20+ SAMPLE Lean Six Sigma
-

Lean Six Sigma Online Training
download now -
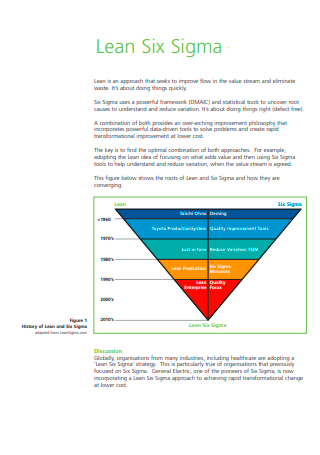
Lean Six Sigma Example
download now -

Primer Lean Six Sigma
download now -

Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
download now -

Lean Six Sigma in PDF
download now -

Lean Six Sigma Training Programs
download now -

Environmental Professional Lean Six Sigma
download now -

Lean Six Sigma Market
download now -

Standard Lean Six Sigma
download now -
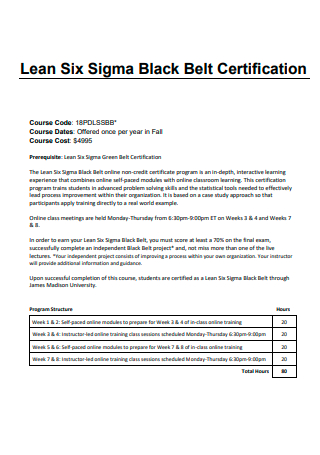
Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification
download now -

Simple Lean Six Sigma
download now -
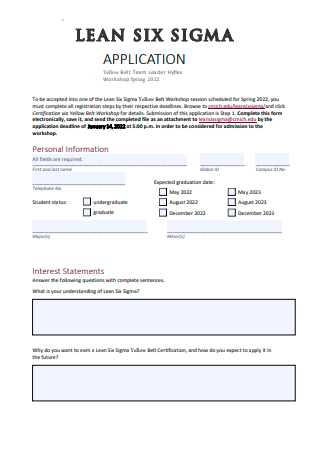
Lean Six Sigma Application
download now -

Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt
download now -
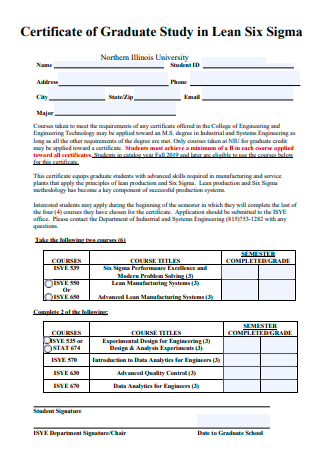
Certificate of Graduate Study in Lean Six Sigma
download now -

Lean Six Sigma and Big Data
download now -

Lean Six Sigma in Business Surveys
download now -

Short Course Lean Six Sigma
download now -

Lean Six Sigma Certificates
download now -

Printable Lean Six Sigma
download now -

Training Curriculum Lean Six Sigma
download now -

Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Application Form
download now
What Is Lean Six Sigma?
According to the American Society for Quality (ASQ), Lean Six Sigma is an evidence-based, data-driven improvement methodology that recognizes a higher priority on fault prevention than defect discovery. By lowering variance, waste, and cycle time and encouraging the adoption of work standardization and flow, the method boosts customer satisfaction and bottom-line results while giving businesses a competitive edge. Every employee should take part in it, and the application happens whenever there is variance and waste. It integrates the tools, techniques, and guiding concepts of Lean and Six Sigma into a well-liked and effective methodology for enhancing your company’s operations. The collaborative nature of the Lean Six Sigma methodology showcases an increase in productivity and profit margins for companies all around the world. Process wastes can be decreased or eliminated using lean concepts. Six Sigma places a strong emphasis on process variation reduction. There is further improvement in the efficiency and quality of the process using the Lean Six Sigma concepts. To put it simply, Lean Six Sigma advocates eliminating any resource consumption that doesn’t add value for the end user because it is wasteful.
According to ASQ Six Sigma Business Solutions, an estimated 82 percent of Fortune 100 companies use the Six Sigma methodology. As Six Sigma is a method many companies use, some companies pursue the Lean Six Sigma approach to reduce waste while increasing productivity to achieve overall customer satisfaction.
Principles of Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma has been effective in many industries and organizations, including agriculture, banking, electronics, financial services, government, hospitals, manufacturing, retail, telecommunication, and transportation. It is also successful in various departments of an organization, with call centers, customer service, finance, human resources, IT, legal, maintenance, marketing, quality, and sales, using the method to run its operations. For a business to achieve a successful Lean Six Sigma program, there are different principles to mark the path to success.
How To Perform Lean Six Sigma for Businesses
Lean Six Sigma projects follow structured techniques and methodologies in five phases. These phases are known as the DMAIC acronym representing the steps that stand for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. Each phase addresses a premise before it proceeds to the next stage of the process, and the duration stems from collected data. After each phase, there is a review from stakeholders and Lean Six Sigma experts before proceeding.
1. Define Phase
This phase is the first project phase that must answer whether the team recognizes the issue or problem from a business perspective. A project leader provides a high-level definition of the problem and must get insights and information from customers and stakeholders to understand their perspectives. After acknowledging the stakeholder and customer feedback, the next step is to determine the product or service the team provides. Determining the boundaries for each proposed solution and its processes requires the expertise of subject matter professionals. The Define phase ends with developing a project charter to pinpoint the problem, processes requiring analysis, and performance improvement objectives.
2. Measure Phase
The second phase establishes the project’s current status by measuring the performance of processes, products, or services according to quality attributes from the first phase. It must answer whether people understand the workflow for the process and if there is a measurement for each step. The process must be well-defined, with each step measuring time, quality, and other attributes linked to customer satisfaction. The team must develop and verify a suitable measurement system for accurate and complete data collection. Subject matter professionals identify the necessary processes to construct and apply performance measurements. At the end of the phase, the team possesses quantified data to constitute consumer problems with accurate assessments of the current situation.
3. Analyze Phase
In the Analyze phase, process and product data undergo root cause analysis to identify the problem’s origins, answering whether the team properly identified the problem and determined its root causes. The project leader uses Lean tools and Six Sigma hypothetical testing to determine the root cause through mathematical procedures. Despite implementing vigorous analytical and statistical procedures, the math must be straightforward. In case the data from the Measure phase is insufficient, further research study and data collection are necessary. The team must produce a detailed problem statement after gathering all information based on facts and statistics. At the end of the Analyze phase, everyone must agree on understanding and clarity of the problem.
4. Improve Phase
During the fourth stage, the team develops improvements to address the symptoms of the problem and to create a solution to the problem to eliminate or control it. It must have an answer for the viability of solutions and if it’s ready for implementation. During the Improve phase, solutions go through development and testing, and depending on the nature of the solution, is the most expensive stage. New procedures require businesses to change or provide new equipment, software, or materials. All solutions must go through tests with training and implementation materials ready for deployment, and at the end of the phase, a solution is set.
5. Control Phase
The final phase of Lean Six Sigma is the Control phase, wherein the team implements the solution. The stage continues until the solution stabilizes and the various aspects of the organization and its functions stabilize. The phase must answer whether the team establishes a new process to eliminate or control consumer problems. All team members must implement and observe any changes in processes for full implementation and continues until everything stabilizes. There must be a control plan to monitor a process, product, or service, including a measurement threshold for acceptable performance or action. The entire phase ends when managers and leaders no longer need help from the project team.
FAQs
What is the difference between Lean Six Sigma and Six Sigma?
The most apparent difference between Lean Six Sigma and Six Sigma is that the goal of Lean Six Sigma is to streamline processes to offer the best value to customers through phased thinking using DMAIC instead of just prevention in Six Sigma.
Why is Six Sigma called Six Sigma?
The term Six Sigma comes from the bell curve structure in statistics wherein a curve represents a mean deviation, with six Sigmas above and below the mean representing an extremely low defect possibility.
What is the primary goal of Lean Six Sigma?
The primary goal of Lean Six Sigma is to achieve customer satisfaction, add value to products or services, eliminate or lessen waste for continuous flow, and focus on value-generating opportunities.
Lean Six Sigma is a method different industries and departments use to apply necessary changes for a project or organization to change processes, products, and services to consumers or stakeholders. Lean Six Sigma eliminates and lessens waste for continuous improvement to run a successful business while satisfying customer needs and providing solutions to problems. The process aims to eliminate root causes and associated costs of time and money for non-value-generating activities. Construct a Lean Six Sigma document for the organization to convert solutions into value by addressing customer concerns and improving their satisfaction through conducting the DMAIC method. Use the sample templates of the Lean Six Sigma document above for reference.
