15+ Sample Manufacturing Proposals
-

Project Manufacturing Proposal
download now -

Manufacturing Intelligence Proposal
download now -

Flexibility in Manufacturing for Proposal
download now -

Proposal for Manufacturing Domain
download now -
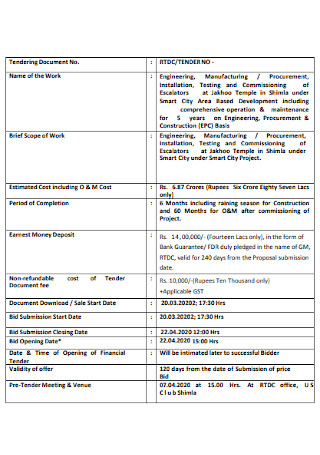
Manufacturing Proposal Format
download now -

Proposal for Publication in Procedia Manufacturing
download now -

Welding and Manufacturing Proposal
download now -

Drug Product Manufacturing Proposal
download now -

Accelerator Manufacturing Proposal
download now -

Knowledge Based Manufacturing Proposal
download now -

Robotics Manufacturing Proposal
download now -

Solar Manufacturing Proposal
download now -
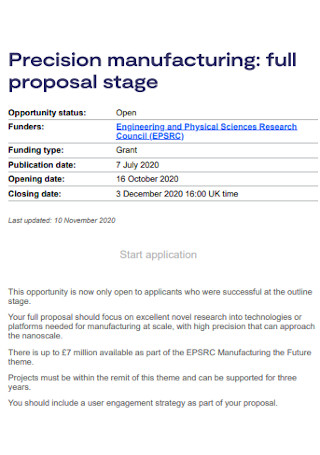
Precision Manufacturing Proposal
download now -

Detergents Manufacturing Proposal
download now -

Business Proposal for Ceramics Manufacturing
download now -

Steel Manufacturing Proposal
download now
FREE Manufacturing Proposal s to Download
15+ Sample Manufacturing Proposals
What Is a Manufacturing Proposal?
Elements Of a Proposal Document
Types of Manufacturing Process
How To Write a Manufacturing Proposal
FAQs
How important is manufacturing?
What is lean manufacturing?
How will manufacturing evolve in the future?
What Is a Manufacturing Proposal?
To better familiarize this type of document, perhaps we should define the two terms behind it first. Manufacturing is defined as the process of the production of goods through the use of labor, tools, machinery, and biological and chemical processing or formulation. Raw materials are transformed into finished products through manufacturing engineering or the manufacturing process.
A proposal document, on the other hand, facilitates the professional relationship between an organization or a company and its respective outside contributors. It allows the organization to establish a formal and logical presentation to an outside contributor.
Take those two terms together and we have the definition of the manufacturing proposal. It is a business document that kickstarts the relationship between the company that manufactures the goods and the outside contributors of the raw materials needed for the manufacturing process to begin. It contains a list of activities needed for the process and illustrates the significance of the process.
Elements Of a Proposal Document
Here are some of the key elements that can be found in a proposal document:
Types of Manufacturing Process
Here are the different types of the manufacturing process; keep in mind that the type of process that works for each business will have a slight variation depending on their individual products, the business ethos, and the raw materials and facilities that are available to them.
- Repetitive Manufacturing – The repetitive manufacturing process is used in basic manufacturing, which produces the same product on an assembly line. These types of rapid manufacturing operations will mass-produce the same or very similar products 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Automotive, electronics, semiconductors, and durable consumer goods are among the industries that use this type of manufacturing process. Because consumer demand for the finished product is stable and predictable, these mass-production industries are ideal for repetitive manufacturing. The assembly line will be relatively consistent, with few changes as one product is manufactured over time.
- Discrete Manufacturing – The cousin of repetitive manufacturing is discrete manufacturing. Like repetitive manufacturing, it operates on production lines, but the finished goods produced during this process frequently vary greatly. The assembly line configuration must frequently be changed when switching between different product models. This is known as a changeover in manufacturing facilities and incurs setup costs in the form of time, labor, and resources.
- Job Shop Manufacturing – Instead of an assembly line, production areas such as workstations and workshops are used in the job shop manufacturing process. Each worker may add something to the product as it passes through their station before being moved on to the next, and so on until the final product is completed. Because it is slower and produces a low volume of highly customized products, this method of manufacturing is ideal for custom manufacturing. Job shop manufacturing isn’t just for low-tech items. This method is also used in the advanced production of fighter jets and rockets for the aerospace and defense industries. To ensure a high-quality build, these products are manufactured by highly trained professionals who use advanced manufacturing techniques and place a strong emphasis on quality control.
- Continuous Process Manufacturing – Continuous process manufacturing is similar to repetitive manufacturing in that it operates 24 hours a day, produces the same or similar products repeatedly, and produces larger order quantities. The main distinction is that the raw materials used here are gases, liquids, powders, and slurries rather than solid-state components. Except for the difference in raw materials, it works almost identically to repetitive manufacturing. In practice, this could be a pharmaceutical company that manufactures large quantities of painkillers. Pharmaceutics, chemicals/industrial gases, fertilizers, and power plants are examples of traditional manufacturing industries that make extensive use of continuous processes.
- Batch Process Manufacturing – The batch manufacturing process differs significantly from continuous process manufacturing and is more akin to discrete and job shop manufacturing. The number of batches generated will be sufficient to meet the needs of a single customer. The equipment will be cleaned in between batches and left alone until the next batch is needed. Because the raw materials used are liquids, gases, powders, and slurries, they are more similar to continuous process manufacturing.
How To Write a Manufacturing Proposal
The process of writing a manufacturing proposal document does not need to be intimidating. Here are the steps needed to make one:
-
1. Start With the Basic Information
The introduction contains the essential information, which includes a cover letter, a title page, and (optionally) an executive summary and a table of contents. Simply explain who you are, why you are submitting this proposal, and what you want the reader to do after reviewing the proposal information in the cover letter. Make sure to include all of your contact information, including your phone number, email address, Business Website, physical address, and so on. The title page is nothing more than a descriptive name for your proposal. An executive summary (also known as a client summary) is a list of the most important points in a lengthy proposal that is provided for busy executives who may not have the time to read the rest of the pages. The table of contents is merely a navigation aid and will only be required if the proposal is lengthy and complex.
-
2. Understand What the Client Needs
This part should be centered on the prospective client. It is important to put yourself in the shoes of your client. Make a list of the organization’s needs, desires, and constraints. At the very least, you’ll need a requirements or a needs assessment page. You may also require more specifics, such as a schedule and budget page. Include all the topics you need to describe your understanding of what the client wants and needs, as well as any type of project restrictions and limitations. Diagrams or blueprints might be required. Your overall objective in this step is to demonstrate that you understand what the client requires from you.
-
3. Expand On the Main Details Of the Proposal
This is the step in which you describe what you intend to do in detail, how it will benefit the client, and how much it will cost. This section’s pages vary greatly from project to project, but it should at the very least include a services provided page, a benefits page, and a cost summary page. You should also include the following topics: schedule, options, Quality Control, equipment, packaging, shipping, safety, and sampling. Include as many topics as you need to describe your proposed manufacturing process in detail, and make sure to discuss how your process meets or exceeds the previously outlined needs.
-
4. Describe Why Your Company Would be the Ideal Choice
After you’ve thoroughly described your proposal, it’s time to explain why your company is the best fit for the job. To sell a client on your reputation, it is always best to use facts, statistics, or recommendations from others, so include sections like an “about us” page, company history, experience, client list, projects, staff, certifications, and so on to demonstrate that your company has plenty of experience with similar projects and the capability to carry out this manufacturing process. If you have received awards, gathered testimonials from previous clients, or offer a guarantee or warranty, make sure to include all of that as well.
-
5. Add Finishing Touches and Proofread the Document
After you’ve finished the proposal, take some time to make it look nice. After all, the goal is to distinguish yourself from the competition. You can include your company logo, use colored borders on pages, and add custom bullet points and fonts to match your organizational style. After you’ve completed all of your tasks, proofread the entire proposal document. Correct any spelling and grammatical errors, clarify any unclear wording, add missing information, and ensure that the proposal’s pages look professional.
FAQs
How important is manufacturing?
Manufacturing is important not only for producing and delivering goods to the marketplace but also for economic reasons. The mass production of items can provide a significant economic boost, as measured by manufacturing value added (MVA) indicators. These calculate a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) by comparing manufacturing output to the size of the overall economy. Manufacturing institutes, such as The Institute for Supply Management (ISM), examine the figures for manufacturing employment, inventories, and orders, and their reports will then inform financial analysts and researchers. Their reports will usually be the key indicator of the economy’s health as well as the trajectory of the stock market.
What is lean manufacturing?
Lean manufacturing is a manufacturing process that aims to maximize productivity while minimizing waste within a manufacturing operation. According to the lean principle, waste is anything that does not add value that customers are willing to pay for. Reduced lead times and operating costs, as well as improved product quality, are all advantages of lean manufacturing. The methodology of lean manufacturing is based on specific manufacturing principles that have influenced global production systems as well as those of other industries such as the healthcare industry, software industry, and various service industries.
How will manufacturing evolve in the future?
Manufacturing processes are evolving, as are the skills required to carry them out. With the pursuit of more cost-effective methods and increased automation in manufacturing, the number of jobs in this sector is expected to decline. Those who remain, on the other hand, are likely to be more specialized and well-compensated. Manufacturing will require staff skills and training to manage as technology becomes more sophisticated, while new materials and processes are changing specific industries. As more sophisticated robots are introduced into the manufacturing industry, more and more manufacturing processes will be automated.
Manufacturing has proved to be a continuously important aspect of the industry not just to drive the economy, but also to provide goods for the marketplace. But for a company to be able to start a manufacturing process, a proposal document must be created first between the outside source of the raw materials and the company that will turn the said raw materials into finished goods. Having a proposal document between the parties involved ensures the success of the overall manufacturing business with as few hitches as possible or no hitches at all. In this article, you will find examples of ready-made manufacturing proposals for you to download and use as a personal reference.
