing Commission Agreement
download now -

International Sales Commission Agreement Template
download now -

Commission Agreement Template
download now -

Partner Commission Agreement
download now -

Agent Commission Agreement
download now -

Commission Agreement Example
download now -

Agent Commission Agreement Sample
download now -

Referral Commission Agreement
download now -

Sales Affiliate Agreement
download now -

Buyer Agency Commission Agreement
download now -

Simple Commission Agreement
download now -

NPO Commission Agreement
download now -

Seller and Agent Commission Agreement
download now -

International Brokers Commission Contract
download now -

Real Estate Commission Agreement
download now -

Revised Commission Agreement
download now -

Standard Commission Agreement in PDF
download now -

Consignment Commission Agreement
download now -
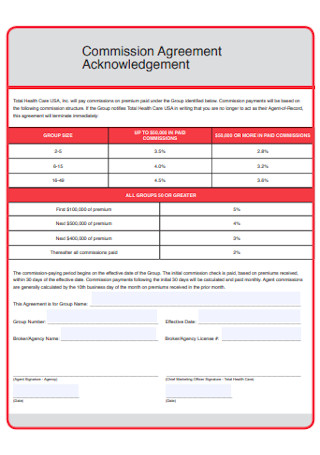
Commission Agreement Acknowledgement
download now -

Buyer Broker Commission Agreement
download now -

Sample Referral Commission Agreement
download now -
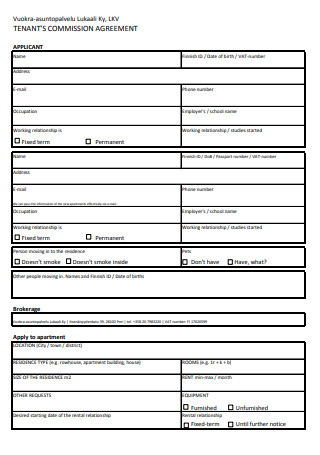
Tenant’s Commission Agreement
download now
FREE Commission Agreement s to Download
64+ Sample Commission Agreements
What is a Commission Agreement?
The Different Forms of Sales Commission
How to Construct a Sales Commission Agreement Sample
FAQs
What are the best sales jobs for beginners?
What are the six high-paying sales jobs in the U.S.?
What are the advantages of commission-based compensation?
What are some tips to improve commission sales?
Are commissions taxable?
What is a Commission Agreement?
A commission agreement is a written agreement between a business organization and an individual. The business possesses services or goods for sale, while the individual markets the services or goods on its behalf. The company promises to compensate the individual through a commission, which is a fee for every successful business transaction that increases company sales. There are two basic types of commission arrangements: sales and real estate commission agreements. A sales commission contract lays out the payment details a company has to pay to a salesperson, where a salesperson can be an employee or independent contractor. A real estate commission contract is an arrangement between a seller and an agent, where the seller agrees to give an agent a portion of the sales once a buyer purchases his property.
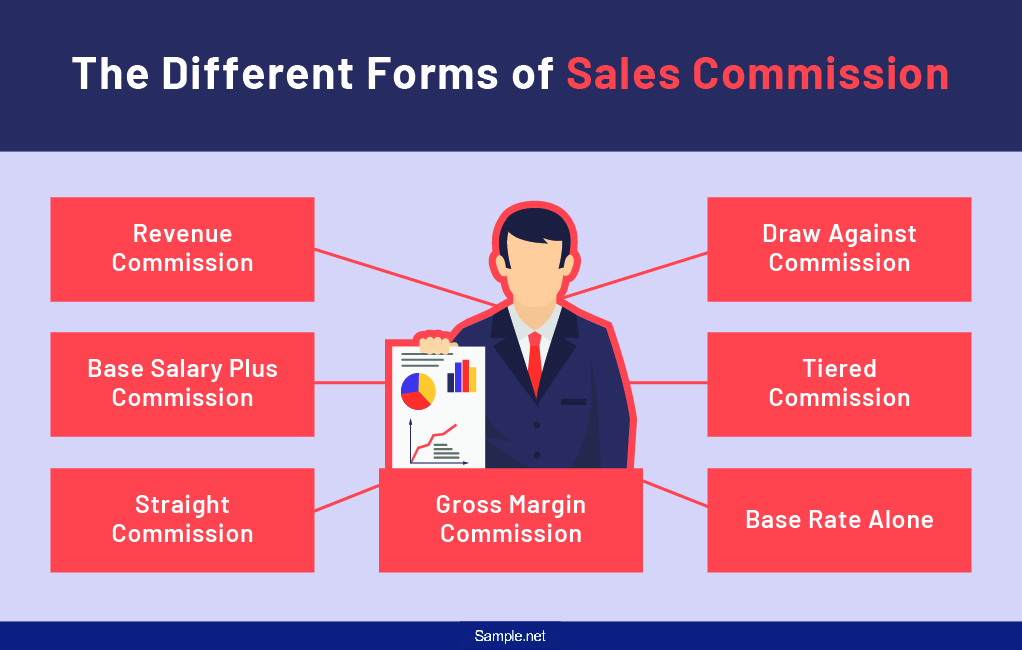
The Different Forms of Sales Commission
Every company needs to have a sales commission structure that increases its profitability. According to Forbes, in 2016, there were about 5.7 million sales representatives in the United States, which means that more and more people are seeing the benefit of getting into a career that focuses on sales. The following are different forms of sales commissions a company can take advantage of.
How to Construct a Sales Commission Agreement Sample
A sales commission agreement can be between a company and an employee, or it can be between a company and an independent contractor. The contract outlines the payment structure and the relationship between the two parties involved. The following are steps on how to construct a sample of a sales commission contract.
Step 1: Write a Statement of Authorization
An authorization statement permits the salesperson to sell the services or products of a company or employer. In this section of the contract, the employer specifies the limits of selling. A salesperson will only be permitted to sell within the bounds of the company’s territories. Moreover, the document should clearly state that a sales agent is prohibited from rebranding their products for selling.
Step 2: Include an Agreement Concerning Sales Documentation
The sales representative must agree to use documentation tools approved by the company to keep a record of his sales. This allows the company to estimate its return on investment and revenue, receive accurate sales reports, increase productivity, improve its campaigns, and more. Tools for documentation may include forms, software, CRM databases, etc.
Step 3: Protect Confidential Information
Insert a non-compete and non-disclosure clause to protect confidential information. A non-compete clause prohibits a sales representative from working or selling for a competitor for a specific period after completing a contract with his previous employer. A non disclosure agreement refrains an employee from sharing a company’s intellectual property, such as patents and trade secrets.
Step 4: Detail the Commission Structure
This is the heart of the agreement. In this section of the contract, both parties must clearly understand the structure of compensation. The agreement should address the questions: What are the terms for obtaining commission? When will the sales agent receive his commission? What are the consequences in case a buyer cancels a transaction, asks for a refund, or doesn’t pay?
Step 5: Finalize the Agreement
In this last section of the agreement, a statement that makes both parties agree to the conditions of the agreement is written. By dating and signing the contract, the employer and sales representative become bound to the agreement. Also, don’t forget to add the governing law and arbitration clause to regulate the contract.
FAQs
What are the best sales jobs for beginners?
The following are sales jobs that will help you, as a beginner, to begin your sales career. (1) Purely commission-based job positions. This will help you strengthen your passion for selling since you have no base salary to rely on. (2) Inside sales. This can be a good training ground for you. It involves dialing more than a hundred people a day just to sell a service or product. (3) Insurance sales. This allows you to develop your skills in prospecting clients, presenting policies, and closing a deal.
What are the six high-paying sales jobs in the U.S.?
According to CNBC, there are six high-paying sales jobs in the United States: (1) a sales engineer with a salary ranging from $68,000 to $185,000, (2) a software sales agent with a salary ranging from $50,000 to $141,000, (3) a realtor with a salary ranging from $27,000 to $111,000, (4) a pharmaceutical sales representative with a salary ranging from $52,000 to $84,000, (5) a medical device sales agent with a salary ranging from $38,000 to $87,000, and (6) a recruiter with a salary ranging from $37,000 to $77,000.
What are the advantages of commission-based compensation?
There are two main advantages of a commission type of pay. First, it motivates your employees to work competitively, and second, it helps a company manage its payroll expenses effectively. Note that professionals who are highly talented in marketing and sales get more from their commission than basic salaries.
What are some tips to improve commission sales?
If you are a person with a passion for entrepreneurship, then a career in commission sales may be for you. Here are some tips to help you improve your sales: (1) Search for a potential product to market. (2) Clearly define and know your prospects or target market. (3) Learn to manage your time and money.
Are commissions taxable?
Yes, commissions are taxable. Commissions are normally a part of an employee’s regular pay, therefore, they are taxable. Note that state and federal taxes along with FICA taxes are withheld from commission payments. On the other hand, for independent contractors, commissions are directly given to them. Since the individual is not under employment, income tax and FICA taxes are not withheld in this matter.
A commission agreement protects the rights of a salesperson to receive a commission, and at the same time, it protects the trade secrets of a company. If you are not yet confident enough to construct a commission agreement, you can download one of our printable contracts above. If you decide to create one, you can ask help from a lawyer to ensure that the document is enforceable.
