Financial Plan Samples
-

Bakery Financial Plan
download now -

Monthly Financial Plan
download now -

Restaurant Financial Plan
download now -

Gym Financial Plan
download now -
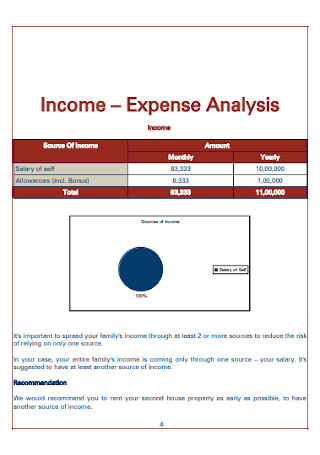
Sample Financial Plan
download now -

Personal Financial Plan
download now -

Family Financial Plan
download now -

Personal Financial Plan Example
download now -

Financial Planning Checklist
download now -
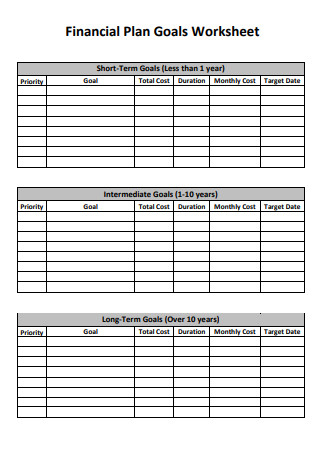
Financial Plan Goals Worksheet
download now -
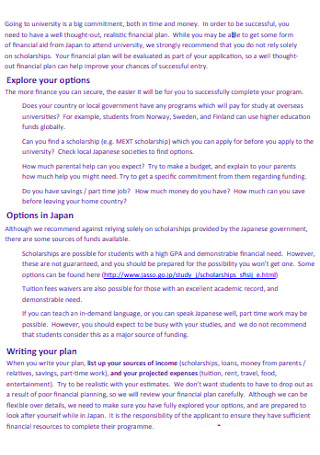
Sample Writing Financial Plan
download now -

Cooperative Development Financial Plan
download now -

Twenty Year Long Term Financial Plan
download now -

Financial Plan Case Study
download now -
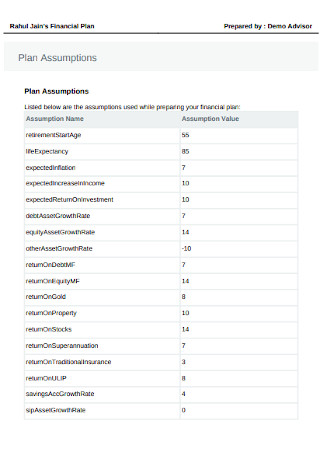
Financial Plan Assumptions
download now -

Draft Financial Budget Plan
download now -

Retirement Financial Plan
download now -

Long Range Financial Plan
download now -
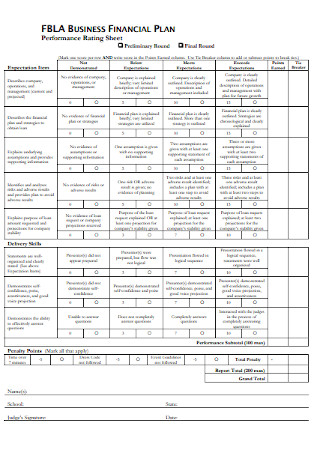
Financial Plan Performance Rating Sheet
download now -
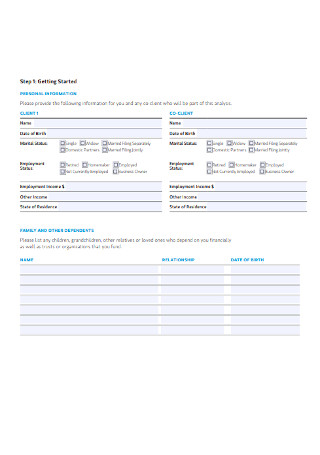
Financial Plan Client Profile
download now -
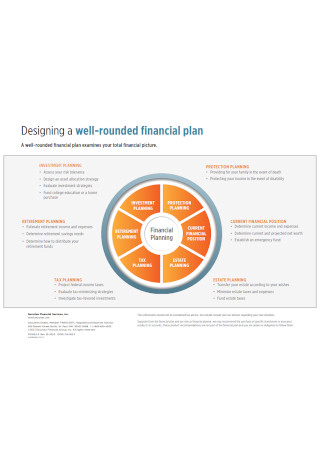
Well Rounded Financial Plan
download now -

Characterstics Personal Financial Plan
download now -

Transportation Financial Plan
download now -

Risk Assessments in Long Term Financial Plan
download now -

Ten Year Financial Plan
download now -

Water System Financial Plan
download now -

Sample Business Financial Plan
download now -
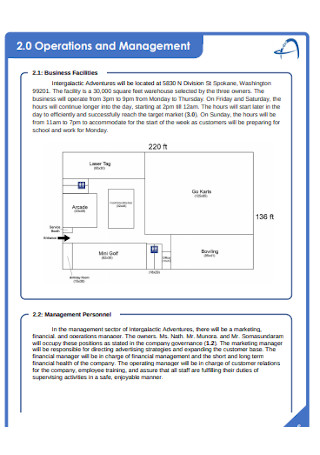
Business Financial Plan Operations
download now -

Annual Business Financial Plan
download now -
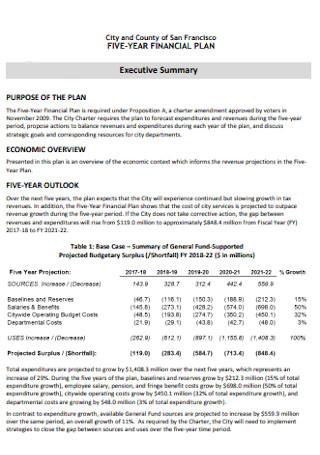
Proposed Five Year Financial Plan
download now -
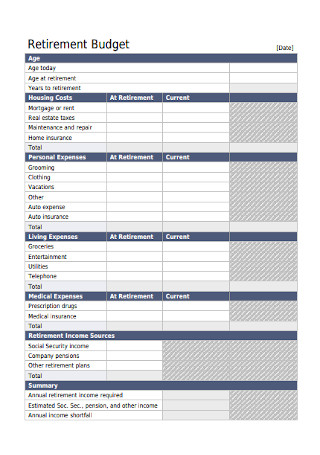
Financial Plan Retirement Budget
download now -

Components of Financial Plan
download now -
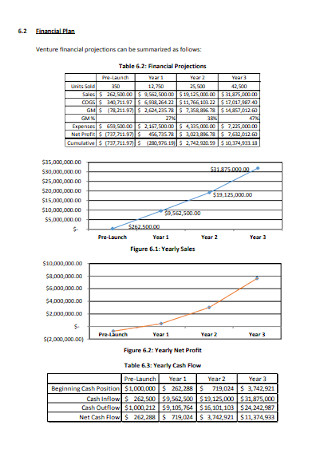
University Business Financial Plan
download now -

Medical and Financial Plan
download now -

Bar Business Financial Plan
download now -

Medium Term Financial Plan
download now -
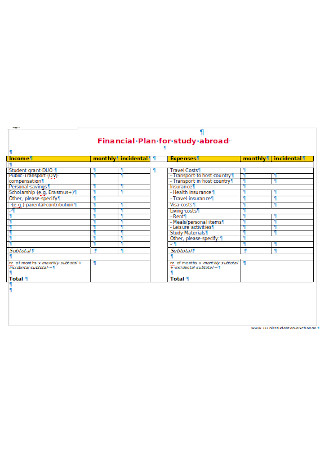
Abroad Study Financial Plan
download now -
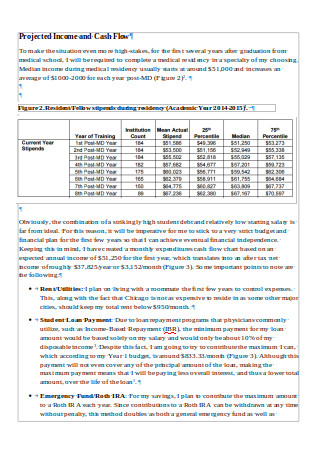
Sample Personal Financial Plan
download now -

Personal Financial Plan Template
download now -
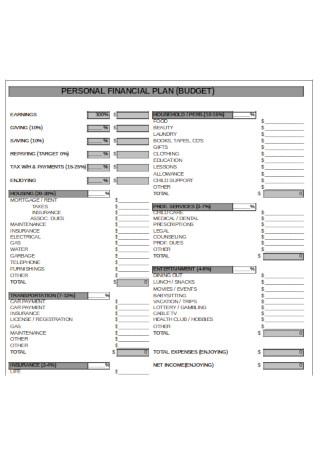
Personal Financial Budget Plan Template
download now
FREE Financial Plan s to Download
Financial Plan Format
Financial Plan Samples
What is a Financial Plan?
Types of Financial Plans
How to Create a Financial Plan
How does a financial plan help in investment decisions?
How can a financial plan prepare for emergencies?
What role does risk management play in a financial plan?
What is the importance of a timeline in financial planning?
How does debt management fit into a financial plan?

Download Financial Plan Bundle
Financial Plan Format
Title Page
- Name of the individual or business
- Date of the plan
- Contact information
Table of Contents
- A clear outline of sections with page numbers
Executive Summary
- A brief overview of the financial plan
- Summary of financial goals and objectives
- Key highlights from the financial analysis
1. Current Financial Situation
Personal Finances (for individuals):
- Income sources (e.g., salary, investments)
- Expenses (fixed and variable)
- Assets (cash, investments, real estate)
- Liabilities (loans, credit card debt)
Business Finances (for businesses):
- Income Statement (Revenue and Expenses)
- Balance Sheet (Assets, Liabilities, and Equity)
- Cash Flow Statement
2. Financial Goals
- Short-term goals (e.g., savings for emergencies, debt repayment)
- Medium-term goals (e.g., buying a house, expanding business)
- Long-term goals (e.g., retirement savings, business exit strategy)
- Prioritization of goals with timeframes
3. Budget Plan
- Monthly or annual budget based on current income and expenses
- Allocation for savings, investments, and discretionary spending
4. Investment Plan
- Asset allocation strategy (e.g., stocks, bonds, real estate)
- Risk tolerance analysis
- Projected returns and timelines
5. Risk Management and Insurance
- Analysis of potential risks (health, property, liability)
- Recommendations for insurance coverage (life, health, disability, business liability)
6. Tax Strategy
- Tax-saving opportunities
- Optimization of deductions, credits, and tax-deferred accounts
7. Retirement Planning
- Retirement income needs
- Current retirement savings and gap analysis
- Recommendations for contributions to retirement accounts (e.g., 401(k), IRAs)
8. Estate Planning
- Wills and trusts
- Power of attorney and healthcare directives
- Succession planning (for businesses)
9. Debt Management Plan
- Current debts and interest rates
- Strategies to pay off or refinance debt
- Consolidation opportunities (if applicable)
10. Financial Forecast and Projections
- Five or ten-year financial outlook
- Sensitivity analysis for different scenarios (best-case, worst-case)
11. Action Plan
- Step-by-step actions to achieve financial goals
- Timeline for implementation
- Responsible parties for execution
12. Monitoring and Reviewing
- Schedule for reviewing the plan
- Metrics to track progress
- Contingency strategies for unforeseen circumstances
Appendices
- Supporting documents (e.g., financial statements, loan agreements)
- Glossary of financial terms (if needed)
What is a Financial Plan?
A financial plan is a document or strategy that details how an individual or organization will allocate financial resources to achieve specific goals. It typically includes income analysis, expense tracking, debt management, savings, investments, and risk mitigation strategies. A financial plan is dynamic and can adapt to changes, making it an essential document for financial security and growth. You can also see more on Financial Budget Plan.
Types of Financial Plans

1. Personal Financial Plan
A personal financial plan is a customized strategy for managing an individual’s or household’s financial life. It includes budgeting to ensure expenses don’t exceed income, saving for future goals like education or travel, and investing in long-term wealth creation. Retirement planning is also an integral part, ensuring financial independence post-employment. This plan evolves over time, adapting to changes like new income sources, family additions, or lifestyle shifts.
2. Corporate Financial Plan
Corporate financial plans focus on ensuring a business has sufficient resources to achieve its strategic objectives. These plans include forecasting revenue, managing cash flow, budgeting for operational expenses, planning for future investments, and managing debts. It also involves risk management and aligning financial goals with broader business objectives. For growing businesses, corporate plans ensure scalability without compromising profitability. You can also see more on Financial Action Plan.
3. Emergency Financial Plan
An emergency financial plan prepares individuals or businesses to handle unforeseen financial crises. For individuals, it includes building an emergency fund of 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses and securing health, life, and disability insurance. For businesses, it involves maintaining sufficient working capital and setting aside contingency funds to sustain operations during downturns.
4. Education Financial Plan
An education financial plan is aimed at saving for educational expenses, such as college tuition or professional courses. It includes setting aside funds in dedicated savings plans like 529 accounts, exploring scholarships, and budgeting for associated costs like books and housing.
5. Investment Plan
An investment plan focuses exclusively on growing wealth over time through strategic allocation in assets like stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, or even alternative investments like cryptocurrency. It considers the investor’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. A well-structured investment plan is diversified and periodically reviewed to maximize returns and minimize risks. You can also see more on Annual Budget Plan.
How to Create a Financial Plan

Creating a financial plan requires a structured approach to assess your current situation, define goals, and implement strategies to achieve them. Follow these five steps to build a comprehensive financial plan:
1. Assess Your Current Financial Situation
Start by evaluating your current income, expenses, savings, debts, and investments. This step provides a clear picture of where you stand financially. Use tools like spreadsheets, budgeting apps, or financial software to track your cash flow. Identify areas where you may be overspending and opportunities for savings. A detailed sample analysis is essential to set realistic goals and align your plan with your financial capacity.
2. Define Clear Financial Goals
Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for the short, medium, and long term. Examples include paying off debt within five years, saving for a down payment on a house, or building a retirement fund. Clear goals act as the foundation for your plan and guide your decisions. Prioritize goals based on urgency and importance to ensure resources are allocated effectively.
3. Create a Realistic Budget
Develop a monthly budget to manage your income and expenses. Allocate a portion of your income toward necessities, discretionary spending, savings, and debt repayment. A popular method is the 50/30/20 rule: 50% for needs, 30% for wants, and 20% for savings and debt. Stick to your budget by avoiding unnecessary expenses and tracking progress regularly. This ensures that you’re living within your means and steadily building wealth. You can also see more on College Budget Plans.
4. Develop an Investment and Savings Strategy
Choose investment options that align with your goals, risk tolerance, and timeline. For short-term goals, prioritize low-risk, high-liquidity options like savings accounts or fixed deposits. For long-term goals, consider higher-risk options like stocks, mutual funds, or real estate. Simultaneously, establish an emergency fund covering 3-6 months’ expenses. This dual strategy ensures financial growth while providing a safety net.
5. Monitor and Adjust Regularly
A financial plan is not static—it should evolve with your life circumstances and economic changes. Review your plan at least annually or when major events occur, such as a salary increase, marriage, or the birth of a child. Adjust your goals, budget, and investments as needed to stay on track. Regular monitoring ensures your plan remains relevant and effective in achieving your objectives. You can also see more on Estimate Budget.
How does a financial plan help in investment decisions?
A financial plan outlines your financial goals and risk tolerance, providing a clear framework for choosing appropriate investment options. By aligning investments with your objectives, it minimizes risks and ensures that you’re on track to achieve financial success.
How can a financial plan prepare for emergencies?
A financial plan includes an emergency fund that covers at least 3-6 months of expenses. It accounts for unexpected situations like job loss or medical emergencies, ensuring you can maintain financial stability during tough times without disrupting long-term goals.
What role does risk management play in a financial plan?
Risk management is crucial in financial planning. It includes purchasing insurance (health, life, or property) to mitigate potential financial losses and diversifying investments to reduce risks. A comprehensive financial plan incorporates strategies to protect assets and income streams against unforeseen events like illnesses, accidents, or market downturns. You can also see more on Financial Advisor Business Plan.
What is the importance of a timeline in financial planning?
A timeline provides structure and ensures accountability in financial planning. By assigning deadlines to goals (e.g., saving $50,000 in five years), you create a sense of urgency and track progress effectively. Timelines also help prioritize short-term versus long-term objectives, ensuring steady progress.
How does debt management fit into a financial plan?
Debt management is a critical component of financial planning. It involves strategies to pay off existing debts, such as using the snowball or avalanche method, and avoiding high-interest loans in the future. Reducing debt improves cash flow and allows you to allocate resources toward savings and investments. You can also see more on Project Execution Plan.
