23+ SAMPLE Security Assessment Plan
-
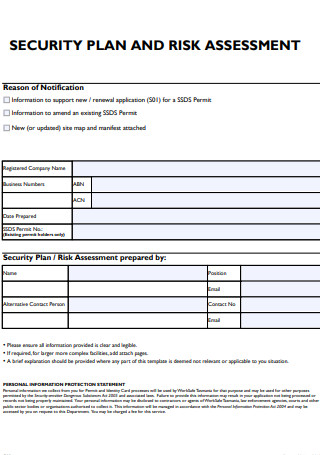
Security Plan and Risk Assessment
download now -

Security Assessment Plan
download now -
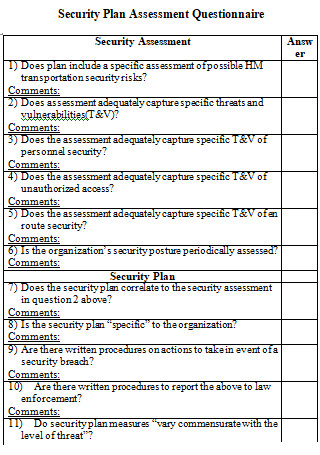
Security Assessment Plan Questionnaire
download now -

Sample Security Assessment Plan
download now -

Security Assessment And Authorization Plan
download now -

Security Assessment Plan Template
download now -

Information System Security Assessment Plan
download now -

Security and Privacy Controls Assessment Test Plan
download now -

Developing Security Assessment Plan
download now -

Independent Security Assessment Plan
download now -

System Security Assessment Plan
download now -

Approving Security Assessment Plan
download now -

Security Assessment Plan Framework
download now -

Security Testing Assessment Plan
download now -

Security Assessment Plan in DOC
download now -

Security Assessment Plan Extensible
download now -
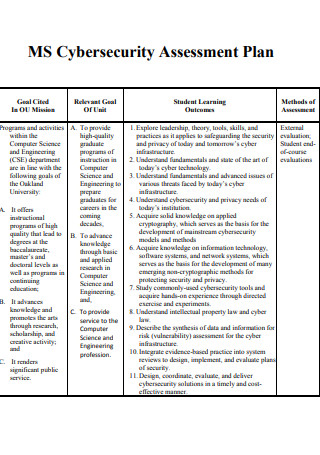
Cybersecurity Assessment Plan
download now -

Effective Security Assessment Plan
download now -

IT Security Assessment Plan
download now -

University Security Assessment Plan
download now -

Security Assessment Plan Example
download now -

Facility Security Assessment Plan
download now -

Printable Security Assessment Plan
download now -
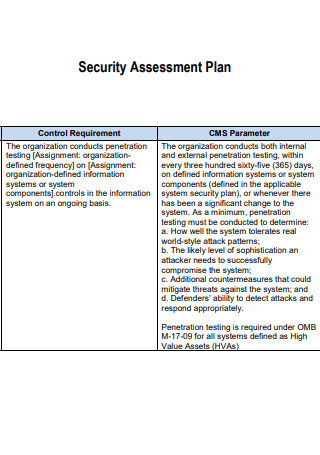
Standard Security Assessment Plan
download now
FREE Security Assessment Plan s to Download
23+ SAMPLE Security Assessment Plan
a Security Assessment Plan?
Benefits of Conducting Security Assessment Plans
How To Conduct a Basic Security Assessment
FAQs
What is the purpose of a security survey and inspection?
What is a checklist for risk assessment?
Why is it necessary to do a security survey?
What Is a Security Assessment Plan?
Security assessment plans are periodic exercises that evaluate your organization’s preparedness for security threats. They include vulnerability scans of your information technology systems and business processes, as well as recommendations for mitigating the risk of future attacks. According to statistics, 20% of firms report being attacked six or more times each year, and 80% report having encountered at least one cybersecurity issue significant enough to demand a board-level meeting in the last 12 months.
Benefits of Conducting Security Assessment Plans
While digitalization has enhanced services and patient care delivery in today’s healthcare industry, it has also resulted in significant side effects: cybersecurity assaults and breaches. Today’s information technology departments must be attentive in finding network weaknesses before being attacked by cybercriminals. Regular security evaluations are critical for your organization — here’s why.
How To Conduct a Basic Security Assessment
For some firms, small enterprises, establishing a team to develop and execute information security procedures may seem like a significant enough task in and of itself, much alone the added work of proactively looking for holes in your security system. However, you cannot afford to miss a security audit. These steps will guide you through a basic security assessment and provide you with the skills necessary to begin developing a consistent approach for identifying critical business threats.
Step 1: Catalogue and identify your information assets
The first step in managing a security assessment is to create a detailed inventory of your informational assets. It’s critical to note that different roles and departments will have varying viewpoints on what the most valuable assets are, which is why you should solicit advice from multiple sources. For salespeople, the most critical information asset can be your company’s CRM. At the same time, IT’s most vital information asset is likely the servers they maintain, and HR’s most critical information asset is confidential employee information. After identifying all of your information assets and essential stakeholders across all departments, you’ll need to sort them according to their level of sensitivity and strategic value to the firm. You’ll need to speak with the administrators of all primary systems across all departments to obtain accurate and complete information.
Step 2: Recognize threats.
Hackers are frequently at the top of the list when considering data security concerns, but dangers to your business’s data security can take various forms. As this list of 2019 data breaches demonstrates, while hackers exploiting vulnerabilities in a business’ firewalls or website security programs has been extremely common, various other threat types contributed to data breaches in 2019. When developing a list of all the different hazards your organization confronts, you must consider a variety of various threat kinds. Finally, natural calamities and power outages may create devastation just as much havoc as humans, so you must also account for those types of dangers. Following this phase, you should have a comprehensive list of the threats to your assets. According to research, almost 34% of organizations worldwide are impacted by insider threats each year. 66% of firms believe that malicious insider attacks or unintentional breaches are more likely than external attacks. Insider occurrences have surged by 47 percent in the last two years.
Step 3: Recognize vulnerabilities.
A vulnerability is a flaw in your system or procedures that could result in an information security breach. For instance, this is a massive vulnerability if your business keeps customers’ credit card information but does not encrypt it or test the encryption process to ensure it functions correctly. Allowing weak passwords, failing to update software security patches, and restricting user access to sensitive information are all habits that expose your business’s sensitive data to attack. Another danger you may face during the coronavirus health crisis is a staffing shortage. Security safeguards may be overlooked if IT security staff is working remotely or, worse, is ill. Also, it is critical to consider physical weaknesses. For instance, if your workers work with paper copies of sensitive information or take business equipment outside the office, this might result in data misuse, just as flaws in your software and electronic systems do.
Step 4: Examine internal controls.
Following vulnerability identification in your systems and processes, the next stage is to create controls to mitigate or remove vulnerabilities and threats. This could be a control designed to eradicate the exposure or address hazards that cannot be eliminated. Technical controls, such as computer software, encryption, or tools for detecting hackers or other breaches, or non-technical controls, such as security rules or physical controls, are all examples of controls. Controls can also be classified as preventative or detective controls, depending on whether they prevent incidents or detect and inform you when an incident occurs. Adequate controls demand experience and expertise. If your organization lacks in-house security and compliance subject matter experts, it is critical to seek support from professional services businesses with extensive experience resolving IT security challenges.
Step 5: Calculate the probability of an incident occurring.
Using the data you’ve obtained – about your assets, the risks they face, and the controls you’ve implemented to mitigate those threats – you can now categorize the likelihood that each of the vulnerabilities you discovered will be exploited. Numerous organizations use the terms “high,” “medium,” and “low” to represent the likelihood of a risk occurring. Thus, if a critical application used to run your business is out of the current, and there is no method in place for periodically checking for and installing updates, the chance of an incident affecting that system is likely to be significant. On the other hand, if you handle a high volume of personal health information, have automated mechanisms in place to encrypt and anonymize it, and periodically test and verify those systems’ performance, the risk of an incident is low. You will need to make this decision based on your knowledge of the vulnerabilities and the controls implemented inside your company.
Step 6: Determine the severity of the threats to your information security.
Prioritizing your security risks will assist you in determining which ones require immediate attention, where you should focus your time and resources, and which dangers can wait. This stage may benefit from using a simple risk matrix that enables you to visualize the data you already have about each vulnerability/threat pair you’ve found. Risks that are both likely to occur and have severe repercussions would be prioritized as high. In contrast, risks that are unlikely to happen but have minor implications would be prioritized as low, with everything else falling somewhere. You can create a risk matrix that is as simple or as sophisticated as you choose. If you’re a large firm with several risks competing for your time and attention, a more detailed 55 risk matrix will almost certainly be beneficial; smaller organizations with fewer hazards to prioritize will generally get by with a simple 33 matrix.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a security survey and inspection?
A security survey is a comprehensive on-site examination and analysis of a facility to ascertain the presence and value of assets; to assess the existing security program; to identify gaps or excesses; to define the level of protection required, and support recommendations to enhance overall security.
What is a checklist for risk assessment?
When preparing to undertake a risk assessment, a risk assessment checklist guarantees that you have assessed every aspect of your firm. With a list, you can be sure that you’ve addressed risk from every angle and have gathered all of the information necessary for your firm to establish a risk management plan. Risk assessments are a legal duty for all employers and self-employed individuals. They must evaluate the risks to their employees and to anybody else who work activities may impact.
Why is it necessary to do a security survey?
The survey collects the data essential to establishing the right level of safety and security for your firm to successfully manage risk and liability and plan for ongoing operations during a potential crisis. Also, a security survey ensures that the money you’ve invested in security is being used effectively. As security threats and the assets that require protection evolve, so should your security system. Conducting regular security audits will assist you in identifying flaws in your current system.
Employee records, customer information, loyalty schemes, transactions, and data collection are all examples of critical pieces of information that businesses typically maintain. This prevents third parties from misusing the information for fraudulent purposes, such as phishing scams and identity theft. The Security Assessment Plan explains the data obtained before assessing the regions evaluated and the proposed scheduled actions performed.
