25+ Sample Construction Safety Checklist
-

Construction Tool Safety Checklist
download now -
Construction Safety Checklist
download now -
Balfour Beatty Construction Safety Checklist
download now -

Construction Safety Inspection Checklist
download now -

Construction Site Safety Checklist
download now -

Construction Safety Hazards Inspection Checklist
download now -
Construction Covid-19 Safety Checklist for Employer
download now -
Employer Construction Safety Checklist
download now -
Construction Site Health Safety Audit Checklist
download now -
Construction Site Safety Inspection Checklist
download now -
Construction Safety Activity Checklist
download now -
Construction Safety Start-up Checklist
download now -

Pre-Construction Safety Checklist
download now -
Daily Construction Safety Checklist
download now -

Construction Safety Meeting Checklist
download now -

Construction Safety Officer Checklist
download now -
Construction Worksite Assessment Safety Checklist
download now -
General Construction Safety Checklist
download now -
Project Construction Safety Checklist
download now -

Construction Contractor Safety Checklist
download now -
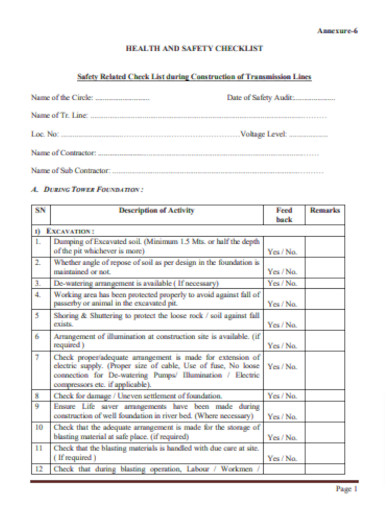
Construction Safety Health Checklist
download now -

Construction Safety Checklist Outline
download now -

Basic Construction Safety Checklist
download now -
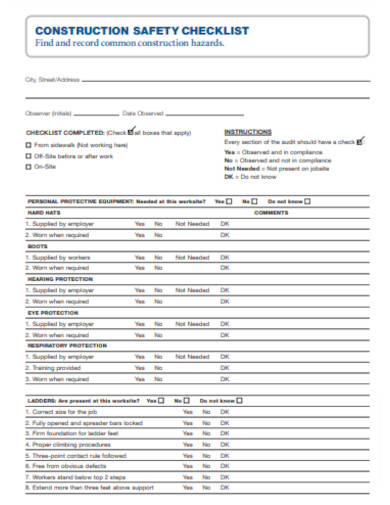
Simple Construction Safety Checklist
download now -
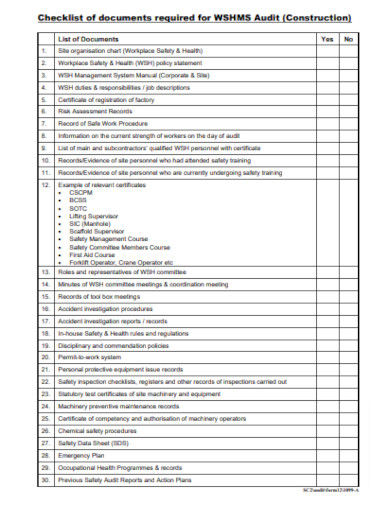
Construction Safety Audit Checklist
download now -
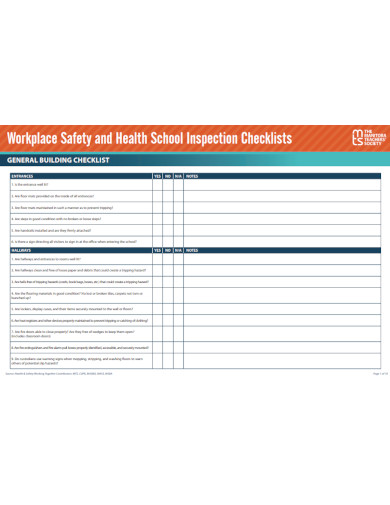
Workplace Construction Safety Checklist
download now
FREE Construction Safety Checklist s to Download
25+ Sample Construction Safety Checklist
Introduction: The Imperative of Safety in Construction
Pre-construction planning
Groundwork and Site preparation
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Machinery and Equipment Safety
Working at Heights
Electrical Safety
Handling and Storage of Materials
Fire Safety
Hazardous Materials
First Aid and Medical Emergencies
Continuous Training and Workshops
Noise Management
Documentation and Record Keeping
Mental Well-being of Workers
Technological Integration
Weather Preparedness
Legal and Compliance Aspects
Continuous Feedback Mechanism
OSHA
OSHA Construction Safety Checklist
Construction Site Safety Rules
FAQ’S
Why is a construction safety checklist important?
How often should a construction safety checklist be reviewed?
What is a construction safety checklist?
Who is responsible for maintaining and enforcing the construction safety checklist?
How can I ensure all workers are familiar with the safety checklist?
How should I handle a situation where an item on the checklist is non-compliant?
Introduction: The Imperative of Safety in Construction
The risks in construction are significant and should not be underestimated. Whether it’s working at heights or handling heavy machinery, workers are always exposed to dangerous situations. A safety checklist acts as a reference point, making sure that all potential risks are taken into account. Safety is paramount in every industry, and the construction sector is no exception. Overlooking safety protocols can lead to accidents, delays, and hefty liabilities.
Pre-construction planning
Risk assessment and mitigation strategies: Before commencing any project, it’s crucial to identify potential risks. Utilizing risk matrices and expert consultations can guide mitigation strategies.
Identification of potential hazards: A comprehensive survey of the site reveals hazards like unstable ground, nearby power lines, and more.
Groundwork and Site preparation
- Securing the perimeter: Secure barriers prevent unauthorized entry, protecting both the public and site assets.
- Safe storage solutions for materials: Ensuring materials are stored safely prevents accidents and streamlines operations.
- Accessibility and clear paths: Clear paths minimize risks from tripping or equipment mishandling.
- Soil Testing: This assesses the ground’s bearing capacity, essential for determining structure stability.
- Hazard Assessment: Identify any existing hazards like underground utilities, old structures, or natural obstacle
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Ensuring that all workers have access to and use the right PPE is pivotal.
- Helmet and Boots: Essential gear to protect against falling objects and mishaps.
- Visibility Vests: Ensure workers are visible, especially in low-light conditions.
Machinery and Equipment Safety
Machines are the workhorses of construction. Their colossal power, however, comes with risks.
- Regular Inspections: All machinery should be inspected to ascertain operational safety.
- Operational Training: Only trained personnel should operate machinery.
Working at Heights
A significant chunk of construction hazards are associated with height.
- Safety Harnesses: Any worker operating at a height should be secured with harnesses.
- Scaffolding: Ensure it is sturdy, and its integrity is checked regularly.
Electrical Safety
Electricity is indispensable, but its potential for harm is significant.
- Insulated Tools: Workers should use insulated tools to prevent accidental electrocutions.
- Grounding: Temporary electrical circuits should be grounded to protect against electric shocks.
Handling and Storage of Materials
Improper handling can lead to accidents and material wastage.
- Storage Zones: Materials should be stored in designated zones, away from operational areas.
- Material Handling Training: Workers should be educated about safe material handling practices.
Fire Safety
Fires can be devastating, both in terms of life and property.
- Fire Extinguishers: Strategically placed extinguishers, suited for different fire types.
- Evacuation Routes: Clearly marked and free of obstructions.
Hazardous Materials
Many construction materials can be hazardous if mishandled.
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS): Should be available on-site for all hazardous materials.
- Storage: Hazardous materials need specialized storage solutions.
First Aid and Medical Emergencies
Immediate medical attention can drastically reduce injury severity.
- First Aid Kits: Accessible and stocked with essential supplies.
- Emergency Protocols: Well-defined procedures and contacts for medical emergencies.
Continuous Training and Workshops
Keeping workers updated on safety protocols is not a one-off event.
- Orientation Sessions: For new hires, ensuring they grasp foundational safety concepts.
- Refresher Courses: For experienced workers, to keep them updated.
Noise Management
Chronic exposure to loud noise can lead to lasting hearing issues.
- Decibel Monitors: To ensure noise levels are within acceptable limits.
- Noise Barriers: Temporary walls or structures to dampen noise.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Safety is as much about reflection as it is about action.
- Incident Logs: Documenting every incident, however minor, can provide insights.
- Safety Manuals: Updated and accessible to all workers.
Mental Well-being of Workers
Physical safety is intertwined with mental well-being.
- Regular Breaks: To ensure workers are not overly fatigued.
- Counseling: Providing resources for workers to discuss mental health issues.
Technological Integration
The modern construction site is rapidly integrating technology for enhanced safety.
- Drones: For site surveys, ensuring no area goes uninspected.
- Sensors: Embedded in machinery or structures, they can provide real-time feedback.
Weather Preparedness
Nature’s elements can pose significant challenges.
- Weather Forecasts: To prepare and adapt to upcoming weather conditions.
- Weather-specific Gear: For instance, cooling vests for hot conditions or waterproof gear for rains.
Legal and Compliance Aspects
Safety also has legal ramifications.
- Regular Audits: To ensure compliance with local regulations.
- Insurance: Protecting against unforeseen financial burdens due to accidents.
Continuous Feedback Mechanism
For safety protocols to evolve, feedback is pivotal.
- Feedback Boxes: Anonymous suggestions can lead to tangible improvements.
- Regular Safety Meetings: Where workers can voice concerns and suggestions.
OSHA
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set forth specific guidelines and standards to ensure the safety and health of workers in the construction industry. Here’s a concise OSHA construction safety checklist based on their regulations. However, always refer to the OSHA official website or their publications for comprehensive and up-to-date details.
OSHA Construction Safety Checklist
General Safety and Health Provisions
- Job safety program established and communicated.
- Periodic inspections scheduled and conducted.
- Corrective action taken when hazards are identified.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Adequate PPE provided and used properly.
- Regular inspections of PPE to ensure they’re in good condition.
Fall Protection
- Guardrail systems, safety nets, or personal fall arrest systems in place.
- Fall protection training for all employees.
Scaffolding
- Properly constructed to bear the load.
- Guardrails and toe boards installed for platforms higher than 10 feet.
- Regular inspections by a competent person.
Ladders and Stairways
- Ladders inspected regularly for defects.
- Proper angle positioning for straight and extension ladders.
- Handrails installed on stairways with four or more risers.
Tools and Equipment
- Regular inspections for wear, damage, and malfunctions.
- Proper grounding of electrical tools and equipment.
- Safety guards in place for power tools.
Electrical Safety
- Only qualified workers handle electrical tasks.
- Ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in use.
- Electrical equipment and cords regularly inspected.
Trenching and Excavation
- Trenches inspected daily and after conditions that might increase hazards.
- Proper protective systems in place.
- Means of access and egress from the trench provided.
Cranes and Hoists
- Regular equipment inspections by a competent person.
- Load charts available and adhered to.
- Operators trained and, where applicable, certified.
Material Storage and Disposal
- Stored materials are stable and secure.
- Waste disposal conducted safely and per regulations.
Hazard Communication
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) available for all hazardous substances.
- Proper labeling of hazardous materials.
- Training provided to workers on the hazards of materials they’re exposed to.
Welding and Cutting
- Proper ventilation in welding areas.
- Fire extinguishers available when welding or cutting.
- Personal protective equipment (e.g., welding shields) in use.
Fire Protection and Prevention
- Fire protection equipment readily available and maintained.
- Workers trained in fire protection procedures.
- Proper storage of flammable and combustible materials.
Sanitation
- Drinking water provided.
- Toilets and washing facilities available and clean.
Noise Exposure
- Hearing protection provided in areas exceeding OSHA’s permissible exposure limits.
- Periodic noise monitoring conducted.
Confined Spaces
- Permit system in place for entry into confined spaces.
- Workers trained on hazards and proper procedures.
- Rescue and emergency services available during confined space operations.
Construction Site Safety Rules
Construction sites are teeming with potential hazards, from moving machinery to risks associated with working at heights. To ensure the safety and well-being of workers, visitors, and even nearby residents, adhering to strict safety rules is paramount. The following is a comprehensive list of construction site safety rules. Note that these are general rules, and specific job sites or tasks may have additional requirements:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate PPE, which may include helmets, safety goggles, gloves, high-visibility vests, and steel-toed boots.
Ensure PPE is well-maintained and replaced if damaged.
2. Access and Egress:
Only authorized personnel should enter the construction site.
Clearly mark entry and exit points.
3. Training:
All workers must undergo proper safety training before starting work.
Training should be updated regularly and provided when new equipment or processes are introduced.
4. Machinery and Equipment:
Only trained and authorized personnel should operate machinery and equipment.
Regularly inspect and maintain all equipment.
Always power down and secure machinery when not in use.
5. Working at Heights:
Use guardrails, safety nets, or personal fall arrest systems when working at elevated levels.
Inspect scaffolding regularly to ensure its stability.
6. Electrical Safety:
Keep a safe distance from overhead power lines.
Use ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) for electrical equipment.
Regularly inspect wires and cables for damage.
7. Trenching and Excavation:
Inspect trenches daily and after any event that might alter their conditions.
Provide secure access and egress from excavated areas.
Ensure protective systems are in place to prevent collapses.
8. Hazard Communication:
Clearly label and store hazardous materials.
Maintain and make available Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for all hazardous substances on site.
9. Housekeeping:
Keep work areas free of unnecessary debris to prevent tripping hazards.
Dispose of waste materials in designated areas.
10. Fire Safety:
Store flammable materials securely.
Ensure fire extinguishers are easily accessible and that workers know how to use them.
11. Noise Management:
Use hearing protection in high-noise areas.
Regularly monitor noise levels to ensure they are within safe limits.
12. Tool Safety:
Use the right tool for the job.
Regularly inspect tools to ensure they are in good condition.
Store tools safely when not in use.
13. First Aid:
Maintain a well-stocked first aid kit accessible to all workers.
Train designated personnel in first aid procedures.
Clearly mark the location of the first aid station.
14. Emergency Procedures:
Develop and communicate an emergency action plan.
Conduct regular emergency drills.
Clearly mark emergency exits and assembly points.
15. Reporting:
Encourage workers to immediately report unsafe conditions or practices.
Document and investigate all incidents and near misses.
FAQ’S
Why is a construction safety checklist important?
The checklist helps identify potential hazards and ensures that preventive measures are in place. By adhering to a safety checklist, construction sites can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, injuries, and project delays.
How often should a construction safety checklist be reviewed?
Ideally, a construction safety checklist should be reviewed daily before work commences. However, for some aspects, such as equipment maintenance or site audits, weekly or monthly checks might be more appropriate.
What is a construction safety checklist?
A construction safety checklist is a tool used by construction professionals to ensure that all safety measures and protocols are followed on a construction site. It serves as a comprehensive list of safety elements that need to be reviewed and implemented to safeguard workers, equipment, and the overall site.
Who is responsible for maintaining and enforcing the construction safety checklist?
While everyone on the construction site plays a role in maintaining safety, the site manager or safety officer is typically responsible for enforcing the checklist and ensuring all safety measures are adhered to.
How can I ensure all workers are familiar with the safety checklist?
Conduct regular safety training sessions, toolbox talks, and safety orientations for new employees. Make the checklist accessible to all workers, and emphasize its importance regularly.
How should I handle a situation where an item on the checklist is non-compliant?
Address any non-compliant items immediately. Depending on the severity, this could mean halting work until the safety concern is resolved. Ensure that corrective measures are documented and communicated to all relevant parties.
Safety in construction is a dynamic, evolving field. Regular updates, training, and feedback can ensure that a construction site is not just a place of productivity but also security. The value of a comprehensive safety checklist lies not just in its adherence but also in its regular evolution, mirroring the requirement checklist of the modern construction site.
