20+ Sample Risk Registers
-
Risk Assessment and Risk Register
download now -

Safety Risk Registers
download now -
Sample Risk Register Template
download now -
Corporate Risk Register
download now -

Risk Log Register
download now -
Contract Stage Risk Register
download now -

Risk Opportunity Register
download now -

Risk Management Register
download now -

Project Risk Register Analysis
download now -
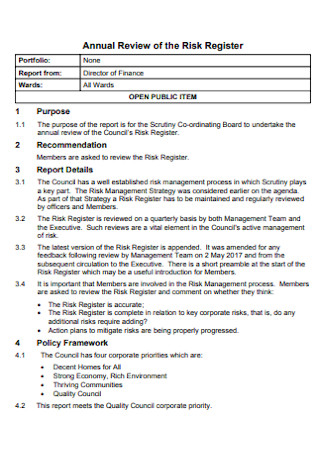
Annual Review of the Risk Register
download now -

Strategic Risk Register
download now -

Construction Project Risk Register
download now -

Mangos Risk Register
download now -
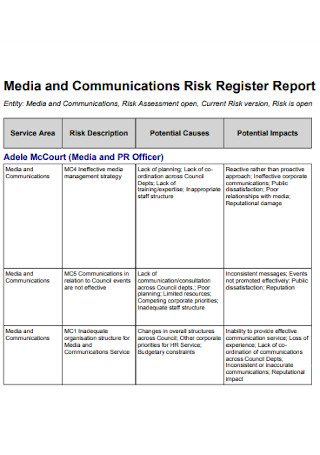
Communications Risk Register Report
download now -

Absolute Necessity of Risk Register
download now -
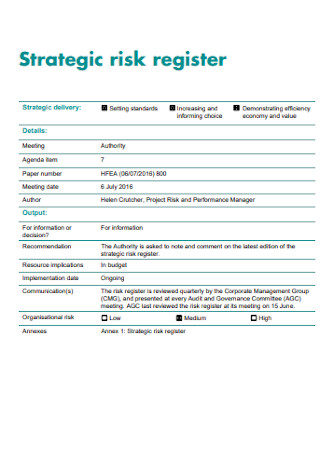
Sample Strategic Risk Register
download now -
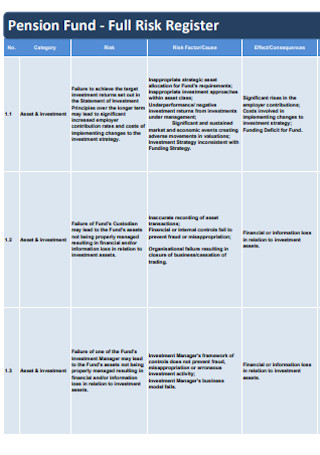
Full Risk Register
download now -
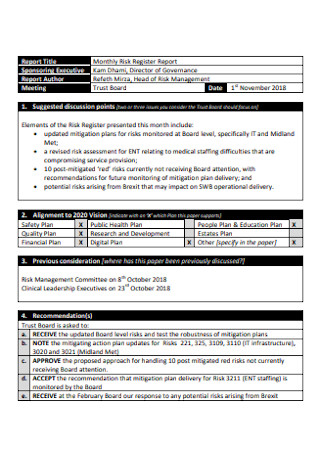
Monthly Risk Register Report
download now -
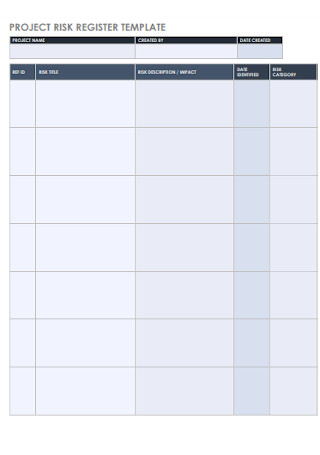
Project Risk Register Template
download now -
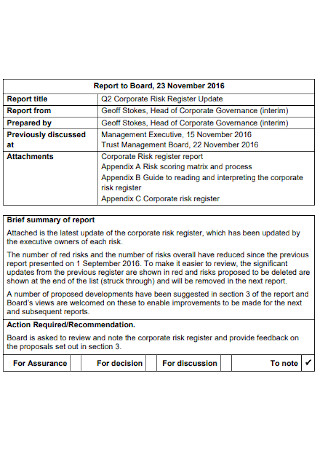
Corporate Risk Register Report
download now -
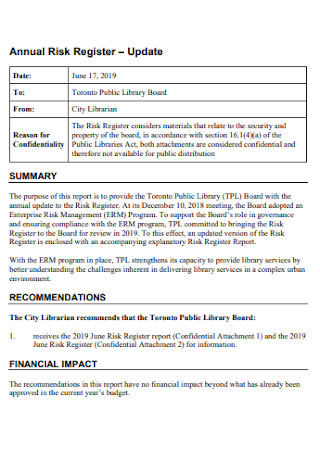
Annual Risk Register
download now
FREE Risk Registers s to Download
20+ Sample Risk Registers
What Is a Risk Register?
Key Elements Included in a Risk Register
Step by Step Process in Creating a Risk Register
FAQs
What is the purpose of a risk register?
What are the 2 types of risk assessment?
What are the most common types of hazards in the workplace?
What are examples of risk categories?
What Is a Risk Register?
A risk register or also known as a risk log is an essential tool devised and most commonly used in project management. It is a document that contains all the pieces of information about the risks that are identified, how those risks are investigated and interpreted as well as the plan of action on how those particular risks may be prevented from happening and how to deal with them at the moment they happen.
This is a document that integrates well with other documents within the company. It is not a type of document that can function on its own. It is highly recommended to draw a connection between the risk register and a work breakdown structure as it will show risks on different levels.
Key Elements Included in a Risk Register
Step by Step Process in Creating a Risk Register
Step 1: Identify the Risks
First and foremost, you have to point out the potential risks that may fall upon the company. Put them into writing to be more organized. In order to identify all the risks, you have to fully know and understand the different project operations and transactions that are performed in the company. This will highlight all the possible risks that may happen in the future. Make sure that this is clear and detailed. This is the most important step in creating a risk register as this will carry on until the last step.
Step 2: Identify the Consequences
After identifying the potential risks, know the possible outcomes. Ask yourself what will happen if the mentioned risks were to come into existence? It will be a good idea to go into detail and identify every consequence for each risk listed in the document. Step 1 and step 2 are closely in connection with one another. It is similar to a cause and effect.
A tip that may help in completing steps 1 and 2 is by utilizing the SWOT analysis. This will make sure that you spot out every possible factor that may become a hurdle or obstruction to the activities of the company. Also, it is important to learn from past mistakes. This will lead to the improvement of the project process and overall success. Make use of a lesson learned document as well.
Step 3: Identify the Probability and Impact
The next step would be identifying the chances of those risks coming into life. How high are the chances that they will actually happen? Another question would be, how bad will it be for the company if ever they were to come into being?
Step 4: Identify the Different Rankings
After coming up with the likelihood of the risks happening and the severity of their impact, it is time to rank them in order. These risks may be ranked low, medium, or high. Allocate the different risks depending on the outcome of step 3 and put them into the categories that they best fit.
Just like in the first two steps, steps 3 and 4 are tightly linked together. This will determine the rating and impact of the risks to your operational plans and production level expectations. A tip that may help in relieving the burden of these 2 steps would be to make use of a risk assessment tool.
Step 5: Monitoring the Risks
These would be an essential step in order to keep the risks in check. This will make sure that the risks are contained and will not disrupt the flow of process in the company. Go over the different systems and plans of action that are up and running. If there are no such things or they are not effective then proceed to step 6.
Step 6: Developing Actions and Response Plan
After monitoring the different risks and their impacts, it is time to resolve them. Just like in the ranking order of the risks, the plan of actions can be divided into 4 different categories.
1)Avoid – This means that the devised plan would completely put an end to the aforementioned risks. This can be done by extending the project schedule and revising the goal statement. A possible approach also is hiring technical experts to entirely eradicate risks.
2)Transfer – From the word itself, it means that you will pass on the risks to a different individual or what you may call a third party. This can be done by securing insurances and warranties.
3)Mitigation – This is the simplest and the most common approach to risk response. This means that you will mitigate or lessen the probability and severity of the risks that may fall upon the company. Your plan of action will be mainly focused and designed to mitigate the risks.
4)Accept – In some cases, companies have to accept that the risks cannot be avoided, transferred and mitigated. In this case, companies accept what will happen and in turn focus on building contingency plans.
It is important to remember that risks are dynamic and they tend to change a lot. The current plan of action for your response may not be enough to approach and resolve the fast-changing pace and rapidly rising chances of risks. Making the risk register simple and dynamic will be the answer to this kind of problem. It is a must to make sure that the document is easy to maintain and can easily cope up with the environment of the industry. It is important that this document can be easily accessed by the people who have the authority to go over them and make some revisions in order to adapt to the current needs and situation.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a risk register?
The main purpose of this type of document is to keep track of all the risks that have happened or may happen in the near future. This is a reference that project managers are using in order to address and resolve the risks and complications that may hinder the completion of a project. This can also be proof that you are complying with the regulatory laws and standards.
What are the 2 types of risk assessment?
There are 2 types of risk assessment, namely: quantitative analysis and qualitative analysis. The quantitative analysis makes use of quantities or values. This will determine the chances of achieving the target objective of the project scope. Also, with the use of probabilistic values, meaning it is based on probability and statistics, it computes the exposure rate of the project along with the cost and schedule. It also points out the risk to be prioritized based on their impact and severity.
On the other hand, a qualitative risk assessment makes use of predetermined tools and methods. While in quantitative there is a need for actual numbers, a qualitative risk assessment is categorized as very high, high, medium and low. This would also focus more on the daily activities that will happen if the said risks were to occur. Another important thing to pay attention to in a qualitative risk assessment is the element that it brings about. This will mostly feature the likelihood of the risks happening and consequences if ever they were to happen.
What are the most common types of hazards in the workplace?
Biological – These hazards cause health issues. Included here are viruses and bacteria.
Chemical – This is a rare hazard in the workplace or office. However, if you are working in a factory or a laboratory, this is what you should be cautious of. These can cause serious health issues and also cause physical injuries.
Physical – These physical hazards are the most common. These are the environmental factors surrounding the workplace.
Safety – These kinds of hazards are sometimes included under the category of physical hazards. These kinds of hazards will result in a dangerous workplace.
Ergonomic – These kinds of hazards are also under the physical category. These results in musculoskeletal risks. Examples are poor posture and poor office setup.
Psychosocial – These hazards focus on the mental health of the employees. Examples are stress, violence in the workplace and the most disturbing is sexual harassment.
What are examples of risk categories?
Risks can be classified into many different categories. These are:
Operational risks – This means that the cause is an operational failure.
Schedule risks – The cause of this is the delay in the operation and process.
Budget risks – This usually means overspending.
Programmatic risks – These are risks that are out of the control of the business.
Infrastructure risks – This is due to the failure of the building or the different facilities.
Project Management Body of Knowledge, a risk register or risk log is a document that possesses all the pieces of information about the risk analysis and the devised plan of actions. By documenting the different risks, you can make sure that everything is accounted for and there will always be an underlying plan of action. Be prepared for the future and start having a risk log. The available templates above make the process of creating a risk register easy.
