Maintenance Plan Samples
-

Electrical Maintenance Plan
download now -

Jewelry Maintenance Plan
download now -

Garden Maintenance Plan
download now -

Factory Maintenance Plan
download now -

10 Year Building Maintenance Plan Template
download now -

Free Asset Register and Maintenance Plan Template
download now -

Planned Maintenance Schedule Template
download now -

Assets Maintenance Plan Template
download now -

Asset Maintenance Plan Template
download now -

Asset Management Maintenance Plan Template
download now -

Sample Asset Maintenance Plan Template
download now -

Strategic Asset Maintenance Plan Template
download now -

Schedule Maintenance Plan
download now -

Maintenance Plan
download now -

Sample Maintenance Plan
download now -
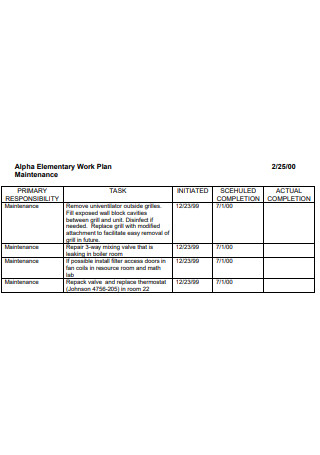
Alpha Elementary Work Plan Maintenance
download now -

Building Maintenance Practices
download now -

Operation Network and Maintenance Plan
download now -
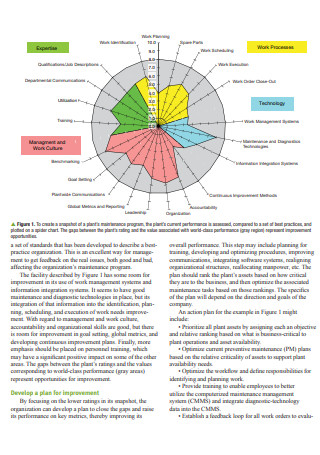
Develop a Maintenance and Reliability Plan
download now -

Post Construction Maintenance Plan
download now -

Maintenance Plan Example
download now -

Maintenance Planning and Scheduling
download now -

Sample Maintenance Planning
download now -

Air Conditioner Maintenance Plan
download now -

Business Maintenance Plan Designer
download now -

Software Website Maintenance Plan
download now -

Vehicle Hardware Maintenance Plan
download now -

Generic Hospital Maintenance Plan
download now -
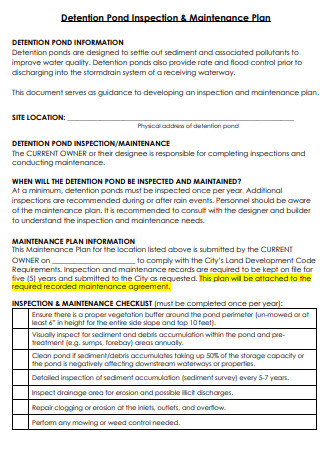
Hotel Maintenance Plan
download now -

Home Maintenance Plan
download now -

House Maintenance Plan
download now -

Manufacturing Maintenance Plan
download now -

Warehouse Maintenance Plan
download now -

Sample Workshop Maintenance Policy and Plan
download now -

Office Maintenance Program
download now -

Sample Operation and Maintenance Plan
download now -

Facility Maintenance Plan
download now -

Preventive Maintenance plan and Inspections
download now -

Sample Housing Authority and Maintenance Plan
download now -

Pump System Maintenance Plan
download now -

Comprehensive Maintenance Plan
download now -

Simple Maintenance Plan
download now -

Sample Free Maintenance Plan
download now -

Maintenance Plan Contract
download now -
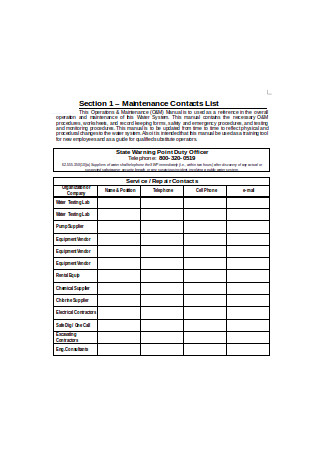
Maintenance Contacts List Plan
download now -

School Maintenance Plan
download now -

General Maintenance Plan
download now -

Maintenance Plan Format
download now -
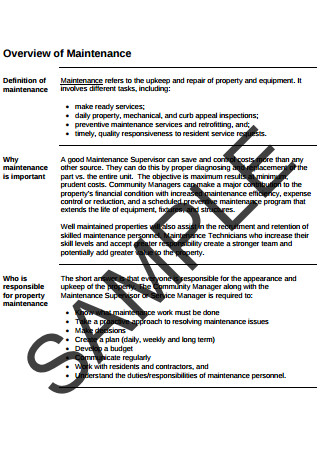
Property Maintenance for Managers
download now -

Preparation of Maintenance Plan
download now -

Inspection And Maintenance Plan for Dams
download now -
Maintenance Management Plan
download now -

Maintenance Department Plan
download now -

Maintenance Program Plan
download now -

Managing your Maintenance Plan
download now -
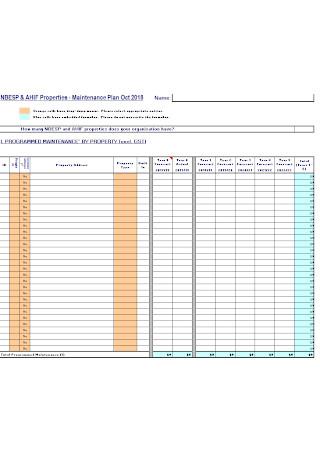
Monthly Property Plan
download now
FREE Maintenance Plan s to Download
Maintenance Plan Format
Maintenance Plan Samples
What is a Maintenance Plan?
Purpose of a Maintenance Plan
How to Create a Maintenance Plan
FAQS
How do I start creating a Maintenance Plan for my business?
What challenges might arise when implementing a Maintenance Plan?
What role does technology play in a Maintenance Plan?
How does a Maintenance Plan reduce costs?
How often should a Maintenance Plan be reviewed?
Download Maintenance Plan Bundle
Maintenance Plan Format
1. Introduction
- Brief overview of the purpose of the maintenance plan.
- Highlight the importance of the plan in ensuring the system/equipment’s optimal functionality and lifespan.
2. Objectives
- Define the goals of the maintenance plan (e.g., reducing downtime, enhancing performance, ensuring compliance with standards).
- Clearly state measurable outcomes.
3. Scope
- Specify what is covered under the maintenance plan (e.g., systems, equipment, areas).
- Exclude items that are not covered to clarify responsibilities.
4. Roles and Responsibilities
- Identify key stakeholders (e.g., maintenance team, operators, contractors).
- Define specific roles and responsibilities for each party involved.
5. Maintenance Schedule
- Provide a detailed timetable, including:
- Frequency: Daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, annual tasks.
- Specific Tasks: List tasks for each time frame.
- Include flexibility for emergency maintenance.
6. Procedures
- Describe step-by-step procedures for each maintenance activity:
- Tools and equipment required.
- Safety measures to follow.
- Methods of inspection, testing, and repair.
7. Resources and Tools
- List required tools, spare parts, and equipment.
- Mention any software or systems needed to track maintenance tasks.
8. Documentation
- Explain the importance of documenting maintenance activities.
- Include:
- Checklists for routine tasks.
- Logs for completed activities.
- Reports for significant repairs or upgrades.
9. Performance Monitoring
- Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of maintenance (e.g., downtime percentage, response time).
- Include methods for tracking and analyzing data.
10. Emergency Response Plan
- Outline steps to handle unforeseen issues or failures.
- Include emergency contact information and escalation procedures.
11. Review and Updates
- Specify the frequency for reviewing and updating the maintenance plan (e.g., annually).
- Mention who is responsible for the review process.
12. Conclusion
- Summarize the plan’s purpose and its expected benefits.
- Reiterate the commitment to maintaining optimal functionality and efficiency.
What is a Maintenance Plan?
A maintenance plan can open a lot of windows of opportunities to your business or organization. With the help of a maintenance plan, you can identify and specify all of the factors, elements, components, and variables that you must consider so you can ensure that a process, an equipment, a program, or any types of asset is at its best working condition. To help you easily have an idea of what a maintenance plan is, it is a document which presents all of the maintenance works, resources, requirements, schedules, and other related items that can help a business execute its maintenance program and set of activities. You can also see more on Work Plan.
Purpose of a Maintenance Plan
1. Maximizing Equipment Lifespan
A well-structured Maintenance Plan ensures equipment operates at peak efficiency for an extended period. By addressing minor issues early, it prevents significant breakdowns and reduces wear and tear. Regular maintenance routines preserve the value of assets, delaying the need for expensive replacements. This maximization of lifespan directly benefits an organization’s bottom line. Ultimately, it enhances reliability and reduces operational risks.
2. Minimizing Downtime and Interruptions
Planned maintenance activities help organizations avoid unexpected equipment failures and downtime. Maintenance Plans identify critical periods to perform necessary checks or repairs without disrupting operations. Predictive schedules ensure that systems remain functional, even during high-demand times. Reduced interruptions lead to improved productivity and a smoother workflow. With less downtime, companies can meet deadlines and deliver consistent results. You can also see more on Project Plans.
3. Enhancing Safety Standards
Maintenance Plans prioritize the safe functioning of equipment and systems, reducing the risk of workplace accidents. Regular inspections detect hazards such as faulty machinery, leaks, or electrical issues before they escalate. Compliance with safety standards is integral to the plan, ensuring the workplace remains secure. Employees feel more confident working in an environment where safety is prioritized. This focus on safety reflects positively on organizational culture.
4. Optimizing Resource Management
Maintenance Plans streamline the allocation of resources, including manpower, tools, and spare parts. By pre-scheduling tasks, organizations avoid last-minute emergencies that can strain resources. Efficient planning ensures the availability of critical components when needed, avoiding delays. This optimization reduces wastage and unnecessary expenses. Ultimately, it helps organizations maintain budget control and achieve cost efficiency. You can also see more on Program Management Plan.
5. Improving System Performance
Routine maintenance keeps systems running smoothly and efficiently, ensuring optimal performance. Clean, calibrated, and well-maintained equipment consumes less energy, reducing operational costs. Timely interventions prevent minor issues from escalating into costly failures. Improved performance translates into consistent quality and productivity. Organizations can maintain customer satisfaction by delivering reliable services or products.
How to Create a Maintenance Plan
1. Assess Equipment and Systems
Begin by identifying all equipment, systems, and infrastructure that require maintenance. Understand their functions, criticality, and operating conditions. Gather data on performance history, common issues, and manufacturer recommendations. This assessment lays the foundation for an effective maintenance plan. Prioritizing critical assets ensures focused efforts and resource optimization. You can also see more on Weekly Action Plan.
2. Set Clear Maintenance Objectives
Define the specific goals of your maintenance plan, such as reducing downtime, extending equipment lifespan, or ensuring compliance. Objectives should be measurable and achievable. For example, aim to reduce unplanned breakdowns by 20% within a year. Clear objectives guide the planning process and help measure success. Aligning objectives with organizational priorities enhances the plan’s relevance.
3. Develop Maintenance Schedules
Create a detailed schedule for routine, preventive, and predictive maintenance tasks. Include timelines, frequency, and responsible personnel for each activity. Use checklists to ensure all tasks are performed consistently and thoroughly. Account for manufacturer recommendations and operational demands. A well-organized schedule ensures timely interventions and avoids last-minute disruptions.
4. Allocate Resources Effectively
Identify the tools, spare parts, and personnel required for each maintenance task. Ensure these resources are available when needed to avoid delays. Establish a process for inventory management and procurement. Allocate responsibilities clearly, so team members know their roles and deadlines. Effective resource allocation minimizes inefficiencies and ensures smooth execution. You can also see more on Monthly Action Plan.
5. Monitor, Review, and Optimize
Implement mechanisms to track the performance of your maintenance plan. Use data from completed tasks to evaluate the plan’s effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. Adjust schedules, resources, or strategies as needed to address gaps or inefficiencies. Regular reviews ensure the plan remains aligned with organizational goals. Continuous optimization enhances long-term reliability and efficiency.
A Maintenance Plan is vital for ensuring operational efficiency, safety, and cost control in any organization. By proactively addressing potential issues, scheduling regular upkeep, and optimizing resources, businesses can minimize risks and maximize asset performance. A well-crafted plan reflects a commitment to sustainability and operational excellence, leaving a lasting impact on employees and stakeholders. Invest in a Maintenance Plan to create a future-proof foundation for success. You can also see more on Service Delivery Plans.
FAQS
How do I start creating a Maintenance Plan for my business?
Start by assessing all equipment and systems to understand their criticality and maintenance needs. Gather data on performance history, manufacturer recommendations, and common issues. Set measurable goals, such as reducing downtime or increasing equipment reliability. Then, create a schedule for routine checks, allocate resources, and define responsibilities. Finally, monitor and review the plan regularly to optimize its effectiveness.
What challenges might arise when implementing a Maintenance Plan?
Common challenges include insufficient resources, lack of skilled personnel, and resistance to change. Poor documentation or inadequate scheduling can also hinder the plan’s success. To overcome these, invest in training, ensure clear communication, and involve all stakeholders in the process. Regular reviews and updates help address challenges effectively over time. You can also see more on Quality Assurance Plans.
What role does technology play in a Maintenance Plan?
Technology enhances maintenance planning by providing tools for monitoring, data collection, and analysis. Condition-monitoring systems predict equipment failures, enabling timely interventions. Digital platforms streamline scheduling, resource allocation, and reporting. These technologies make maintenance plans more efficient and reduce manual errors. Adopting technology improves reliability and saves time.
How does a Maintenance Plan reduce costs?
A proactive Maintenance Plan minimizes unexpected breakdowns, reducing emergency repair costs and downtime. It optimizes resource allocation, ensuring tools and spare parts are available as needed. Preventive measures extend equipment life, delaying expensive replacements. Additionally, well-maintained systems consume less energy, lowering operational expenses. The cost savings outweigh the investment in maintenance planning.
How often should a Maintenance Plan be reviewed?
A Maintenance Plan should be reviewed at least annually or whenever significant changes occur, such as new equipment installations. Regular reviews help address inefficiencies, update schedules, and align with operational goals. Monitoring the plan ensures it remains effective and relevant to changing needs. Frequent evaluations enhance the plan’s long-term success. You can also see more on Short Term Action Plan.
