Internal Audit Checklist Samples
-
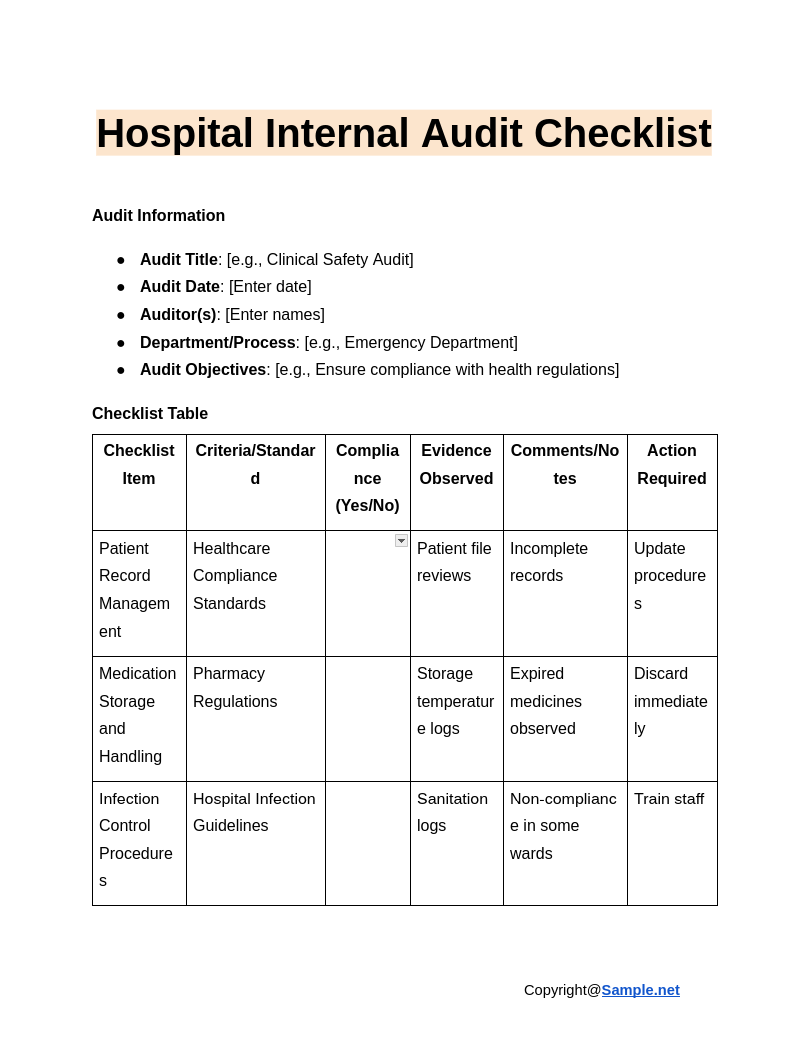
Hospital Internal Audit Checklist
download now -
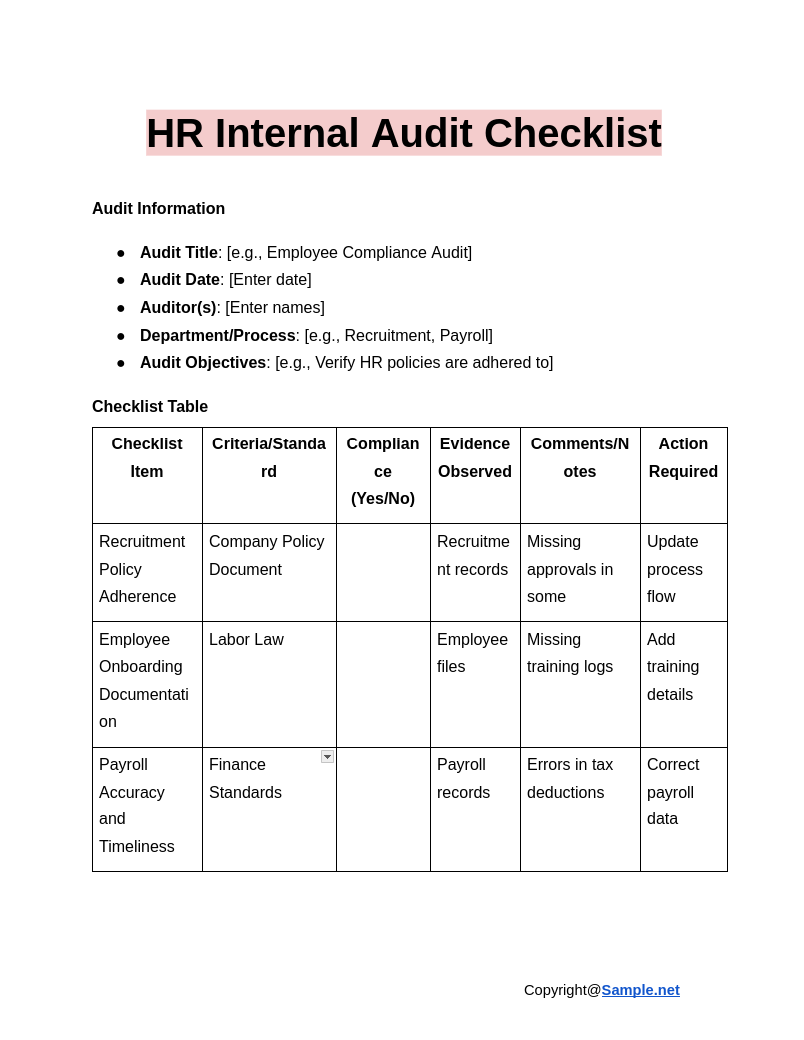
HR Internal Audit Checklist
download now -
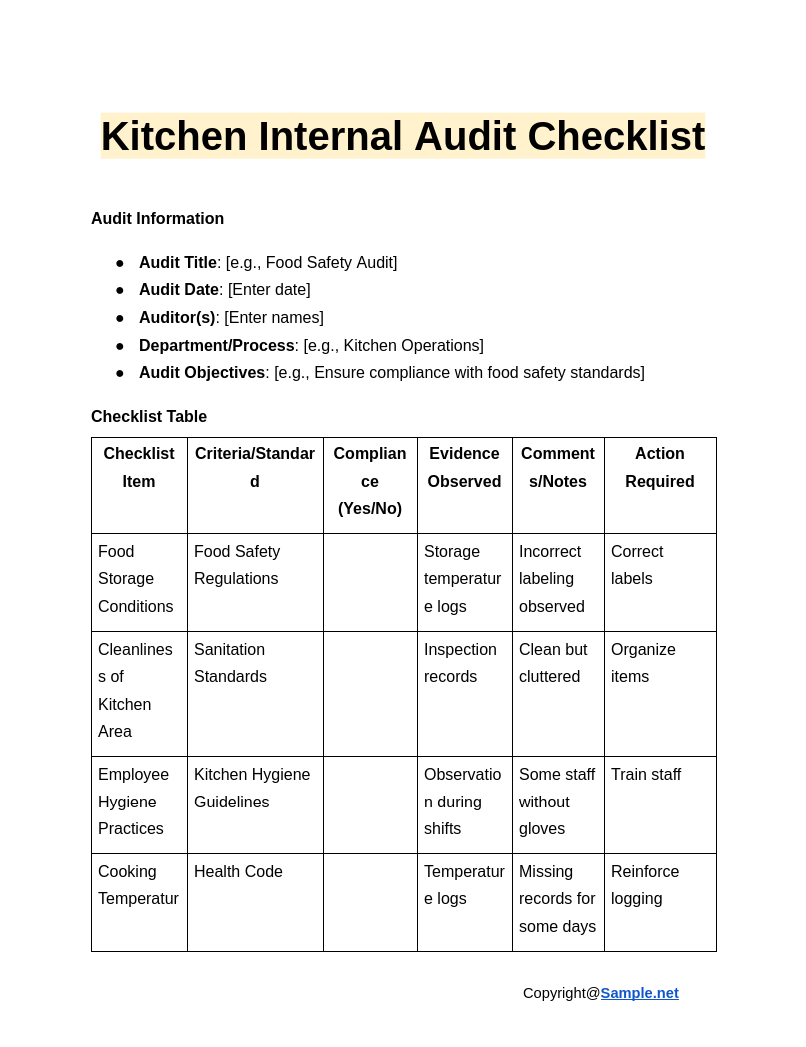
Kitchen Internal Audit Checklist
download now -
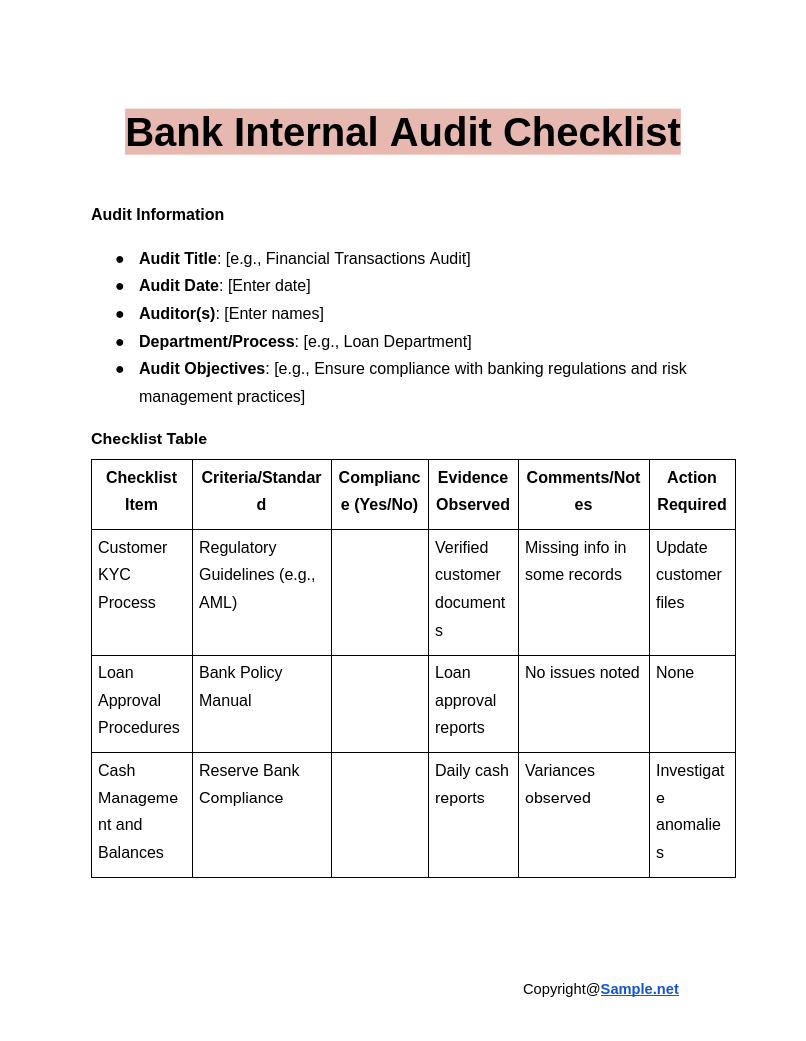
Bank Internal Audit Checklist
download now -

Sample Internal Audit Checklist
download now -
Annual Internal Audit Checklist
download now -
Internal Audit Plan Checklist
download now -
Internal Financial Audit Checklist
download now -

Checklist for Internal Audit Format.
download now -
Outsourcing Internal Audit Checklist
download now -

Internal Management Audit Checklist
download now -
Simple Internal Marketing Audit Checklist
download now -
Basic Internal Audit Planning Checklist
download now -
Internal Audit Report and Checklist
download now -

Internal Audit and Financial Controls Checklist
download now -
Internal Audit Process Checklist
download now -
Formal Internal Audit Checklist
download now -
Internal Audit Verification Checklist
download now -

Internal Audit Service Checklist
download now -
Club License Internal Audit Checklist
download now -
Internal Audit Checklist Form
download now -
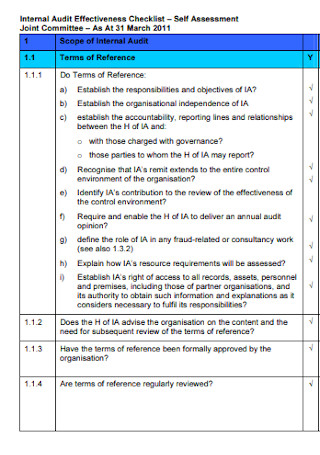
Internal Audit Effectiveness Checklist
download now -

Company Audit Checklist Template
download now -
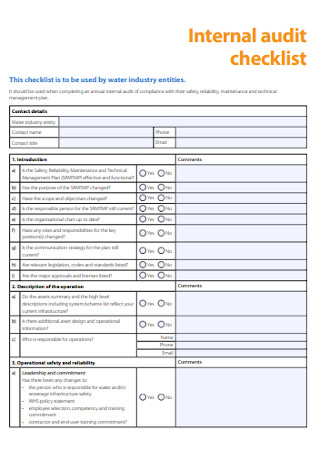
Standard Internal Audit Checklist
download now
FREE Internal Audit Checklist s to Download
Internal Audit Checklist Format
Internal Audit Checklist Samples
What is an Internal Audit Checklist?
Benefits of an Internal Audit Checklist
How To Make an Internal Audit Checklist?
FAQs
What do audit procedures entail?
Who is in charge of appointing an internal auditor?
Who appoints a new internal auditor?
What are the key elements of a good internal audit checklist?
How does an internal audit checklist improve efficiency?
How often should an internal audit checklist be updated?

Download Internal Audit Checklist Bundle
Internal Audit Checklist Format
Audit Information
- Audit Title: [Enter the audit title, e.g., Quality Management System Audit]
- Audit Date: [Enter the date]
- Auditor(s): [Enter names]
- Department/Process: [Enter the specific department or process being audited]
- Audit Objectives: [State the objectives of the audit, e.g., compliance, performance review]
Checklist Table
| Checklist Item | Criteria/Standard | Compliance (Yes/No) | Evidence Observed | Comments/Notes | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example: Process Review | ISO 9001:2015 Clause 8.5 | Yes | Process flow documentation | Clear understanding observed | None |
Audit Findings
- Summary of Non-Conformities: [List all major/minor non-conformities]
- Opportunities for Improvement: [List potential areas for improvement]
- Best Practices Observed: [Highlight positive findings]
Corrective Action Plan
- Non-Conformity: [Description]
- Root Cause: [Analysis]
- Action Plan: [Detailed actions to correct and prevent recurrence]
- Responsible Person: [Name/Title]
- Deadline: [Date for completion]
Conclusion
- Overall Audit Status: [Compliant/Non-Compliant]
- General Comments: [Any additional remarks]
Signatures
- Auditor(s): _____________________________ Date: __________
- Auditee/Process Owner: __________________ Date: __________
What is an Internal Audit Checklist?
An Internal Audit Checklist is a structured set of guidelines, tasks, and criteria that internal auditors use to examine an organization’s processes, controls, and compliance with regulations and standards. It serves as a roadmap to systematically identify risks, evaluate effectiveness, and ensure continuous improvement of internal procedures. You can also see more on Compliance Checklists.
Benefits of an Internal Audit Checklist
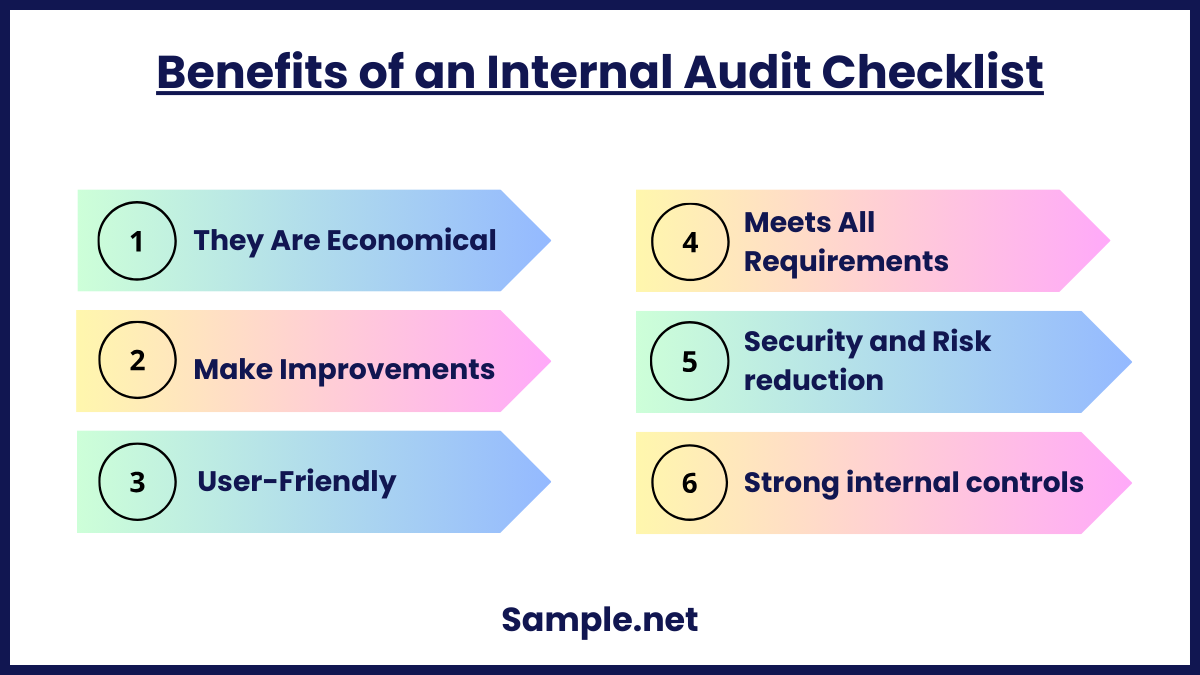
When everything is handled in-house and without the assistance of a professional consultant, an internal audit checklist is a helpful tool to consider. Utilizing a template has several appealing advantages for anyone who already has a lot on their plate. If you’re interested, here are a few additional advantages.
How To Make an Internal Audit Checklist?
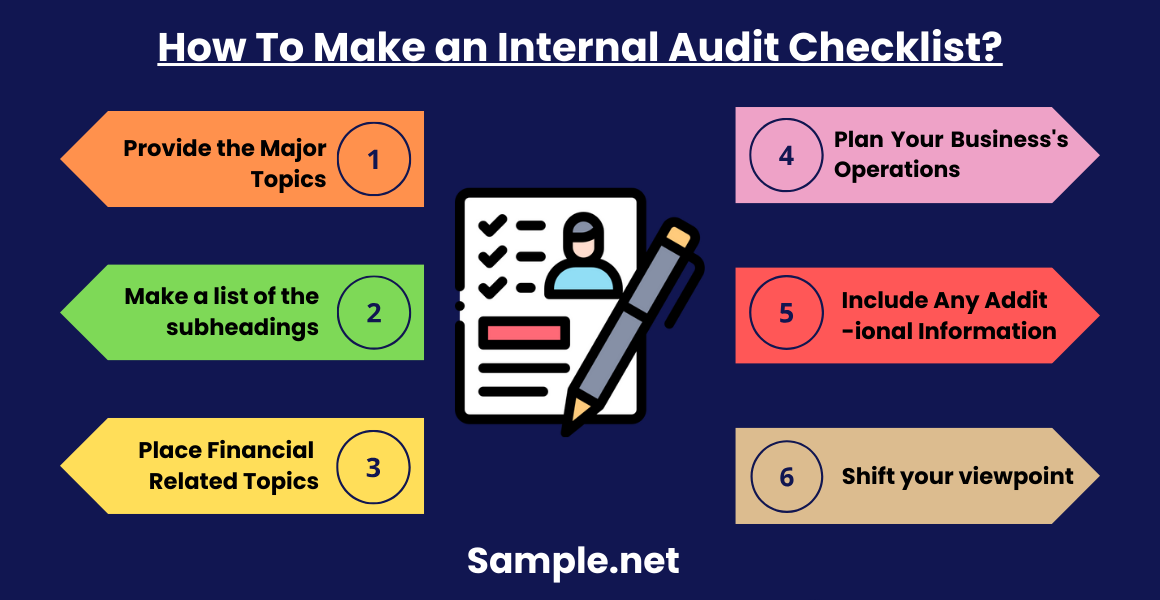
Internal auditing is similar to personal evaluation on a grander scale. Its main goal is to improve an organization’s performance by resolving problems and avoiding them from occurring, and identifying and correcting control and process inconsistencies. An Internal Audit Checklist enables firms to improve by providing information on how they fared over a specific period. You can also see more on Manufacturing Audit Checklist. The stages for creating an Internal Audit Checklist are outlined below.
Step 1: Provide the Major Topics
Outline the audit checklist’s major subject headings to assist in visualizing the audit’s critical components. These subject headings may include information about an organization’s management, finance, and operations. These can be related to the various features of the business on which you should concentrate your audit efforts. To create the checklist, you must use a suitable program, such as a spreadsheet application or simply a paper and a pencil.
Step 2: Make a list of the subheadings.
Now is the time to organize your checklist by placing the subheadings beneath the primary subject headings. You can begin by categorizing management subjects under the management subject title, including employee development plan and management. To aid in auditing the planning procedures, make a list of subheadings such as sales plan, pricing policy, and annual budget. This section will assist in ensuring that a sales plan is in place, a pricing policy is in place, and the business is operating within a reasonable budget. To escort an audit connected to personnel management, you can include subheadings such as employee expectations, job descriptions, and punishment processes.
Step 3: Place Financial Functions-Related Topics
Outline the topics and functions that fall under the finance subject heading. You can include issues relating to accounting practices as well as business financial planning. This division is typically responsible for determining the type of accounting system used and ensuring that the various accounting statements are prepared accurately. It then verifies that the owner comprehends the significance of all of these statements.
Step 4: Plan Your Business’s Operations
Put the functions that are associated with the business’s operations under the “operations” subject heading. This will include production-related topics as well as marketing and promotion. For example, you’ll want to evaluate supplier relationships, inventory control procedures, and training programs when it comes to production. Under the marketing and promotions subheadings, you must address competitors, customer needs, and promotion plans.
Step 5: Include Any Additional Information
Ensure that you take advantage of available assistance for small businesses. You can use the audit checklist provided by the United States Small Business Administration. It can serve as a guide for developing your business’s specific list. Be sure to read it thoroughly for guidance and to include any particular details, such as those about quality and safety requirements, on your audit checklist. You can also see more on Payroll Audit Checklist.
Step 6: Shift your viewpoint.
Auditors are skilled in performing audits and aligning processes to regulatory requirements or industry standards to assist your operations in achieving higher quality outcomes and, as a result, producing higher quality products and services. This does not indicate that they are specialists in every field. It’s important to remember that the auditors’ purpose is to match your procedures with specific legislation or standard. They want you to be compliant, but they may need your help and collaboration to align your department. Only you know everything there is to know about your tactical business areas. During the interview, try to be receptive to an internal auditor’s line of questioning. This can assist you in identifying ways to align your processes with high-quality standards better and, as a result, meet your continuous improvement objectives. You may discover that you’re too close to your circles to explain the procedure adequately, and your documented process thus fails to provide a high-level overview of the steps.
FAQs
What do audit procedures entail?
Audit Procedures are a set of steps used by auditors to gather enough audit evidence to make an opinion on financial statements, determining whether they accurately reflect the organization’s financial situation. There are two types of procedures: substantive and analytical.
Who is in charge of appointing an internal auditor?
An internal auditor is a company’s auditor who the company’s shareholders appoint to perform internal auditing. An internal auditor is usually a company employee. However, occasionally, firms appoint an external expert as an internal auditor.
Who appoints a new internal auditor?
Internal auditors are appointed and compensated by management. The internal auditor is replaced solely by the administration, whereas the shareholders exclusively replace the statutory auditor. You can also see more on Vendor Audit Checklist.
What are the key elements of a good internal audit checklist?
A good checklist includes clear objectives, defined criteria, a logical structure, and relevant questions. It should also allow for documentation of findings and action plans for improvement.
How does an internal audit checklist improve efficiency?
By standardizing the audit process, the checklist ensures a consistent approach, reduces redundancy, and streamlines the identification of areas for improvement. This systematic approach saves time and resources. You can also see more on Laboratory Audit Checklist.
How often should an internal audit checklist be updated?
It should be updated whenever there are changes in regulations, organizational goals, or processes. Regular reviews, ideally annually or after significant changes, ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness. You can also see more on Supplier Audit Checklist.
