25+ Sample Weekly Lesson Plan
-
Toddler Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -

Daycare Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -

Kindergarten Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -

Weekly Teacher Lesson Plan
download now -
Sample Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -
Printable Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -
Weekly Lesson Plan Outline
download now -
School Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -

Weekly Lesson Plan Calendar
download now -
Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -
Weekly Lesson Plan Activity
download now -
Teacher Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -
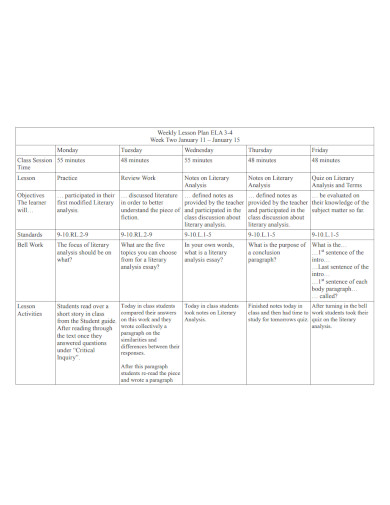
Basic Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -

Leader Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -
High School Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -
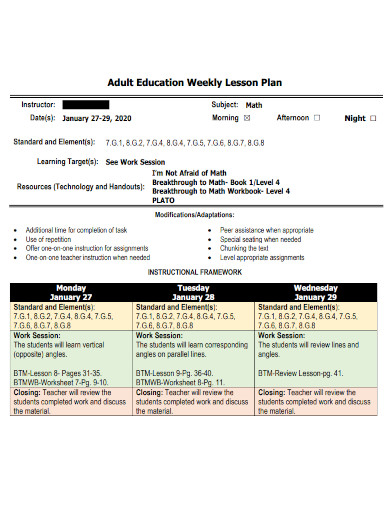
Education Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -
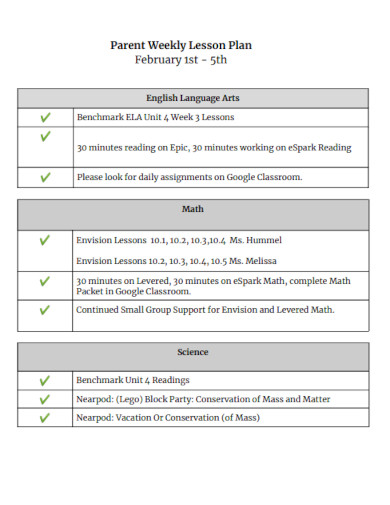
Parent Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -
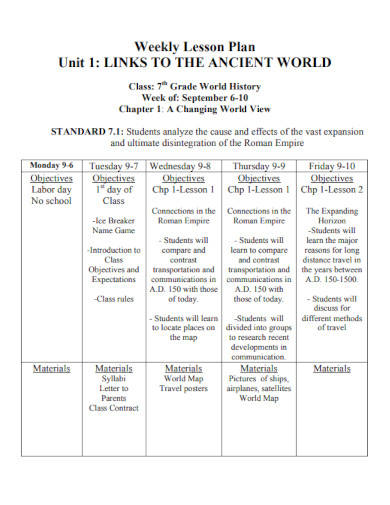
Weekly Lesson Plan for Class
download now -
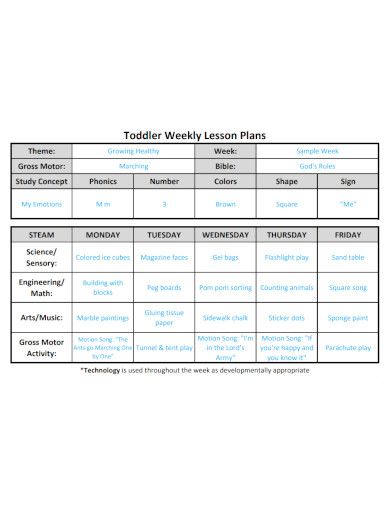
Toddler Weekly Lesson Plan Example
download now -
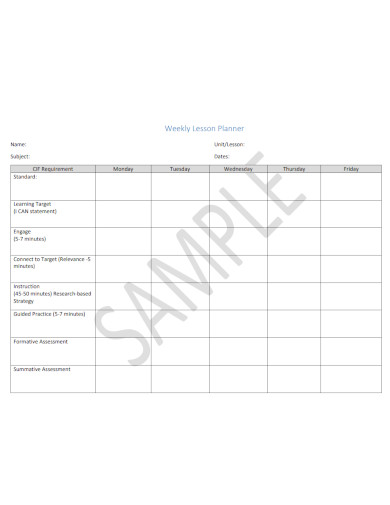
Simple Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -
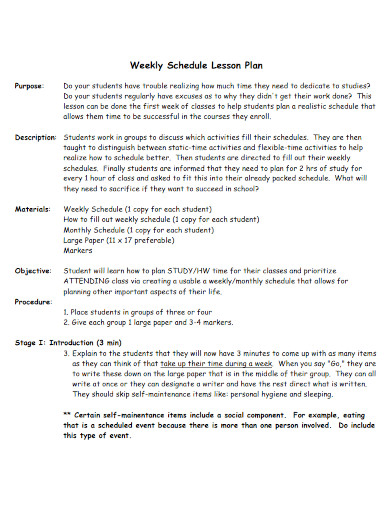
Weekly Schedule Lesson Plan
download now -
Preschool Remote Learning Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -
Toddler Class Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -
Standard Weekly Lesson Plan
download now -

Weekly Lesson Plan Format
download now -
Weekly Lesson Plan for Children
download now
What Is a Lesson Plan?
A lesson plan is a written outline of the skills students will acquire during a lesson, how the educator intends to teach it, and how they will assess students’ comprehension of the material after the lesson. Using lesson plans can assist educators in being better prepared to instruct students. They also make them more effective educators because they plan courses ahead of time. Most lesson plans contain multiple components that aid instructors in designing the various aspects of the lesson, from preparation to conclusion.
Benefits of a Lesson Plan
Being organized when instructing a class facilitates a more efficient lesson. Planning allows you to prepare numerous activities for your students, encouraging them to remain engaged throughout the lesson. Learning how to write a lesson plan can be beneficial if you are a current or aspiring educator. Here are some of its advantages if you’re still intrigued.
Tips to Have an Effective Teaching
Effective instruction describes a successful educator’s knowledge, strategies, and behavior. It is the capacity to positively influence a student’s life and academic career, including teaching essential skill sets, introducing new concept proposals, and managing classroom concerns. Educators typically seek to employ effective teaching strategies to help their pupils learn consistently and increase their understanding of the subject matter. Effective teaching can be achieved by adhering to the following guidelines.
1. Enjoy the Educational Field
Teachers who are enthusiastic about their work can motivate their students. It is essential to develop engaging lesson plans to demonstrate to students that you care about their academic development. If you show enthusiasm for the subject you teach, your students may be inspired to participate more actively in classroom activities or conduct independent research on the material. Maintaining a pleasant demeanor throughout the day can aid in making your classroom space inviting to all students. Effective instructors recognize they can play a significant role outside the classroom in a student’s life. Providing support in the school for their social and emotional requirements may be beneficial, such as encouraging teamwork during classroom activities and providing helpful advice outside of class.
2. Connect With Students
Developing positive relationships with students is facilitated by a genuine interest in their lives and interests. Although it is essential to maintain a separation between your home and work life, some teachers share their interests with their students. Try to communicate frequently with a student’s family to gain additional context about them and save time when discussing their progress. Effective instructors are well-versed in their subject matter and devote considerable time to curriculum development. They exert effort daily to ensure that they can deliver high-quality instruction and meet grading deadlines. Consider revising your coursework daily to respond to student questions in class effectively. Researching classroom strategies recommended by other teachers and educational specialists may also prove helpful.
3. Plan Your Weekly Activities
Successful instructors optimize their lesson plans to maximize their weekday classroom time. Educators frequently design lesson plans with multiple learning stages, such as a lecture followed by individual assignments or group-based classwork. It is also essential to provide sufficient time during the school day for students to complete their projects or activities. Teachers who simplify complex concepts can assist their students in learning more efficiently. They employ multiple mediums, such as fishbone diagrams, presentations, demonstrations, and supplementary videos, to convey lesson content. When assigning assignments, they outline specific measures to address any potential issues. When introducing new concepts to your class, using a constant speech pattern and incorporating a readable font size in lecture materials may be beneficial.
4. Establish Realistic Expectations
Effective teachers convey their expectations to their pupils and incorporate them into their practices. They may revise the standards to accommodate various learning styles better and ensure that every student can achieve their objectives. For instance, if a student communicates a concern regarding a grade, constructive teaching practice entails listening to and addressing their situation. It is essential to outline your policies at the start of the semester so that students can ask questions and convey their opinions. Educators who respond with adaptability to unforeseen events can better meet the requirements of their students. For instance, you may predict that one activity will aid students in comprehending a lesson, only to discover that another action is more conducive to their learning. While arranging a daily lesson, promptly address any feedback report and account for varying circumstances.
5. Find Resources
Effective instructors augment their knowledge from various sources to improve their teaching methods. Stay up-to-date on new teaching methods so that you can provide optimal support for students. You can review scholarly articles, read books, and watch informative videos using a streaming service. You can also discuss helpful hints with other educators via social media or online forums. Additionally, effective teaching requires consistent reflection on one’s strategies and behavior. Identify areas for development so that you can enhance your teaching and progress as an educator. To evaluate the quality of your instruction, solicit feedback from students, their families, and the school administration, then determine which aspects to implement. Checking your students’ progress can also be a helpful reflection tool, as their day-to-day responses to activities can reveal whether or not your teaching manner is effective.
6. Maintain a Sense of Humor
If you appreciate telling jokes or making humorous comments outside of the classroom, it may be beneficial to incorporate humor into lesson delivery. Students may retain more information if you include an engaging element, such as a reference to a humorous character or film they may have seen. It is essential to adhere to your work schedule, but a few well-timed connections can improve the learning environment you create. Effective teaching entails assisting students in understanding how to apply the concepts they learn to other aspects of their lives, including their prospective careers.
How to Write a Lesson Plan
Educators use lesson plans to outline coursework for students in writing. The plans, which provide instructors with an overview of their teaching goals, learning objectives, and strategies for achieving them, can aid students in comprehending the course’s timeline and preparing for upcoming material. Here are some measures you can take to create your lesson plan, should you be interested.
1. Identify Educational Goals
Before lesson planning, it may be beneficial to identify the lesson’s learning objectives. Learning objectives are typically statements that articulate what students can anticipate to learn when new information is taught. This would be a knowledge-based learning objective, for instance, if you expect that students will better understand and recall specific concepts.
2. Plan Educational Activities
Consider the activities students will engage in to acquire skills and knowledge as you construct your lesson plan. Activities should directly relate to learning objectives, allowing students to engage with, practice, and receive feedback evaluation. Estimate the time required for each activity sheet, and if necessary, include additional time for explanations or discussions.
3. Collect Your Study Materials
Good lesson plans commence with the acquisition of all necessary planning materials. This includes templates, guides, and any other information you’d like to have in the lesson plan. Examine your curriculum to determine how to present the concepts to students most effectively. During this phase, you can also assemble your students’ supplies. In addition, writing a preliminary lesson plan draft can help you visualize its intended direction. You can use pen and paper or a computer to create a rough manuscript, which can then be reviewed during revision. Having a rough draft allows you to identify any missing components, issues with the instructions, or prospective student obstacles.
4. Plan Your Tasks
Organize your lecture plans in a binder or folder for reuse and review. This method also helps keep everything in one place, preventing stray documents from cluttering your desk or office. If a student requires a copy of the lesson plan from the previous week, you have one in your binder. Additionally, the organization improves the planning phase by grouping ideas and materials for simple access.
5. Assess Student Progress
To evaluate the effectiveness of your lesson plan, you must specify how you will assess pupils after the lesson has concluded. Include grades, deadlines, and student comprehension of the materials among your success metrics. If you decide to eliminate grades, you may need an alternative to the metric system, such as meeting each student to discuss the student lesson plan. Students can also evaluate one another’s work.
FAQs
Are lesson plans daily or weekly?
Lesson plans can take various formats, including daily, weekly, monthly, and annual lesson plans. Typically, lesson plans outline learning objectives, learning outcomes/goals, required materials, and assessment techniques used in that class.
Why are learning outcomes important?
Learning outcomes facilitate faculty and teacher student agreement on the purpose and objectives of a course or academic program. Faculty begin to provide a transparent path to student success by delivering plain and comprehensive learning outcomes.
What is the motivation for a lesson plan?
The objective of the lesson’s motivation section is to generate interest in the topic. This is also an excellent opportunity to assess the student’s prior knowledge of the lesson’s subject or topic.
Using weekly lesson plans provides educators and students with numerous significant benefits. These strategies provide a framework for teaching and learning, enabling a more organized and efficient educational experience. The essence of weekly lesson plans is to provide structure, consistency, and adaptability to facilitate effective teaching and learning needs. They enable educators to deliver engaging and well-organized lessons while catering to students’ diverse requirements.
