67+ Sample Intervention Plans
-

Behavior Intervention Plan Template
download now -
Student Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Crisis Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Academic Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Reading Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Behavior Modification Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Functional Behavior Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Preschool Behavior Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Classroom Behavior Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Informal Behavior Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Student Academic Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Intervention Lesson Plan Template
download now -

Intervention Specialist Lesson Plan Template
download now -

Special Education Behavior Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Behavior Intervention Lesson Plan Template
download now -

High School Behavior Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Math Intervention Lesson Plan Template
download now -

Free Sample Behavior Intervention Plan Template
download now -

Reading Intervention Lesson Plan Template
download now -

Intervention Action Plan Template
download now -

Small Group Intervention Lesson Plan Template
download now -
Behavioral Intervention Plan
download now -
Sample Reading Intervention Plan
download now -
Strength-Based Social Work Intervention Plan
download now -

High School Classroom Intervention Plan
download now -
Academic Grade Intervention Service Plan
download now -

Behavior Health Intervention Plan Sample
download now -

Middle School Behavior Intervention plan for English-Language
download now -

Functional Behavior Student Attendance Intervention Plan
download now -

Family Behavior Intervention Plan
download now -
Positive Behavior Elementary Intervention Plan
download now -
Preschool Behavior Intervention Program Plan
download now -

Sample Behaviour Intervention Plan
download now -

Kindergarten Reading Intervention Plan
download now -

Simple Intervention Plan Chart
download now -

Intervention Assessment Planning Process
download now -
Special Education Safety Intervention Plan
download now -

School Academic Written Intervention Plan
download now -

Response to Nutrition Intervention Plan
download now -
Crisis Prevention and Intervention Plan
download now -

Suicide Intervention Plan
download now -
Response to Intervention Management Plan
download now -

Event Crisis Intervention Plan
download now -
Behavior Intervention Plan Form
download now -

Standard Behavior Intervention Plan
download now -

Pre-School Intervention Plan
download now -
Pyramid Model Intervention Plan
download now -

Digital Response to Intervention Plan
download now -
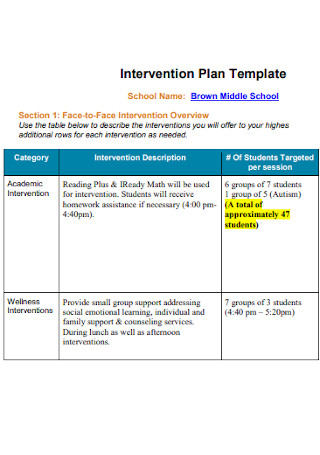
Public School Intervention Plan Template
download now -
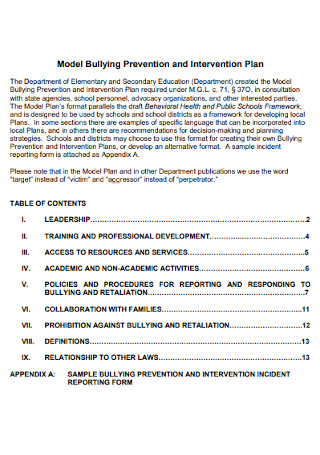
Model Bullying and Intervention Plan
download now -
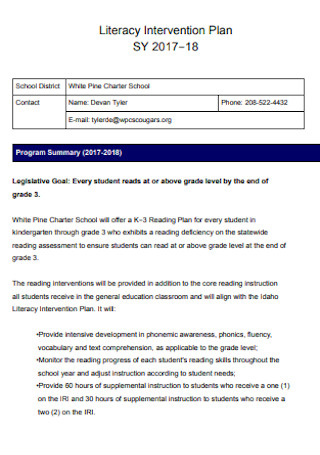
Literacy Intervention Plan
download now -
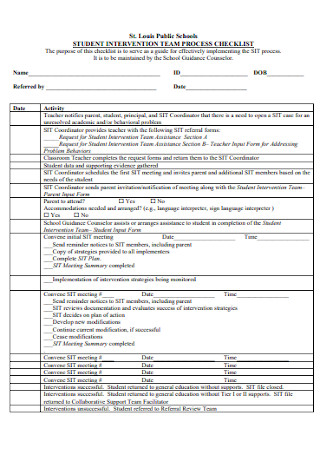
Student Intervention Plan Checklist
download now -
Action Research Intervention Plan
download now -
School Plan for Comprehensive Intervention
download now -

Basic Behavior Intervention Plan
download now -
Medical Intervention Plan
download now -

Intervention Plan Format
download now -
Behavior Intervention Plan Template
download now -
Lesion Intervention Plan
download now -
Printable Behavior Intervention Plan
download now -

Sample Intervention Plan for Child
download now -
Intervention Evaluation Plan
download now -

Sample Intervention Plan Example
download now -

Free Intervention Plan
download now -
Emergency Intervention Plan
download now -

Emotional Behavior Intervention Plan
download now -
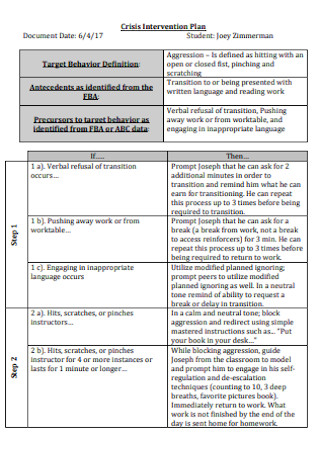
Sample Crisis Intervention Plan
download now -

Standard Intervention Plan
download now
FREE Intervention Plan s to Download
67+ Sample Intervention Plans
What Is an Intervention Plan?
Why Are Intervention Plans Important?
The Components of a Good Intervention Plan
How to Form an Intervention Plan
FAQs
What are the steps of an intervention?
What is an intervention plan in research?
What are some tips to make effective intervention strategies?
What Is an Intervention Plan?
An intervention plan is an action plan focused on helping or developing a person’s skills, behavior, or any goal to achieve. Intervention plans are commonly used to develop the progress of students who are currently struggling with their studies or performance. And as the intervention plan has a common goal, intervention strategy, feasible timeline, and a monitoring system, you can expect a great development towards the subjects being intervened.
Why Are Intervention Plans Important?
In case you are wondering why there is a need to set an intervention plan in the first place, here are some reasons that can be an eye-opener for you:
Identifies Weaknesses and Strengths
Intervention plans can help a teacher understand the strengths and weaknesses of each student in school. For example, one student may struggle towards a visual student learning contract style because that student works better with auditory learning instead. And it is crucial to understand the weaknesses and strengths of the subjects to intervene because they will help you realize what the best solutions for them would be until their strengths would be optimized and their weaknesses would transform as strengths.
Provides Development Plans
An intervention plan’s most common goal is to create a development plan that suits best for the subject or person of concern. So bear in mind that these plans are not solely for the purpose of assessing or criticizing the performance of certain subjects as they also aim for improvements. And that is just the right balance to observe in intervening because simply telling someone what is right or wrong without even trying to help them won’t make a huge difference.
Involves Progress Measurements
Since a development plan is incorporated in an intervention plan, how sure are you that actual progress happens? Do you really think a student improved with positive behavior after pushing through the development plan? That is why intervention plans also work as tracking logs where progress is being gauged regularly. Because if one plan went through but no progress took place, that is a sign that changing the plan must occur. So be sure to be responsible for tracking the progress of the subjects to make the whole intervention work effectively.
Promises Collaborative Efforts
An impressive asset of an intervention plan is how the process involves collaborative efforts. For example, a student would learn from the teacher’s method of a behavioral intervention plan. And at the same time, the teacher gives effort in helping the student to improve. So in order for the plan to work, both parties must work together like in a collaboration agreement. A student can show determination to learn and develop from the teacher’s recommendations and the teacher shows enough concern about the student through the plan.
Flexible for Different Subjects and Purposes
Don’t forget that intervention plans are not limited to student behavior and performance only. You can intervene with clients, employees, stakeholders, or anyone. At the same time, interventions can focus on a variety of purposes such as mental health management intervention plan, positive behavior modification plan, literacy intervention plan, or an occupational therapy modification plan. And despite what purpose the plan involves, be sure to clarify it in the intervention plan’s statement of purpose.
The Components of a Good Intervention Plan
With numerous possible examples of intervention plans out there, it is easy to get confused as to what the plan’s content should be. However, there is a common format for how standard invention plans are made. And they consist of the following important components:
How to Form an Intervention Plan
Albeit intervention plans sound like invading someone’s privacy, bear in mind that its intention is for the betterment of the subjects involved. So don’t be intimidated in making it because you can surely ace the process by following these steps on how to create a solid intervention plan:
-
Step 1: Create SMART Goals
First things first, make your intervention plan’s SMART goals. You will easily know how to write an intervention plan when you have already set specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and timely goals in the process. You will be able to clarify who your target audience is, what type of intervention method you use, what the purpose of the plan is, how long the intervention will take, and other intervention-related data of your plan. Because maybe you get confused such as ending up making an employee crisis intervention report but you were actually aiming for a student behavior intervention plan. Make it make sense.
-
Step 2: Optimize a Sample Intervention Plan Template
With over 46+ sample intervention plan templates listed in this article, you won’t run out of options easily. Select a ready-made intervention plan template you can edit and print anytime. You could opt for a sample intervention plan for students, an academic intervention plan template, a child support modification plan template, a depression management intervention plan template, and more printable templates to choose from. The best part with premade templates is even beginners won’t have a hard time making intervention plans since you will be guided with the standard layout and format of such plans.
-
Step 3: Complete the Components of an Intervention Plan
As previously discussed on the components of standard intervention plans from the subjects to the final decision, be sure to insert them in your plan. These examples slowly complete your plan in the first place. And besides those basic components, you can also add more examples that you think are useful for the intervention plan. You could insert another section for the intervention plan project budget, intervention plan checklist, or any other purpose.
-
Step 4: Write and Present the Data in Easy-to-Read Structure
As much as possible, write the whole intervention plan with an easy-to-follow structure. Maybe the subjects involved in the intervention would have a hard time understanding the plan’s content since you used too many technical terms, long flowery words, and other unnecessary details that could be omitted in the plan. That also goes to show how you present your data in the plan. Instead of just writing in long paragraphs, make use of other data presentations such as bar graphs, charts, and tables. The key is to reread everything and check if everything is understandable enough. If not, changes are a must.
-
Step 5: Don’t Forget to Monitor for Progress
Remember that intervention plans are not a one-time process. After implementing the plan, you still have to track if the subjects in the plan improved as planned or did not go according to the plan at all. Just like evaluation reports, measurement systems are a must if progress was made or the other way around. Good job if progress took place. But if things got worse or there was no improvement at all, then be sure to adjust the intervention plan and rectify it.
FAQs
What are the steps of an intervention?
An intervention consists of the following steps: formulate a plan, collect information, assign the intervention team, work on the appropriate consequences, take note of results, set an intervention meeting, and conduct a follow-up report.
What is an intervention plan in research?
In research, intervention plans mark the service descriptions to offer in reacting to a crisis. It likely tackles the problem statement, strengths, qualities, needs, and specific preferences.
What are some tips to make effective intervention strategies?
An intervention plan is already a good tip to set intervention strategies. But besides that, you can start small, learn how to interpret the outcome accurately, set an intervention scale, provide the best monitoring progress system, and share whatever system works best from your previous interventions.
Don’t wait for student behavior, employee performance, or any related problem to get worse. Intervene in the most professional and effective way possible with a sample intervention plan template as your guide. You would be surprised at how great of a development a person can do with proper guidance in an organized plan such as an intervention plan. Make your own intervention plan now!
