50+ Sample Patient Safety Plans
-
Patient Safety Plan Template
download now -

Patient Health Safety Plan
download now -

Sample Patient Health Safety Plan
download now -

Patient Safety Policy Plan
download now -

Psychiatry Patient Safety Plan Template
download now -

Patient Safety and Quality Plan
download now -

Patient Safety Improvement Plan
download now -

Medical School Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Patient Health Clinic Dafety Plan
download now -

New Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Patient Safety Plan Format
download now -
District Hospital Patient Safety Plan
download now -
Patient Safety Plan Worksheet
download now -

Basic Patient Safety Plan Template
download now -

Patient Safety Officer Plan
download now -

Patient Safety Action Plan
download now -

Patient Safety Strategic Plan
download now -

Simple Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Patient Education Safety Plan
download now -

Patient Surgery Safety Plan
download now -
Patient Safety Training Plan
download now -

Standard Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Patient Safety Strategy Plan
download now -
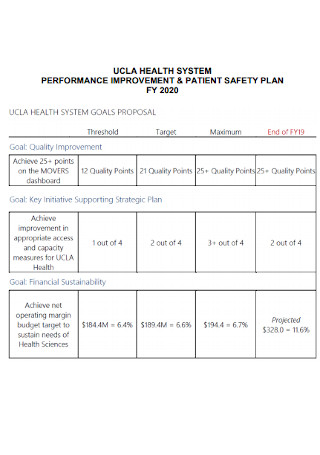
Performance Improvement and Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Medical Device Patient Safety Plan
download now -
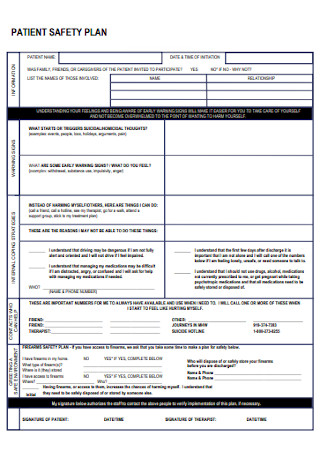
Mental Health Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Fire Patient Safety Plan
download now -
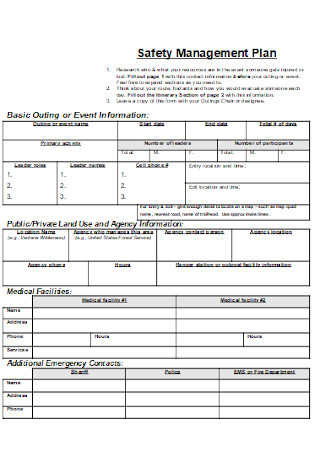
Patient Safety Management Plan
download now -

Health Quality and Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Integrating Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Sample Patient Safety Strategy Plan
download now -

Formal Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Memorial Hospital Patient and Safety Plan
download now -
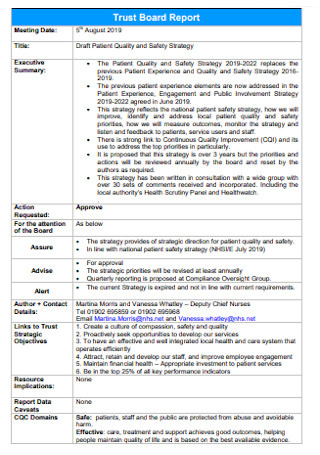
Patient Quality and Safety Strategy Plan
download now -

Patient Laboratory Safety Plan
download now -
Site Specific Safety Plan
download now -

Patient Safety Framework Plan
download now -

Patient Safety in Oregon Plan
download now -
Health Services Patient Safety Plan
download now -
Patient Safety Management Plan
download now -

Patient Safety Plan Checklist
download now -

Patient Safety Report Plan
download now -

Patient Recovery Safety Plan
download now -
Patient Field Safety Plan
download now -

Stadard Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Water Safety Plan
download now -

Patient Performance Safety Plan
download now -

National Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Family Patient Safety Plan
download now -

Student Suicide Safety Plan
download now
What Is a Patient Safety Plan?
A patient safety plan is an essential document that details a framework of an integrated and comprehensive program. It intends to monitor, evaluate, and improve the quality and safety of the patient care delivered. It presents guiding principles with set expectations to provide the best care possible for all patients. The patient safety plan facilitates the role of the medical organization in evaluating the quality, safety, and appropriateness of the program, including the assessable improvements to be made based on studies and facts. Medical physicians and attendants formulate the patient safety plans along with the medical institution.
According to a recent study made by John Hopkins Medicine dated in 2016, the United States recorded more than 250,000 deaths per year resulting from medical errors. It is said to be the third leading cause of death in America. The statement is very alarming, and it stresses the importance of a comprehensive patient safety plan.
Elements of a Patient Safety Plan
All safety plans differ in their format. However, the details must include the necessary information that ensures the patients’ security when unforeseen circumstances arise. Here are the components of a patient safety plan for mental health patients.
How to Create a Patient Safety Plan
Patient safety plans hold a vital role not only for the organization but the people in it as well. It is of utmost significance that the system ensures security to all persons concerned. All persons involved share the same goal: the best possible outcome. Here are steps to assure a comprehensive patient safety plan.
Step 1: Build a Rapid Response System
The rapid response system ensures the framework of the safety plan. It is composed of a team that disseminates it in a series of organized steps. The system must include the status of the patients, the team members, environment, and progress in achieving the goal. It outlines potential decision-making models according to various scenarios.
Step 2: Ensure Employees Understand Safety Procedures
All persons involved in the organization must understand their roles and responsibilities in the organization’s safety. It is necessary to train new employees about safety protocols and update staff about policy changes. Guarantee that the members understand the duties of upholding patient safety. All medical organizations must explicitly describe these safety policies and procedures. It is also essential for employees to voice concerns in managing and reporting issues.
Step 3: Promote a Safety Compliance Plan
The administration needs to evaluate employees’ compliance with the protocols. Necessary changes and adjustments to the provisions are imperative after the evaluation. By generating a safety compliance plan, corporations promote safe treatment conditions for everyone.
Step 4: Exercise Utmost Care for Patients
Always place the patient first before anything. Patient-centered care is often related to the quality of service. Patient-centered care is vital in the structure for establishing and developing desired wellness outcomes.
Step 5: Communicate the Importance of the Safety Plans to Patients
Medical professionals give importance to educating patients to lower the risk of medical errors. Through gathered information, patients gain knowledge to understand what facts apply to them and their medical condition. Through this, more patients are proactive in their recoveries. Patients who possess sufficient knowledge receive better and more dependable treatment through asking the right questions and knowing potential obstacles.
Step 6: Organize a Secure Layout of the Building
The building must be structurally sound and provides excellent air quality and flow, noise dampening, and critical information access. It must also have fixtures that promote hygienic practices throughout the building. Safe building designs also include proper ventilation, dispensaries, and waste disposal.
FAQs
What are the significant patient safety issues in American hospitals?
According to the World Health Organization, in high-income countries, an estimate of one out of 10 patients are harmed during hospital care, and 50% of the time, these cases are preventable. Millions of patients endure injuries or die due to inadequate and unsafe health care each year. Medical practices and hazards linked with health care appear as significant hurdles for patients’ safety. The safety issues faced by American hospitals include diagnostic errors. Diagnostic errors are one of the most common issues faced by hospitals. Delayed or missed results can cause suffering, adverse effects, and even death. Another issue on the list is maternal care. According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, about 700 women suffer death in the United States due to complications during pregnancy and delivery. Another relates to the delay in recognizing behavioral health needs. Failure to clean, disinfect, and sterilize medical equipment also contributes to safety issues.
What factors affect patient safety?
The factors affecting patient safety are under the classification of five elements. The five categories that influence patient safety are related to the patient, illness, health care professional, health care setting, and task. Patient-related factors include the patient’s knowledge about safety, the experiences related to health care and their coping mechanisms, and demographic characteristics. Illness-related factors involve the severity of the patient’s condition, treatment methods, and prior experiences with illnesses. The health professional’s belief about safety and patient interaction comprise the health care professional factors. The factors affecting the health care system involve the type of health care setting and the admission process. Lastly, task-related factors include a patient’s actions or behaviors toward the involvement on safety.
How many health systems are present in the United States?
The total number of all US hospitals reach 6,090 in 2021, according to the published article in Health Forum from data by the American Hospital Association(AHA). A vast majority of the hospitals in the US are under the classification of community hospitals. All nonfederal, short-term general medical organizations are under this classification. Despite all the healthcare systems made available in the US, there are still instances when patients lack accommodation. At a present time of a crisis, it’s beneficial for people to be able to access health care organizations in their areas. The overwhelming number of infections surprised our health departments to the point that the government started building more health care facilities.
How can medical errors be prevented or reduced?
Medical errors are one of the leading causes of death in the US, and medical practitioners and patients contribute to possible prevention methods. The most important way to prevent errors is to participate actively in health decisions. Many studies claim that the engagement of patients in healthcare is a crucial part of preventing medical errors. As a patient, it is beneficial to keep your medical doctor updated on any health conditions. It must include what over-the-counter medication you take, including supplements and vitamins. If you’re unsure of the given information regarding prescriptions, do not hesitate to ask your doctor about it. The doctor’s notes may be unclear but always ask about the advantages or side effects of the medicine. Consider talking to a licensed pharmacist regarding medication issues as well. The most crucial part of preventing or reducing medical errors is to ask questions and do your research. Never hesitate to ask your doctor questions about your health concerns.
What are patient safety indicators?
Patient Safety Indicators(PSI) provide information that focuses on safety-related adverse events following operations, surgeries, and other medical procedures. The PSI is used to help assess and identify issues that arise correlated to the procedures done. It helps to further the study on complications that arise following certain surgeries and seek to study these complications to prevent or lessen adverse events.
Safety should always be the priority in everyday life. It is necessary to protect ourselves and our well-being first and foremost. Start by eating healthy, exercising daily, and taking medication to ensure our immune system handles what life throws. It’s better to be protected rather than to face a difficult situation. The pandemic changed lives drastically, but even then, life must continue. Health care workers are doing the best they can to ensure patient’s safety despite being short-handed. Borrowing the words of Captain Scott Kelly. “Safety has to be everyone’s responsibility… everyone needs to know that they are empowered to speak up if there’s an issue.” A patient safety plan involves not only the medical worker but yourself as well. Check out the patient safety plans above and prioritize your safety.