Audit Plan Samples
-

Bank Audit Plan
download now -

Clinical Audit Plan
download now -

Environmental Audit Plan
download now -

Brand Audit Plan
download now -
Audit Plan Gantt Chart Template
download now -

HACCP Audit Plan Template
download now -

Security Audit Plan Template
download now -

Audit Test Plan Template
download now -

Audit Plan Template
download now -

Annual Audit Plan Template
download now -

Communication Audit Plan Template
download now -

Safety Audit Plan Template
download now -

Food Safety Audit Plan Template
download now -

Free Compliance Audit Plan Template
download now -

Sample HACCP Audit Plan Template
download now -

Audit Remediation Plan Template
download now -

Audit Project Plan Template
download now -

Audit Action Plan Template
download now -

Audit Strategic Plan Template
download now -

Audit Compliance Plan Template
download now -

Audit Work Plan Template
download now -

Smart Audit Action Plan Template
download now -

Internal Audit Strategic Plan Template
download now -

Audit Corrective Action Plan Template
download now -

Free Audit Planning Memo Template
download now -

Sample Audit Plan Template
download now -

Internal Audit Plan Template
download now -

Risk Assessment and Audit Plan
download now -

Finance Audit Plan Template
download now -
Sample Internal Audit Plan Template
download now -

Sample Planning an Audit Template
download now -
Basic Audit Plan Template
download now -

IT Audit Plan Template
download now -
External Audit Plan Template
download now -
Annual Audit Plan Template
download now -
Strategic Audit Plan
download now -

Annual Audit Plan Example
download now -
Yearly Audit Plan Template
download now -
Simple Audit Plan Template
download now -
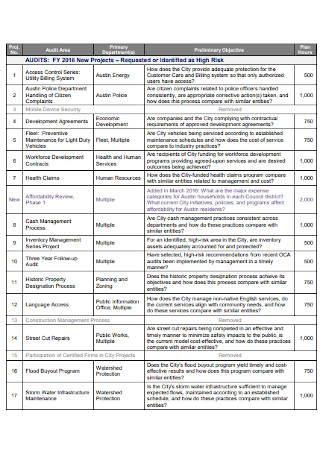
Amended Audit Plan Template
download now -

Formal Audit Plan Template
download now -
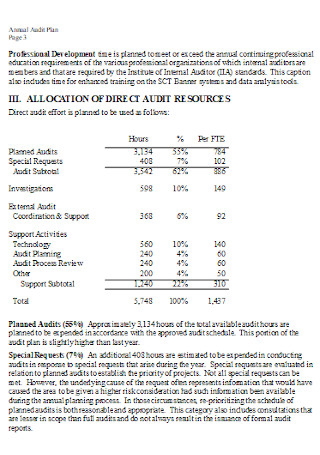
Year Annual Audit Plan
download now -

District Audit Plan
download now
FREE Audit Plan s to Download
Audit Plan Format
Audit Plan Samples
What is an Audit Plan?
Purposes of an Audit Plan
How to Create an Audit Plan
FAQS
What methodologies are commonly used in audit plans?
What challenges can arise during the implementation of an audit plan?
How does an audit plan contribute to organizational growth?
How does an audit plan contribute to organizational growth?
How does technology impact audit plans?

Audit Plan Format
1. Title Page
- Title: “Audit Plan for [Company/Organization Name]”
- Audit Period: [Start Date] to [End Date]
- Prepared by: [Audit Team or Firm Name]
- Date of Preparation: [Date]
2. Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Objective and Scope of Audit
- Audit Approach and Methodology
- Audit Timeline and Milestones
- Resources and Responsibilities
- Risk Assessment
- Deliverables
- Appendices
3. Executive Summary
- Overview of the audit purpose.
- Summary of key objectives.
- High-level approach.
- Expected outcomes.
4. Objective and Scope of Audit
- Objective: Define the purpose of the audit (e.g., compliance, financial, operational, IT).
- Scope:
- Areas to be covered.
- Processes, departments, or systems included.
- Exclusions or limitations.
5. Audit Approach and Methodology
- Approach:
- Risk-based.
- Checklist-based.
- Sample testing.
- Methodology:
- Data collection methods (e.g., interviews, document review, observation).
- Tools/software to be used.
- Analytical techniques.
6. Audit Timeline and Milestones
- Detailed schedule with the following stages:
- Planning Phase
- Fieldwork/Execution Phase
- Reporting Phase
- Review and Follow-up Phase
- Key deadlines and milestones.
7. Resources and Responsibilities
- Audit team members, their roles, and contact information.
- Responsibilities of the audited entity (e.g., providing access to documents, scheduling interviews).
8. Risk Assessment
- Key risks identified during planning.
- Risk rating (low, medium, high).
- How the risks influence the scope or methodology.
9. Deliverables
- Audit report format and expected content.
- Interim reports, if applicable.
- Final report deadline.
10. Appendices
- Supporting documentation, such as:
- Audit checklist or framework.
- Reference documents.
- Risk matrix.
- Organizational charts or process maps.
What is an Audit Plan?
An audit plan is a comprehensive document prepared by auditors to define the scope, objectives, timeline, and methodology of an audit. It outlines the specific areas to be audited, the risks to be addressed, and the procedures to collect and evaluate evidence. The audit plan acts as a roadmap, guiding the audit team in systematically examining financial statements, operational processes, or compliance adherence. It ensures the audit is performed efficiently, effectively, and in alignment with regulatory standards. You can also see more on Work Plan.
Purposes of an Audit Plan
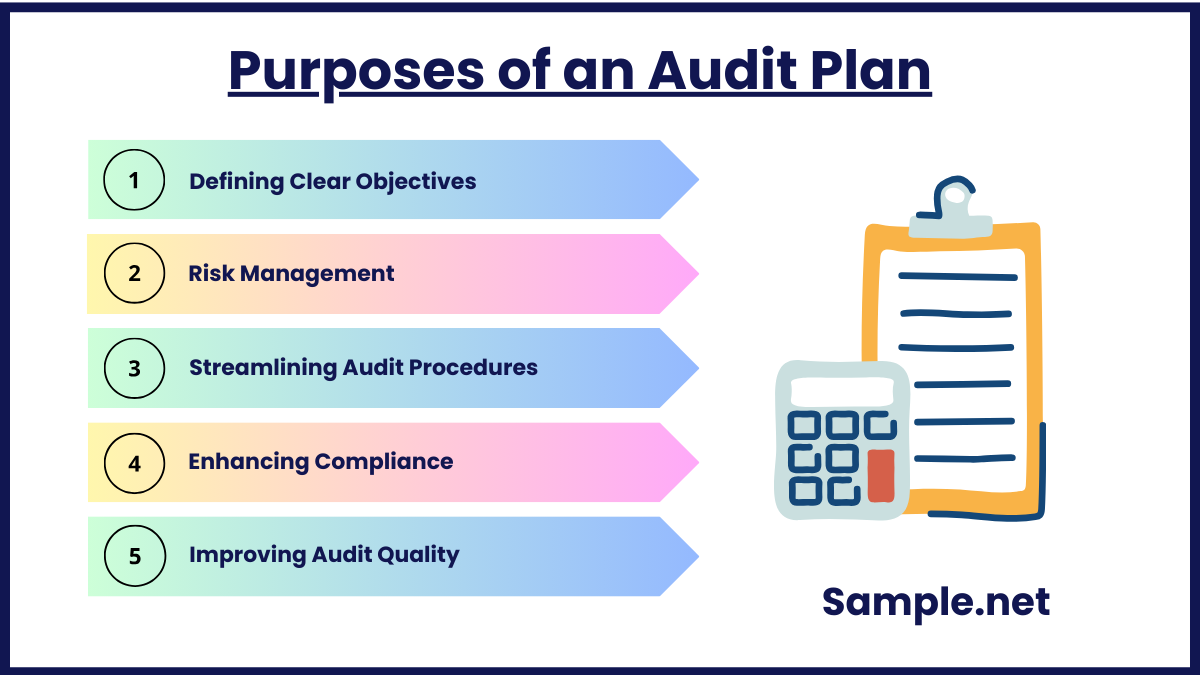
1. Defining Clear Objectives
An audit plan provides a structured framework for identifying and achieving specific audit objectives, such as ensuring compliance with regulations, detecting irregularities, or verifying the accuracy of financial statements.
2. Risk Management
By assessing and prioritizing risks, an audit plan focuses on high-risk areas, helping auditors allocate resources effectively and prevent errors or fraud.
3. Streamlining Audit Procedures
The plan organizes and outlines the procedures, timelines, and resources required, ensuring that the audit process is efficient and systematic. You can also see more on Project Plans.
4. Enhancing Compliance
Audit plans ensure adherence to applicable laws, standards, and organizational policies, promoting accountability and minimizing legal or regulatory risks.
5. Improving Audit Quality
By fostering consistency, accuracy, and thoroughness, the audit plan enhances the reliability and credibility of audit findings, benefiting both internal stakeholders and external regulators. You can also see more on Skills Development Plan.
How to Create an Audit Plan
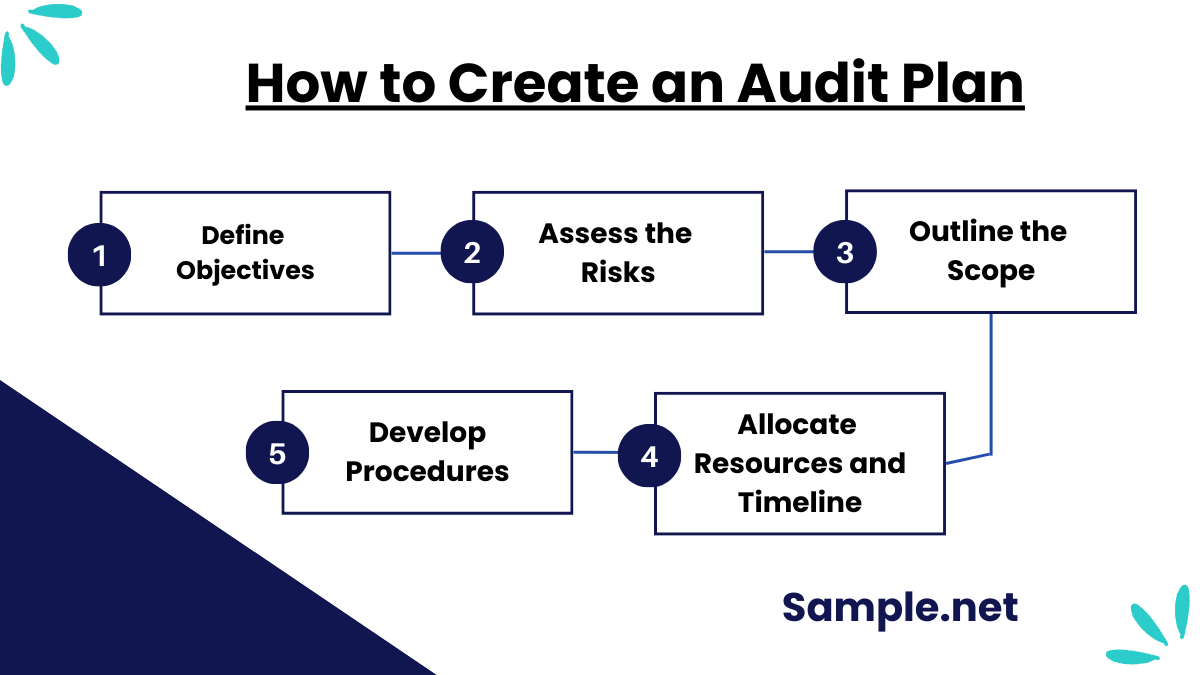
Step 1: Define the Objectives
Start by clearly identifying the objectives of the audit. Determine what areas or processes need auditing and the purpose of the audit, such as ensuring compliance or identifying inefficiencies. Engage stakeholders to align objectives with organizational goals and regulatory requirements. This step sets the foundation for a focused and meaningful audit process.
Step 2: Assess the Risks
Conduct a risk assessment to identify high-risk areas that require priority. Evaluate the likelihood and impact of potential issues, such as financial misstatements or operational inefficiencies. Use this assessment to allocate resources effectively and tailor the audit procedures to address significant risks. You can also see more on Program Management Plan.
Step 3: Outline the Scope
Define the audit’s scope, including the departments, processes, or systems to be reviewed. Specify the time period and any limitations. This step ensures the audit remains focused and avoids scope creep, enhancing its efficiency and effectiveness.
Step 4: Develop Procedures
Design the methodology and procedures to gather and analyze evidence. This includes selecting sampling techniques, defining testing methods, and outlining reporting protocols. Ensure the procedures align with auditing standards to maintain consistency and credibility.
Step 5: Allocate Resources and Timeline
Assign roles and responsibilities to the audit team and develop a timeline for each phase. Include milestones for planning, execution, reporting, and follow-up. Effective resource allocation ensures the audit is conducted within the specified time frame without compromising quality. You can also see more on Service Delivery Plans.
FAQS
What methodologies are commonly used in audit plans?
Common methodologies include sampling, walkthroughs, substantive testing, and control testing. These methods ensure comprehensive evidence collection and accurate evaluations.
What challenges can arise during the implementation of an audit plan?
Challenges include insufficient resources, lack of stakeholder cooperation, scope creep, and changes in regulatory requirements. Effective planning and communication can address these issues. You can also see more on Short Term Action Plan.
How does an audit plan contribute to organizational growth?
By identifying inefficiencies, ensuring compliance, and improving transparency, an audit plan helps organizations optimize processes, mitigate risks, and build stakeholder trust, fostering growth.
How does an audit plan contribute to organizational growth?
By identifying inefficiencies, ensuring compliance, and improving transparency, an audit plan helps organizations optimize processes, mitigate risks, and build stakeholder trust, fostering growth. You can also see more on Management Action Plan.
How does technology impact audit plans?
Technology enhances audit plans by enabling data analytics, automated testing, and real-time monitoring. IT tools improve accuracy, efficiency, and scope of audits, especially in complex environments.
