8+ Sample Risk Management Action Plan
-

Risk Management Action Plan Template
download now -
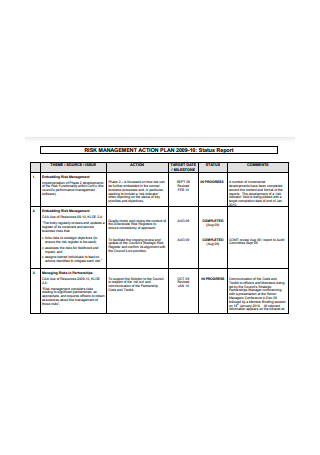
Basic Risk Management Action Plan
download now -
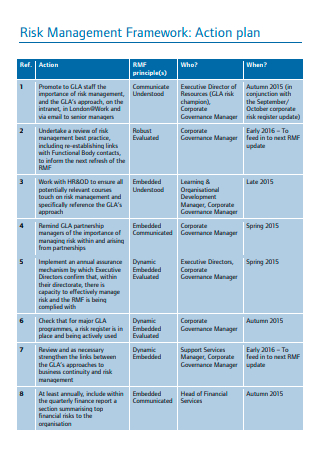
Risk Management Framework Action Plan
download now -

Risk Management Action Plan in PDF
download now -
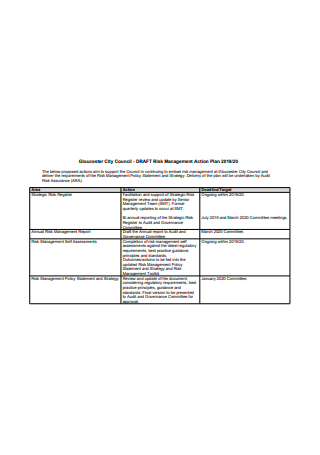
Draft Risk Management Action Plan
download now -

Risk Management Strategy and Action Plan
download now -
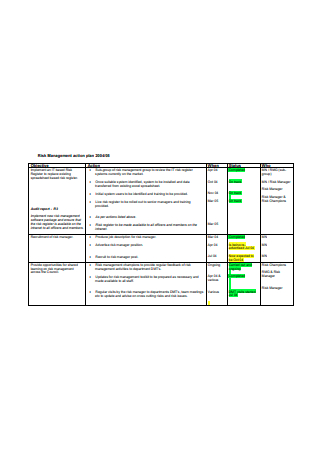
Standard Risk Management Action Plan
download now -
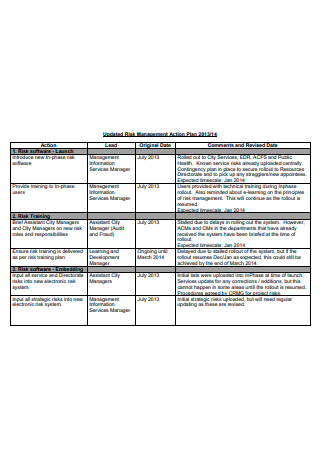
Printable Risk Management Action Plan
download now -
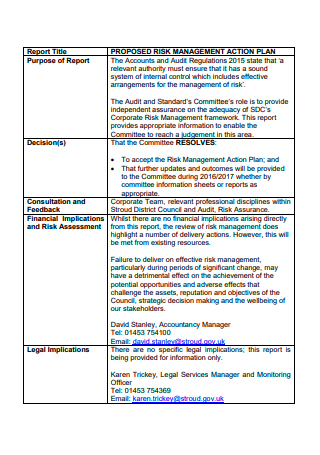
Risk Management Action Plan Format
download now
FREE Risk Management Action Plan s to Download
8+ Sample Risk Management Action Plan
a Risk Management Action Plan?
Benefits of Risk Management Planning
Basic Methods of Risk Management
How To Process Risk Management
FAQs
What should a risk management action plan contain?
How are risks assessed?
What is the definition of effective risk management?
What Is a Risk Management Action Plan?
A risk management plan is a critical document that assists the project manager in determining appropriate responses, anticipating risks, and forecasting the severity and impact of a threat. If you’d like to familiarize the structure and format of a risk management free plan, you can consult a risk management free plan template. A risk management strategy is critical in project management, and it identifies, classifies, and responds to risky situations while ensuring that the actions are taken benefit the project. It aids in weighing the likelihood of a project versus the risk. According to a recent poll conducted by North Carolina State University’s Poole College of Management, more than a quarter of all respondents (26.6 percent) do not have enterprise-wide risk management (ERM) processes in place.
Benefits of Risk Management Planning
If you’re reading this article, you’re already informed of the apparent benefits of risk management planning, and you’re familiar with the concept. However, just in case you aren’t, what if I told you that risk management has additional benefits? Here are some of it:
Basic Methods of Risk Management
As people age, they typically face increased health risks. Pure risk management comprises recognizing, evaluating, and containing these risks—a defensive method for anticipating the unexpected. Risk management’s fundamental principles—avoidance, retention, sharing, transferring, and loss prevention and reduction—may be applied to all aspects of an individual’s life and can pay dividends in the long run. Here are five of these strategies and how they might be used to risk management.
Avoidance
Avoidance is a risk-reduction strategy that involves abstaining from actions that may result in harm, illness, or death. Cigarette smoking is one such activity, as abstaining from it may reduce both health and financial hazards. Health insurers can increase premiums depending on age, region, family size, and smoking status under the Affordable Health Care Act, colloquially known as Obamacare. The law provides for a premium surcharge of up to 50% for smokers.
Sharing
Employer-based advantages that allow the company to pay a percentage of the employee’s insurance premiums are frequently used to share risk. In essence, the corporation and all employees who participate in the insurance benefits share the risk. The idea is that as more people share the risks, premium costs will decrease proportionally. Individuals may find it advantageous to participate in risk-sharing by selecting employer-sponsored health and life insurance plans wherever possible.
Retention
Retention is the acceptance and acknowledgment of a danger as a given. Typically, this accepted risk is a cost associated with mitigating more immense stakes in the future, such as opting for a cheaper premium health insurance plan with a higher deductible rate. The initial risk is the increased out-of-pocket medical expenses that may occur as a result of health problems. If the situation gets more severe or life-threatening, health insurance benefits will cover most costs beyond the deductible. Suppose the person does not have any significant health problems that would necessitate higher medical spending for the year. In that case, they avoid out-of-pocket payments, effectively lowering the enormous risk.
Transfering
Health insurance is a form of risk transfer since it transfers the financial risks connected with health care from the individual to the insurer. Insurance firms take on financial risk in exchange for a premium fee and a written contract between the insurer and the insured. The contract specifies all of the terms and circumstances that must be met and maintained for the insurer to assume financial responsibility for risk coverage. Accepting the terms and conditions enables an individual to shift the majority of the risk to the insurer. The insurer carefully uses various statistics and algorithms to determine the appropriate premium payments for the required coverage. When claims are filed, the insurer verifies that the conditions for providing the contractual compensation for the risk outcome have been met.
Loss Prevention
This approach to risk management seeks to mitigate rather than eliminate the loss. While recognizing the danger, it maintains a laser-like concentration on containing the loss and preventing it from expanding. Preventative care is an illustration of this in health insurance. Health insurers promote preventive care visits that are frequently co-pay-free and include annual checkups and physical examinations for members. Insurers recognize that identifying possible health problems early and providing preventative care can help reduce long-term medical expenditures. Numerous health plans also offer discounts at gyms and health clubs as an additional prevention method to keep members active and healthy.
How To Process Risk Management
The risk management method establishes a framework for the necessary actions. Five fundamental steps are taken; these processes are collectively referred to as the risk management process. It begins by detecting hazards, analyzing them, prioritizing them, implementing a solution, and finally monitoring them. Each step in a manual system requires extensive documentation and administration. Now, consider how these stages are implemented in a more digital context. Research shows that nine years ago, only 9% of organizations claimed to have a complete enterprise risk management (ERM) process. Today, a higher percentage of businesses (31%) consider their ERM procedures to be finished.
Step 1: Recognize the Risk
The first step is to determine which risks the business faces in its operating environment. Risks come in various forms – legal risks, environmental risks, market risks, and regulatory risks, to name a few. It is critical to ascertain the presence of as many of these risk factors as feasible. These risks are manually recorded in a manual environment. If the firm uses a risk management solution, all this data report is automatically entered into the system. The advantage of this strategy is that these risks are visible with access to the system within the business. Rather than being locked away in a report that must be requested via phone or email, anyone interested in seeing which risks have been detected can view the data in the risk management system.
Step 2: Conduct a Risk Analysis
After identifying a danger, it must be examined. The risk’s scope must be determined. Additionally, it is critical to understand the relationship between risk and other organizational characteristics. It is required to assess how many business operations the risk affects. There are dangers that, if realized, may bring the entire firm to a halt, while others will cause only minor hassles in the analysis. This analysis must be performed manually in a manual risk management system. One of the most critical initial tasks of implementing a risk management solution is to associate risks with various important documents, rules, procedures, and business processes. This means that the system will come pre-configured with a risk framework to evaluate hazards and inform you of their far-reaching consequences.
Step 3: Assess the danger.
Risks must be classified and prioritized. Most risk management solutions categorize risks according to their severity. Risks that may result in minor discomfort are rated low, while risks that may result in catastrophic loss are ranked highest. It is critical to rate risks because it enables the organization to acquire a holistic view of its risk exposure. While the firm may be exposed to several low-level hazards, it may not necessitate senior management engagement. On the other hand, even one of the most severe hazards necessitates immediate attention.
Step 4: Treat the Danger
Every danger must be removed or minimized to the greatest extent practicable. This is accomplished by establishing contact with specialists in the field to which the risk pertains. In a manual environment, this means contacting each stakeholder and scheduling meetings to allow everyone to communicate and discuss the issues. The issue is that the debate is fragmented among numerous email threads, various documents and tracking spreadsheets, and numerous phone calls. Within a risk management solution, all essential parties can be notified. The risk and potential solution can be discussed within the system. Additionally, upper management can maintain a close eye on the solutions proposed and the progress made within the system. Rather than requiring everyone to contact one another for updates, everyone can receive updates immediately from the risk management solution.
Step 5: Risk Monitoring and Assessment
Not all dangers can be removed entirely; some risks will always exist. Market risks and environmental hazards are just two of the numerous changes that must be constantly evaluated. Manual systems are monitored by diligent staff, and specialists must maintain a vigilant eye on all danger variables. The risk management system monitors the organization’s whole risk framework in a digital environment. Any change in a factor or risk is immediately evident to everyone. Also, computers are far superior to humans in continuously monitoring threats. Additionally, risk management enables your firm to maintain continuity. We can advise you on how to develop a risk management strategy for monitoring and reviewing the risk.
FAQs
What should a risk management action plan contain?
A risk management action plan must contain specifics to be effective. These elements include recognizing risks in advance, understanding the impact of risks on a project, planning for probable risks, and monitoring risk.
How are risks assessed?
To conduct an annual evaluation, you need first identify potential hazards. Determine the chance and severity of harm, such as an injury or illness, occurring. Consider both routine and unusual operational conditions, such as maintenance, shutdowns, power outages, emergencies, extreme weather, and so on.
What is the definition of effective risk management?
Effective risk management involves aiming to influence future events as much as possible by acting proactively rather than reactively. As a result, effective risk management has the potential to lower both the likelihood of a risk happening and the influence of that risk.
Preparedness, adaptability, and agility are all essential aspects of risk management. You must react at the drop of a hat to unexpected scenarios and make decisions regarding your meetings and events that have a meaningful business impact, even if it means considering event cancellation. Once the crisis has relinquished, it’s time to evolve your meetings and events program and move forward by implementing new processes and systems that will allow you to respond more effectively the next time. Always remember that staying nimble amid a crisis requires the correct tools and techniques.
