Logic Models Samples & Templates
-
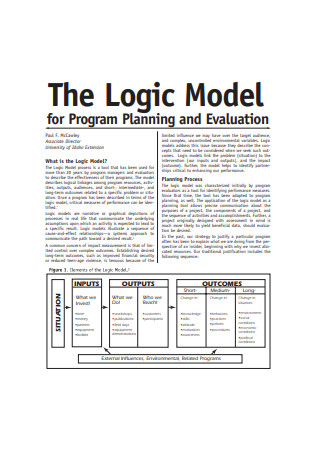
Logic Model Sample
download now -

Program Logic Model
download now -
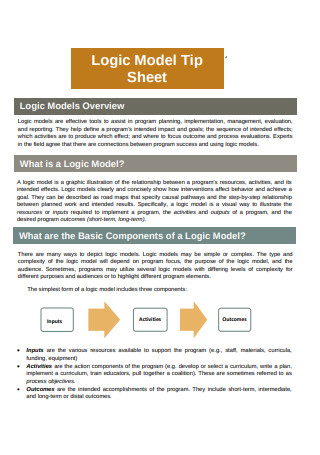
Logic Model Tip Sheet
download now -

Program Logic Model Format
download now -
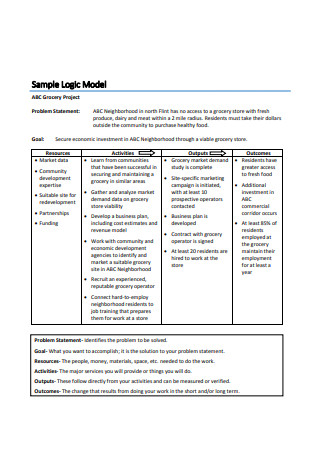
Sample Logic Model
download now -
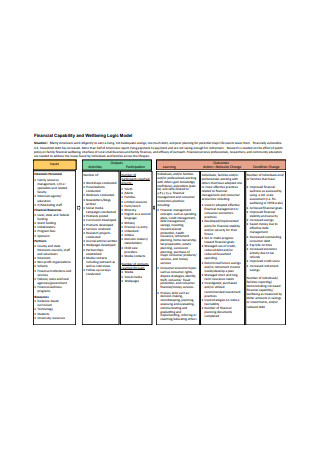
Financial Logic Model
download now -
Logic Model Format
download now -
Project Logic Model
download now -
Program Logic Model Example
download now -
Basic Logic Model
download now -
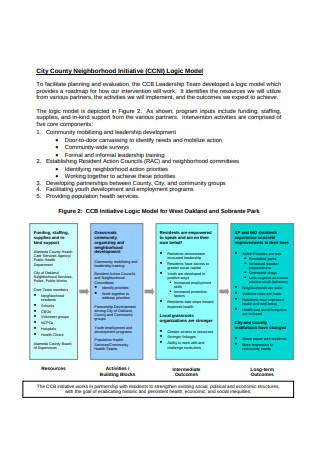
Simple Logic Model
download now -
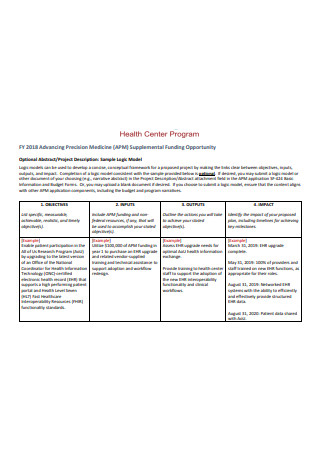
Sample Logic Model Format
download now -
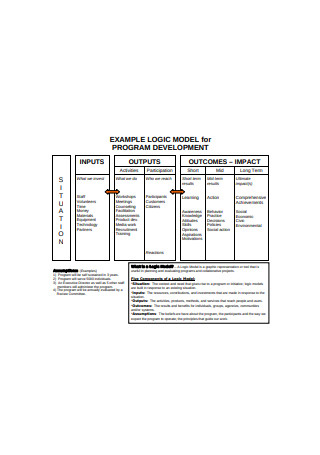
Program Logic Model Sample
download now -
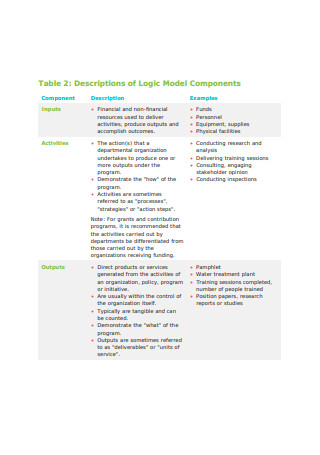
Logic Model Components
download now -
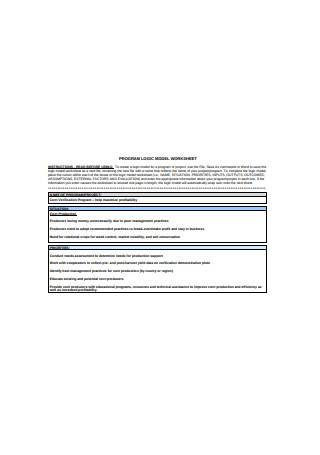
Program Logic Model Worksheet
download now -

Logic Model Worksheet
download now -
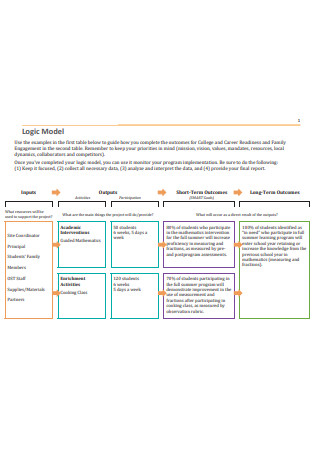
Standard Logic Model
download now -
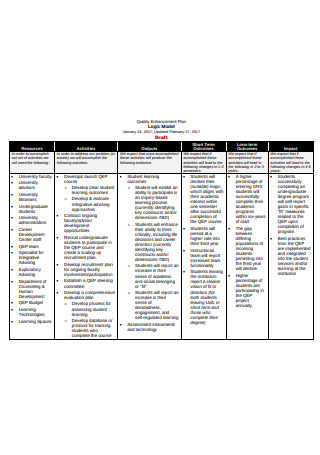
Basic Logic Model Format
download now -
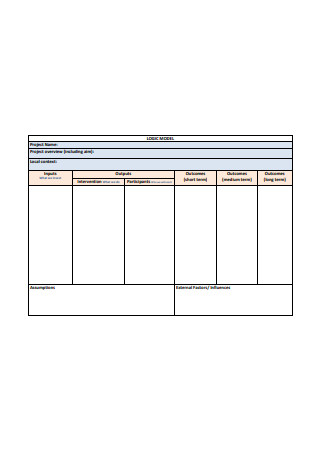
Project Logic Model Format
download now -
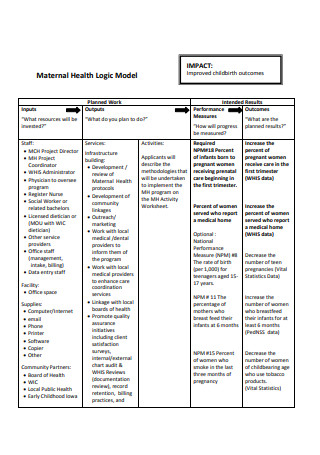
Health Logic Model
download now -
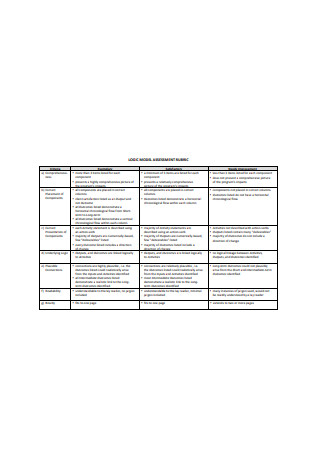
Logic Model Assessment
download now -
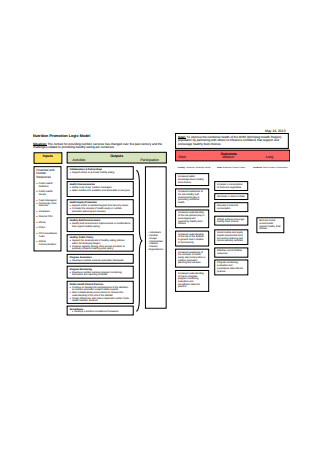
Nutrition Promotion Program Logic Model Worksheet
download now -
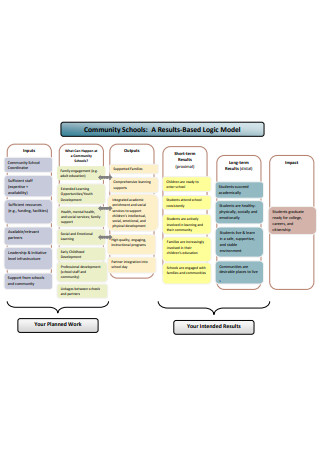
Community Logic Model
download now -

Logic Models for Programme Planning and Evaluation Template
download now -
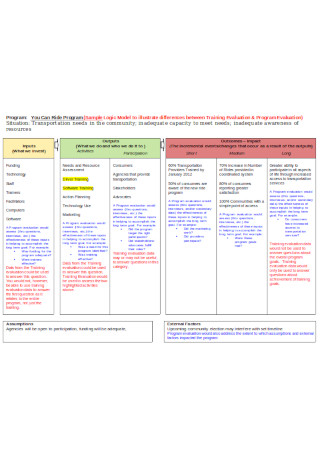
Sample Logical Model Example
download now -
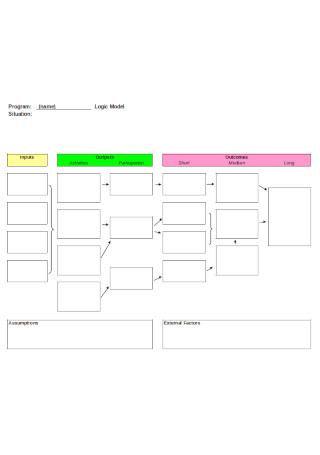
Logical Model Flowchart Template
download now
What Is a Logic Model?
Conjoining the meaning of the words logic and model, this tool is a visual representation that relies on rational thought. A logic model explains the mind behind a proposed project. It is an elaborate model showing how the factors of a proposed solution to a problem in the organization interconnect to achieve the desired solution. This diagram breaks down the features of the initiative and how it contributes to its overall success. Because of its visual nature, this diagram helps in relaying the specifics of the proposal more understandably to non-experts.
A logic model’s appearance strongly resembles a concept map or a project flow chart. The point of difference between the two is that concept maps indicate the relationships of proven statements and claims. It is a web of known knowledge about a specific topic or ideology. On the other hand, the relationships depicted on logic models are theoretical in nature. Predictions and desired outcomes make up most of the diagram.
What Makes it Logical?
Logic, per se, plays a vital role in how we make our decisions. Some of us thoroughly compare the pros and cons of committing to specific organizations. Even on choosing what to wear on a particular day, others carefully decide on how they present themselves. Logic makes sense of the things that compose everyday interactions. As much as it is essential in everyday life, logical decisions bear the same importance in corporate set-ups. In making such decisions, project managers make use of different tools, which include logic models, to have a comprehensive view of the project and its effects. Here are the essential features of the model which embodies the use of logic.
The Rationale Behind Logic Models
Would you do something without thinking about it? It might work well for decisions with no significant implications for one’s daily life. But, when it comes to decisions that can possibly change an individual’s course, we need to consider several factors before making a final decision. We make use of different methods to weigh these decisions. But, before fully utilizing the tool, we need to understand how to use it and its implications too. For a logic model, here are some of the reasons why it remains to be relevant in corporate avenues.
Contains Efficient Multiple Uses
A standard factor to consider when one invests in a product is the number of times that they can use it over and over. Granted that the effectiveness of the product does not wane along with time. It implies that the consumer gets the best out of the product. Similarly, logic models are cost-efficient for companies because of its versatility. This tool is functional for every step necessary in program development, up until program evaluation. For instance, during the implementation stage, a logic model can serve as a reference point to show the true north of the project. Project managers and executives use this tool to align the tasks with the corporate mission and vision.
Supports the Implementation of the Alternative
Another key reason why organizations continue to patronize logic models is that it is a useful tool to push for a project’s implementation. This function is at its prime when pitching the project. When facing people who have limited knowledge of the industry’s terms and technicalities, the language of the presentation needs to be in an understandable form. Layman’s speech is not enough. A visual presentation seals the deal. By presenting the elements of the projects and how it interrelates with one another, it depicts a clear picture of the stakeholder’s role in the project. This increases the probability of getting their cooperation because they know what exactly they need to do to get what they want.
Inclusive to All the Key Stakeholders of the Project
A logic model provides a holistic view. Beginning from all its essential elements, the pieces of information it requires looks into the perspective of the different groups involved in the project. For this reason, it is an inclusive tool that is understandable by everyone. Also, a logic model is easy to use. It is a friendly tool that newcomers and executives in the industry can whip up quickly. Logic models are useful for new employees. It can serve as they familiarize their new routine within the organization. Other than that, they can also use these models to make themselves familiar with the ongoing projects of the company. In cases of introducing intervention methods concerning public health, the stakeholder varies greatly. Health promotion is everybody’s concern. From pharmaceutical executives, healthcare professionals, politicians, to the general public, everyone needs to understand the model at the same level regardless of their expertise in their particular fields.
How to Visualize Your Project Using Logic Models
The composition of a logic model plays a vital role in a project’s implementation. Anyone with a sane mind would only approve projects that show potential and have firm foundations. Otherwise, it is a waste of the company’s resources. And the best way to get the approval and funding for your project is through its careful and comprehensive presentation. If you still have questions on how to make one, here are some helpful steps that you can follow.
Step 1: Understand the Project
In order to perfectly capture the elements, you need to understand the project down to its very core. You can create a model by hearing the details third-hand. But, knowing the details behind every nook and cranny builds up a more comprehensive logic model. Apart from that, understanding the project helps you create rational assumptions of how one factor affects another. It is essential to dissect the project and clearly point out each input, output, outcome, and effects to all the involved stakeholders. Understanding the foundation of the projects also provides you with the sources if there is a need to research more on its use and necessary to supply more information.
Step 2: Assign Symbols for Each Element
The advantage of a logic model significantly relies on its visual composition. Justifiably, substantial effort must is necessary for creating the diagram. After figuring out the details that fall under each element, you need to find a way to show the distinct categories in the model. The best way to do it is by assigning symbols that represent each category. On the other hand, if you want to produce a more sleek looking design, you can make use of one shape but filled with different colors. The colors make it distinct from one another. Regardless of your preference, remember the main goal of the logic model. Your choice should aid in relaying the message directly and straightforwardly, and not in a confusing way.
Step 3: Develop an Outline First
At this point, you already have the details for each element and an idea on how to present them. Now, it is time to combine these two elements to create the model. It may be confusing to dive into making the map directly. You can create an elaborate outline of the details first. A table can help you organize the details in an orderly manner. Place the details of the input, output, outcomes, and effects in separate columns. As for the details within the rows, make sure that one unit from the information has a connection with the next column’s data. In this manner, you can lay out all the relationships of the factors in a linear direction. After making sure that the pieces of information on the table are accurate, you can do the map with all the symbols and colors.
Step 4: Be Careful with Arrowheads
It is a mortal crime to overlook the importance of arrows in creating logic models and road maps. Other than the details of the project, the proper use of the indicators completes the use of logic models. Generally, it provides the direction of the project. It also includes information on how an individual can navigate through the planning, implementation, and evaluation of a particular project. Incorrect arrowheads may lead to confusion on which step goes first and on what is necessary for a specific process. Although a logic model is only one of the supplementary tools in project management, the confusion from this model can also make one question the validity of the others.
Step 5: Assess the Effectiveness of the Logic Model
Before a logic model becomes an integral tool in evaluating other projects, it must be innately useful as a stand-alone tool. The question stands: How do we assess a logic model? Because of the model’s versatility, the basis for its evaluation is its role for a specific project. For models used in program planning, its assessment focuses more on its ability to make the process shorter and more accurate. There are several metrics on how to measure its effectiveness, make sure to use the appropriate one for your use.
Projects are essential for the growth of an organization. As much as executives want to put up one plan immediately after another, it can be very costly to do. For that reason, project proposals are thoroughly assessed to determine if the advantages of the program are worth its price. However, it is not wise to spend more resources during the assessment of the project. With logic models, you can use it for all the levels in a project’s evaluation. Not only is it versatile in terms of its use, but it is also a comprehensive tool that highlights the perception of the different primary stakeholders of the project. If you are currently looking for a tool that will help in your corporate growth, logic models are widely available.
