Agricultural Project Proposal Samples
-

Agricultural Farming Project Proposal
download now -

Agricultural Livelihood Project Proposal
download now -

Agricultural Project Proposal for Funding
download now -

Project Proposal on Agricultural Cooperatives
download now -

Agricultural Experiment Station Project Proposal
download now -

Farm for Biodiversity and Agricultural Project Proposal
download now -
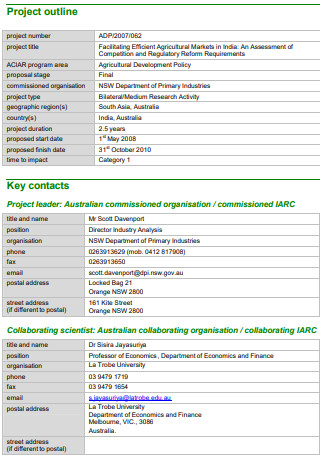
Facilitating Efficient Agricultural Market Project Proposal
download now -

Agricultural Research Project Proposal
download now -

Agricultural Research Agribusiness Project Proposal
download now -

Agroclimatic Zone Agricultural Project Proposal
download now -

Agricultural Research Division Project Proposal
download now -

Agricultural Engineering Project Proposal
download now -

Agricultural Research Project Proposal Preparation
download now -

Upland Agricultural Extension Project Proposal
download now -
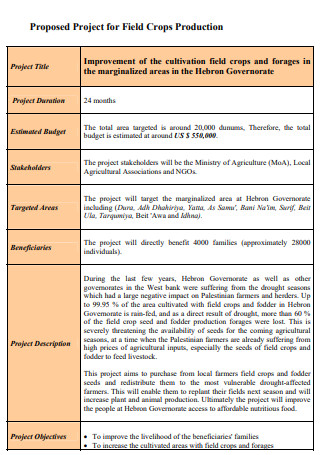
Agricultural Field Crop Production Project Proposal
download now
FREE Agricultural Project Proposal s to Download
Agricultural Project Proposal Format
Agricultural Project Proposal Samples
What is an Agricultural Project Proposal?
Tips On How to Write an Agricultural Project Proposal
How to Create an Agricultural Project Proposal
FAQs
What Are Some Examples of Agricultural Project Proposal Objectives?
What Are Some Different Types of Agriculture?
What Are Common Examples of Agricultural Branches?
Who uses Agricultural Project Proposals?
Can agricultural proposals be used for organic farming?
What resources are needed for an agricultural proposal?
What is the primary goal of an Agricultural Project Proposal?

Download Agricultural Project Proposal Bundle
Agricultural Project Proposal Format
1. Title Page
- Project Title
- Name of the Organization
- Date of Submission
- Project Manager’s Name and Contact Information
2. Table of Contents
- Include a clear list of all sections and sub-sections with page numbers.
3. Executive Summary
- Brief overview of the project.
- Include the project’s objectives, expected outcomes, and the target beneficiaries.
- Mention the project’s duration, budget, and funding sources.
4. Introduction
- Brief background about agriculture in the project area.
- Current agricultural challenges.
- How the project aligns with local/national agricultural strategies.
5. Problem Statement
- Define the specific agricultural problem(s) being addressed.
- Include data and statistics, if available, to support the problem.
6. Project Objectives
- List both general and specific objectives.
- Ensure objectives are SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound).
7. Project Scope
- Define the geographical coverage of the project.
- Outline the crops, livestock, or other agricultural areas involved.
8. Methodology
- Detailed explanation of the project activities, including:
- Selection of farmers or beneficiaries.
- Training and capacity-building programs.
- Implementation phases (preparation, cultivation, harvesting, etc.).
- Use of technology, sustainable practices, and resources.
9. Implementation Plan
- Present a timeline or Gantt chart showing project phases.
- Include specific activities, milestones, and deadlines.
10. Expected Outcomes and Impact
- Short-term and long-term outcomes.
- Positive impacts on beneficiaries, community, and the environment.
11. Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) Plan
- Methods for monitoring progress (surveys, field visits, etc.).
- Evaluation criteria for assessing project success.
12. Budget
- Detailed breakdown of estimated costs for the project.
- Include personnel costs, equipment, materials, training, and M&E costs.
- Indicate potential funding sources or budget gaps.
13. Risk Analysis and Mitigation
- Identify potential risks (e.g., climatic conditions, pest outbreaks).
- Outline strategies to mitigate these risks.
14. Sustainability Plan
- Explain how the project will sustain itself after initial funding ends.
- Describe partnerships, community involvement, and resource management strategies.
15. Conclusion
- Summarize the importance of the project and its potential impact.
- Emphasize the benefits of the project to stakeholders.
16. Annexes (if needed)
- Maps, charts, or graphs related to the project.
- Technical details or additional supporting information.
What is an Agricultural Project Proposal?
A proposal for an agricultural project is a printed document that includes a solution to a specific problem in the agricultural industry. It tries to create a project with the goal of proposing the project to investors to get funding and describing the smart goals and objectives of the solution. An agricultural project proposal can address the lack of progress in tools and equipment used by farmers, which makes the entire process of farming arduous and inefficient. The plan could next recommend improving irrigation systems or acquiring new tools, as well as introducing a new farming approach that rationalizes how it will boost production and the livelihoods of produce and animal growers. That is the best example of a project proposal for agricultural growth, and if you want to learn more about irrigation, you can look at the water project proposal samples as well.
Tips On How to Write an Agricultural Project Proposal
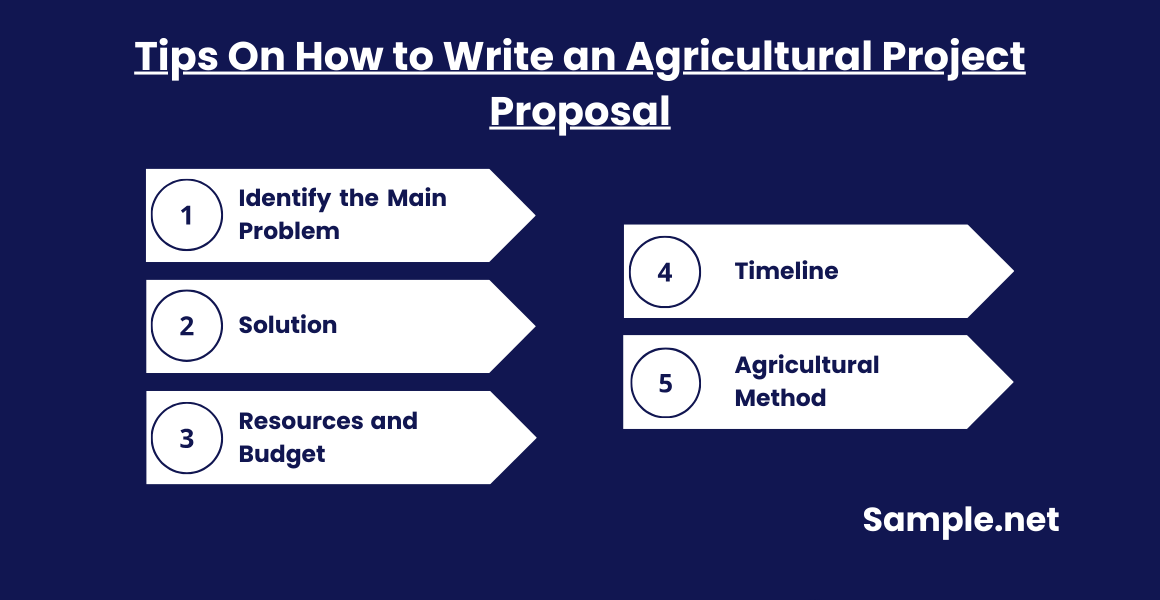
Before we can assess the project’s success, we must first ensure the project proposal’s success. One that would pique the interest of investors as well as the market. You can also see more on Food Security Proposal.
Tip 1: Identify the Main Problem
When writing an agricultural project proposal, the key is to identify the problem, which will then become your goal and part of your objective. It will also be the focal point of your solution, which you will later present to your investors. These issues can range from a lack of local food supply to a lack of commercialized farming in your neighborhood, which can lead to further issues such as unstable pricing and increased water consumption.
Tip 2: Solution
Promptly developed your proposed solution after noticing the problem. The solution would then embrace and solve the major issues you’ve identified, as well as how it could lead to an increase in profit for your investor or in your community. To make your solution stand out, undertake research on similar problems and solutions identified by others, as well as how they apply to your project. You can also see more on Title Project Proposal.
Tip 3: Resources and Budget
The resources section of your project proposal is significant since it includes the various equipment that will be utilized in the project, as well as the land, water supply, and the source of raw materials such as seed or young animals to grow. Identifying the resources that will be used in your project can help you reduce the overall financial cost. It would also be beneficial to purchase these materials ahead of time, as availability may be an issue.
Tip 4: Timeline
The project timetable would include the project’s estimated start and conclusion dates, as well as its length. Giving a schedule would not only assist set expectations but would also make sample budget management easier. Because the cost of production and early financing would have to be considered. Agriculture projects do not usually require a lot of planning, but the actual growing of crops and animals may, depending on what farmers and growers select. The timeline could also include when crops began generating produce and when it was ready to be distributed to the market.
Tip 5: Agricultural Method
The method entails the technique that the project would apply in their agriculture endeavor. It would be the harvesting process, for example, or how the products would be stored prior to distribution, the type of feeds to be given or fertilizers and manures to be utilized, and the type of irrigation system to be used. Outlining it in your project might be beneficial in providing more insight into the entire production. You can also see more on Funding Proposals.
How to Create an Agricultural Project Proposal

Step 1: Define Project Objectives
Begin by setting clear, specific, and measurable goals for your agricultural project. Determine what you aim to achieve, whether it’s increased crop yield, sustainable livestock farming, or advanced irrigation. Specify the expected outcomes, such as improving food security or enhancing local employment opportunities. You can also see more on Food Supply Proposal.
Step 2: Conduct a Feasibility Study
Research the project’s feasibility by analyzing factors like soil quality, climate, market demand, and potential risks. The feasibility study should also include a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) to ensure the project is viable and scalable.
Step 3: Plan Resource Requirements
List the resources needed, such as land, seeds, fertilizers, machinery, and labor. Outline a budget that covers all expenses, including initial investment, operational costs, and contingencies. Ensure to incorporate sustainable practices for resource management.
Step 4: Draft a Timeline
Create a detailed timeline, breaking down tasks and milestones over weeks or months. Include tasks such as land preparation, planting, harvesting, and distribution. Specify responsible personnel and set realistic deadlines to track project progress effectively. You can also see more on Product Supply Proposal.
Step 5: Write the Proposal Document
Organize the proposal with sections like introduction, objectives, project scope, resource planning, financial estimates, and evaluation strategies. Use clear, concise language and support it with data, charts, and references. Proofread to ensure accuracy and persuasiveness.
An Agricultural Project Proposal is vital for initiating successful farming projects, securing funds, and aligning resources. By clearly outlining objectives, resources, and implementation strategies, it serves as a roadmap for agricultural ventures. Following the right steps ensures a well-structured, compelling proposal that attracts investors, partners, and stakeholders, contributing to agricultural development and sustainability. You can also see more on School Project Proposal.
FAQs
What Are Some Examples of Agricultural Project Proposal Objectives?
Some agricultural project proposal objectives emphasize the utilization of improved agricultural technologies and techniques, particularly in disadvantaged areas, as well as capitalizing on the system to boost crop production. Another example would be how to improve sustainability by using a better irrigation system or agricultural technique, which would help reduce pollution produced to nature as well as consumption of other artificial products.
What Are Some Different Types of Agriculture?
Commercial agriculture, which prioritizes producing crops with higher commercial value and employing more advanced techniques to boost crop productivity, is such type of agriculture. Another sort of agriculture involves clearing away forest areas by chopping trees and burning them in order to use the land as a farmable area; this is known as shifting cultivation and may be common in areas where plain and farmable lands are scarce. Herding and livestock ranching are two types of agriculture that may entail feeding their animals on natural pastures by herding rearing animals into them. You can also see more on Budget Proposals.
What Are Common Examples of Agricultural Branches?
Horticulture and animal husbandry are the two most popular types of agriculture. Horticulture is the cultivation of plant-based crops such as vegetables, fruits, and garden and ornamental plants. Animal agriculture is self-explanatory; it focuses on raising livestock and breeding animals for marketable products such as milk, furs, meat, and wool.
Who uses Agricultural Project Proposals?
Farmers, agricultural firms, NGOs, and government agencies use these proposals to launch or expand farming ventures and secure necessary support. You can also see more on Concept Proposals.
Can agricultural proposals be used for organic farming?
Yes, proposals can be tailored to focus on organic farming, detailing specific resources, practices, and sustainability goals for chemical-free agriculture.
What resources are needed for an agricultural proposal?
Essential resources include land, seeds, fertilizers, equipment, labor, and financial investment, depending on the project’s scope and type. You can also see more on Property Lease Proposal.
What is the primary goal of an Agricultural Project Proposal?
The primary goal is to outline a farming project’s objectives, resource needs, and strategies for successful implementation, helping secure funding and approvals. You can also see more on Land Sale Proposal.
