65+ Sample Care Plan Templates
-

Patient Care Plan
download now -

Wellness and Self Care Planner Template
download now -

Personal Self Care Planner Template
download now -

Patient Care Plan Template
download now -

Nursing Home Care Plan Template
download now -

Nursing Care Plan Template
download now -
Child Care Plan Template
download now -

Mental Health Self-Care Plan Template
download now -
Free Blank Nursing Care Plan Template
download now -
Sample Nursing Care Plan Template
download now -
Mental Health Nursing Care Plan Template
download now -

Personal Care Plan Template
download now -

Self Care Plan Template For Students
download now -

Nursing Care Plan Smart Goals Template
download now -

Free Sanctuary Self-Care Plan Template
download now -

Self-Care Action Plan Template
download now -

Emergency Care Plan Template
download now -

Self Management Care Plan Template
download now -

Health Care Project Plan Template
download now -

Parenting Care Plan Template
download now -

Sample Patient Care Plan Template
download now -

Simple Nursing Care Plan Template
download now -

Basic Personal Care Plan Template
download now -

Individualized Diabetes Health Care Plan
download now -
Nursing Process Care Plan
download now -
Hypertension Care Plan
download now -

Acute Pain Care Plan
download now -

Patient Care Plan
download now -

Dementia Care Plan
download now -

Health Anxiety Care Plan
download now -

Fever Care Plan
download now -
Constipation Care Plan
download now -
Imbalanced Nutrition Care Plan
download now -

Anemia Care Plan
download now -
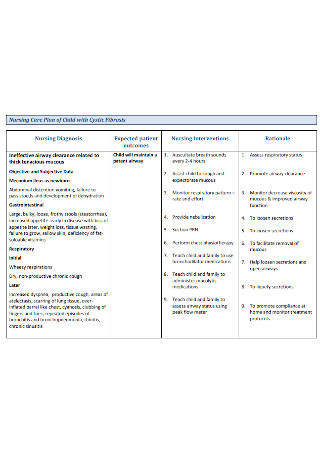
Impaired Physical Mobility Care Plan
download now -
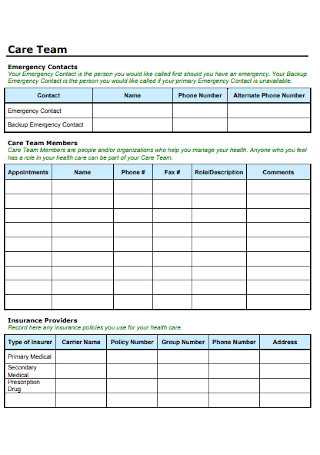
Nausea Care Plan
download now -
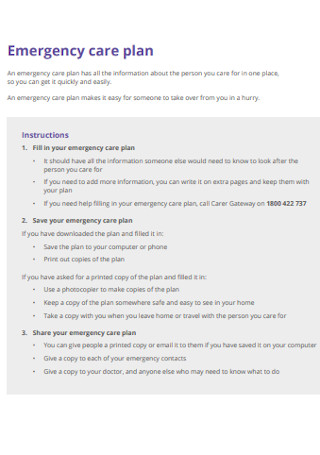
Emergency Care Plan
download now -

Residential Care Plan
download now -

Depression Care Plan
download now -
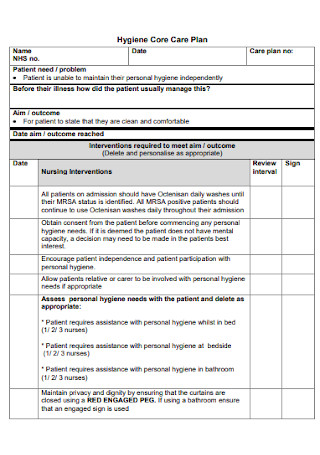
Skin Integrity Care Plan
download now -

Elderly Care Plan
download now -

Dehydration Care Plan
download now -
Electrolyte Imbalance Care Plan
download now -

Family Nursing Care Plan
download now -
Infection Control Blank Care Plan
download now -

Newborn Family Care Plan
download now -

Pneumonia Care Plan
download now -
Health and Wellness Care Plan
download now -
Basic Care Plan
download now -

Health care plan for Children
download now -

Nursing Care Plan
download now -
Sample Mental Health Care Plan
download now -

Supportive Care Plan
download now -

Survivorship care plans
download now -
Medicaid Service Care Plan
download now -
Public Service Care Plan
download now -
Sample Survivorship Care Plan
download now -

Behavioural Care Plan
download now -
Skin Care Plan
download now -
Personalised Care Plan for Last Days
download now -
College Nursing Care Plan
download now -
Care Home Resident Summary Care Plan
download now -
Butterfly Care Plan
download now -

Final Transition and Care Plan
download now -
Sample Individual Health Care Plan
download now -
Educational Health and Care Plan
download now
FREE Care Plan s to Download
65+ Sample Care Plan Templates
What Is a Care Plan?
Common Cases that Require a Care Plan
How To Write a Care Plan
FAQs
What is the difference between assessment and evaluation?
What are the examples of residential care facilities?
What does aged care mean?
Do nursing homes also utilize care plans?
What Is a Care Plan?
Care plans usually refer to nursing care plans. An NCP involves a process of identifying a patient’s needs and recognizing the associated risks. Also, care plans serve as instruments of communication between healthcare professionals to attain a patient’s healthcare goals. Without a care plan, the patient will most likely receive low-quality care. A care plan comes to play when a patient is under the custody of a healthcare facility. There are two types of care plans: a formal and informal nursing care plan. The former only exists in a nurse’s mind, while the latter is written on paper or is computerized. Also, formal care plans can be standardized or individualized. The first-mentioned details guidelines on how to care for a group of patients. The second one meets the needs of individual patients. It is vital to have a care plan because it defines a nurse’s role, serves as a guideline for care, encourages consistency in care planning, and serves documentation purposes.
According to Statista, as of 2016, there were about 2.86 million nurses in the U.S.
Additionally, Statista reports that over 6 million individuals were working at U.S. hospitals in 2016.
In 2017, there were more than 36.5 million admissions in U.S. hospitals.
Common Cases that Require a Care Plan
Several illnesses require a care plan. Note that care plans can come in different forms. Examples include pediatric, cardiac, endocrine, gastrointestinal, genitourinary care plans, and more. So, here are some common cases that require a care plan.
How To Write a Care Plan
The goals of a nursing care plan depend on what illness or disease a nurse is addressing. The steps below are ways to write a care plan correctly.
Step 1: Perform Subjective and Objective Assessment
Subjective assessment refers to client reports (e.g., family history, medical history, etc.). On the other hand, objective assessment applies to the information a nurse gathers from his/her assessment (e.g., physical assessment, vital signs, etc.). By performing an assessment, a nurse can put together a “nursing diagnosis.”
Step 2: Analyze the Data and Organize
After collecting data, you need to analyze them to formulate the right nursing diagnosis. Also, you must organize and prioritize them to prevent confusion. By doing that, you will be able to create goals for the betterment of your patient.
Step 3: Put Together a Nursing Diagnosis
By using the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association or NANDA diagnosis, you can identify and deal with your patient’s needs. The nursing diagnosis will serve as a guide for your intervention. There is a correct way to make a diagnosis, but that is over the bounds of this article.
Step 4: Set Your Priorities
When setting priorities, you can refer to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, which includes physiological, safety, belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. It would be best if you first prioritized physiological needs and safety more than feelings of esteem and self-actualization. That is because physiological problems can be life-threatening.
Step 5: Document Your Plan
The way you document a care plan depends on the policies of the hospital. The written plan you make becomes the patient’s official medical record, which will be reviewed by the next nurse. Note that different programs can have different formats.
FAQs
What is the difference between assessment and evaluation?
Evaluations are for documenting the achievement attained, while assessment focuses on measuring performance, skill, or working results to provide feedback on weaknesses and strengths and give direction for improvement.
What are the examples of residential care facilities?
Examples of residential care facilities are care and board homes. They are small and private facilities composed of less than 20 residents. Each person under custody may have a private room for themselves, especially when the facility is big. Typically, residents will get personal care, food, and staff members to take care of them 24/7. However, medical and nursing care is usually not available for such facilities.
What does aged care mean?
In the name itself, aged care is for the elderly who can’t live anymore in their homes due to disability, illness, an emergency, or bereavement. It can also be because the elderly cannot manage living at home without help. Aged care can be short-term or permanent. Short term aged care is also known as respite care if lesser care is needed, then it’s advisable to live in retirement villages or single living units.
Do nursing homes also utilize care plans?
Yes, care plans are not only used in hospitals but also in other healthcare facilities. What are nursing homes? Nursing homes are facilities that provide services that focus on health care. Services usually include food service, assistance with activities of daily living, round the clock supervision, and nursing care. Also, they provide rehabilitation services like occupational, physical, and speech therapy.
A care plan serves as a guide for nurses in delivering quality care. Also, it is a basis for diagnosis and intervention. Most importantly, by following the steps of a nursing care plan, healthcare providers will be able to achieve their desired goals for every patient. You can check and download one of our care plan templates above for reference and use.
