19+ Sample Ownership Contract Templates
-

Sample Co-O0wnership Contract Template
download now -
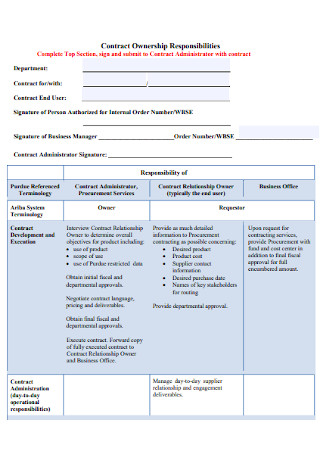
Sample Ownership Contract Template
download now -

Ownership Transfer Contract Template
download now -

Ownership Management Contract Template
download now -

Transfer of Ownership Contract and Agreement
download now -
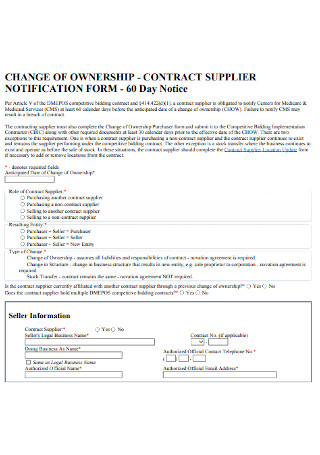
Ownership Contract Form Template
download now -

Employee Ownership Contracts
download now -
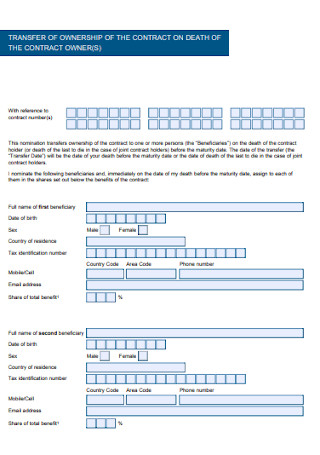
Basic Ownership Contract Template
download now -

Simple Ownership Contract Template
download now -
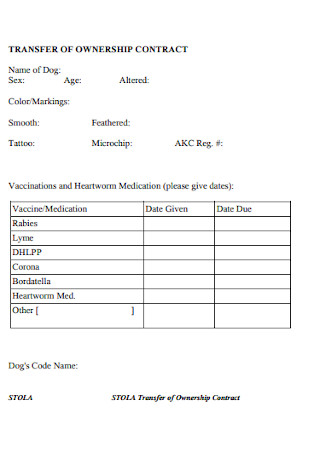
Basic Transfer of Ownership Contract Template
download now -

Ownership Support Contract Template
download now -

Change of Ownership Contract Transfer Template
download now -
Ownership Pharmacy Contract Request Form
download now -

Standard Ownership Contract Template
download now -

Company Ownership Contract
download now -

Sample Ownership Plan Contract
download now -

Formal Ownership Contract Template
download now -

Ownership Purchase Contract Template
download now -

Ownership Investment Contracts
download now -

Sample Ownership Rental Contract
download now
FREE Ownership Contract s to Download
19+ Sample Ownership Contract Templates
What Is an Ownership Contract?
The Different Classifications of Ownership in Businesses
How To Write a Formal Ownership Contract
FAQs
Does ownership also apply to other types of properties?
What is intellectual property?
What if two individuals own the copyright?
What if a property does not have a copyright notice?
What is a trade secret?
What Is an Ownership Contract?
One of the most expensive properties a person can own is either a home or a business. In real estate, an ownership contract is a document that sets the conditions and terms of a property ownership agreement. For example, an unmarried couple may decide to purchase a house. Since it requires a large sum of money, the conditions written in the agreement will protect the ownership rights of both parties if they separate. A contract will make the dissolution easier for both parties, and some couples may consider sharing the property equally. In business, written contracts of ownership cover essential details concerning the relationship of entrepreneurs as co-owners of a company. A business contract will give the parties involved an opportunity to limit liabilities, define responsibilities and expectations, divide risks, and specify monetary obligations.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the rate of homeownership in the U.S. is 65.3%.
Different regions take a slice of the pie, specifically, the Northeast 62.4%, the Midwest 69.2%, the South 67.6%, and the West 60.1%.
When we talk about business ownership, there were about 30.7 million small businesses in the United States in the year 2019. That accounts for 99.9% of the businesses in the country.
The Different Classifications of Ownership in Businesses
There are several classifications of business ownership, and each type may require a specific contract that fits its organization. A particular business type may need a basic business agreement, a co-ownership agreement, a partnership agreement, or an LLC ownership agreement. With that said, here are the different forms of ownership in businesses.
How To Write a Formal Ownership Contract
Every contract a business involves itself in can significantly impact its future. So, here are the steps in creating a valid ownership contract template:
Step 1: Have the Same Goal in Mind
All the parties involved in a contract must agree to the same goal before they sign the agreement. This is a very crucial step that significantly affects the relationship of co-owners if they neglect it. Communicate with your partners and assess if they have a similar goal in mind.
Step 2: Write the Conditions of the Deal
Now that all parties have settled on one goal, each should contribute an asset before entering the business deal. For example, one party may provide its services or goods in return for money from the other partner or co-owner. Write all assumptions you can think about for your contract, especially when it comes to payment. The contract must detail when and how all the parties involved will receive compensation for their business contributions. Write the term, method, schedule, and formula for payment.
Step 3: Create the Contract
After all the parties involved understand what the deal is all about, they should start creating the contract. Remember that all partners or co-owners must reach an agreement before even signing the contract. Note that it is okay to make some changes of the ownership agreement as long as you do it before you or your partners sign it.
Step 4: Ensure Legal Competence
If a partner or co-owner who signs the agreement is legally incompetent, the contract may become unenforceable. A minor who is 18 years old below cannot enter into a contract without the approval of his guardians or parents. An individual who is lacking in sound mind or has mental impairments due to alcohol or drug addiction should not be permitted to enter the agreement. That person will only stir up confusion within the business organization. Additionally, a person who doesn’t have enough authority but signs on behalf of someone in authority cannot attain his purpose unless he has legal authority.
FAQs
Does ownership also apply to other types of properties?
Though the term ownership applies commonly to real estate, it also applies to intellectual property, stocks, artworks, vehicles, boats, and more. Bear in mind that ownership grants an individual the right over a valuable asset under the law’s protection.
What is intellectual property?
Intellectual property can come in the form of copyrights, franchises, patents, trade secrets, trademarks, or even ideas. It is a broad term that describes the intangible things a company owns and protects from third party use without consent. The idea is that intellectual property, which is the product of the human mind, must share the same rights that tangible properties have. Why? One reason is that intellectual property can give a business an advantage over its competitors. Companies do their best to protect intellectual property because of it’s high value in the economy today. The company must have the only right to benefit from its idea and take its stand above the rest.
What if two individuals own the copyright?
Copyright co-ownership can happen in different ways. Examples include two individuals who create the same work, an author who transfers some of his rights to his family member, an author who trades a part of his work to others while keeping a remainder. Copyright co-owners are also legally known as tenants in common. So, when one party dies, his share directly goes to his surviving co-owners. Moreover, each co-owner has a right to independently use the copyrighted work as long as he accounts for it with his co-owners. Therefore, co-owners must coordinate with one another, especially when it comes to the profits they each gain from the copyrighted work.
What if a property does not have a copyright notice?
There are cases where a copyright notice is missing from c work. One reason may be because a copyright notice is no longer a requirement with works published after March 1, 1989. For works that were published before the said date, notices were only required for “visually perceptible” copies such as books, drawings, paintings, architecture, computer programs, and films. One example of a work that is not visually perceptible is a compact disc with a song. A copyright notice will only be a requirement if the author prints the lyrics of the song on an album cover. Moreover, one more reason may be because the owner didn’t work on it, which gives him no right over the copyright.
What is a trade secret?
Trade secrets can come in different forms depending on what type of business a person owns. It can be a system, a design, a method, a recipe, or a formula that outside parties do not know about. It is a means that entrepreneurs use to gain an advantage over their competitors and provide quality service to their customers. All trade secrets are not information open to the public. They are secrets that their holders protect and take benefit from. Note that companies protect their trade secrets by letting their employees sign a non-disclosure or a non-compete agreement upon hiring.
As we have seen, an ownership contract applies to both tangible and intangible properties. Its main purpose is to protect the ownership rights of every party involved in an agreement. It controls and regulates the relationship between partners and co-owners to avoid unnecessary conflicts. Neglecting the use of this vital document may lead to the loss of one’s hard-earned wealth.
