6+ SAMPLE Laboratory Audit Checklist
-
Laboratory Audit Checklist
download now -
Laboratory Health and Safety Self-Audit Checklist
download now -
Laboratory Self-Audit Checklist
download now -
Quality Control Laboratory Audit Checklist
download now -

Clinical Laboratory Audit Checklist
download now -
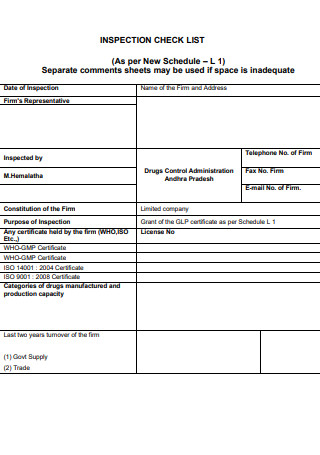
Laboratory Audit Inspection Checklist
download now -
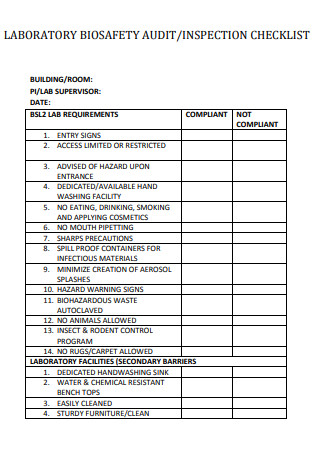
Laboratory Audit Biosafety Checklist
download now
FREE Laboratory Audit Checklist s to Download
6+ SAMPLE Laboratory Audit Checklist
What Is Laboratory Audit Checklist?
What Is the Importance of Laboratory Safety?
What Is the Goal of a Laboratory Audit Checklist?
Guidelines in Laboratory Maintenance
How to Prepare a Laboratory Audit Checklist Preparation
FAQs
What Is the Purpose of an Audit Checklist?
What Are the Areas of Audit in the Laboratory?
What Should be Included in an Internal Audit?
Creating a process audit checklist is a crucial step in the process of performing or planning a procedure audit. An audit checklist is a tool comprised of questions derived from the requirements of the quality management system, the process’s work performance standards, and the documentation created for the inspected process. An audit checklist is a tool that can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of a quality management system. The auditor should keep a few things in mind while putting together the audit checklist for a laboratory process when it comes to auditing a laboratory process.
What Is Laboratory Audit Checklist?
Laboratories must be inspected on a regular basis to verify that they are safe, thus inspectors use a laboratory inspection checklist. This inspection routine covers everything from making sure you’re prepared in the event of a crisis to cleaning up any chemicals you’ve spilled and disinfecting your surroundings. You will even have a waste management strategy in place. Additionally, a clinical audit checklist can be connected with a laboratory audit checklist, both of which are used by multidisciplinary healthcare practitioners to improve the quality of care by comparing the current practice to best practices criteria. With the use of this clinical audit checklist, clinical audit committees will be able to more easily evaluate the performance and efficacy of clinical audits.
Moreover, a self-audit checklist is intended to assist departments in evaluating the processes and procedures that are used to track and report performance measures. The checklist assists in ensuring that sufficient controls are in place to support the City Auditor’s certification of the targets and actuals reported for each measure. Additionally, the Facility Inspection Checklist (FIC) is a safety audit tool that firms can use to assess the safety of their facilities. The frequency of inspections will vary depending on your industry, however, it is advised that you execute the inspections at least once a month. Inspections may be obligatory and scheduled on a regular basis in some industries, depending on local laws. Facility Cleaning Checklist is utilized for buildings or manufacturing facilities, this checklist usually includes precise CDC standards for sanitizing high-risk contact areas and touchpoints, as well as other important information. Office Cleaning Checklist – utilized to guarantee that public or private workplaces, including the pantry and restrooms, are kept clean and organized. Other than this, using a room maintenance checklist, also known as a preventative maintenance checklist, you can maintain your building safe by doing periodic planning, checkups, and maintenance tasks on time.
What Is the Importance of Laboratory Safety?
Maintain laboratory safety for the benefit of those who rely on you. If protocols are not followed, workers may suffer physical injury or even death. Inappropriately handled laboratory materials and chemicals can have disastrous consequences, including the possibility of being injured or even killed. In addition, it safeguards the assets of the company. In order to avoid fires in the laboratory, it is necessary to follow the established procedures. Chemicals that have not been handled and stored properly have the potential to cause explosions and fires if they come into touch with one another. When damage to the property has an impact on the laboratory, it has the potential to have a ripple effect on everything the laboratory does because everything they do is conducted within the same facility as the harm.
The machines must be handled with care in order to ensure that they are safe to use. It may seem pointless to devote time to cleaning and storing your microscope, but it is required in order to keep the lab in good working condition. Maintaining the machinery ensures that it continues to fulfill its function as intended. Cross-contamination risks are reduced as a result of laboratory safety. In order to assist avoid the transfer of sickness and pathogens, laboratory practices are developed and implemented. Because sterilization is the only way to prevent the spread of germs, students and professionals have gadgets that must be sterilized on a regular basis. To talk in-depth, Lab safety and security is concerned with preventing potential risks and dangers from being faced by students and lab staff when they are in the laboratory setting. These regulations are required in order to prevent serious occurrences such as fires, explosions, biological threats, and so on. If you want to keep harmful contamination at bay, you must ensure that your laboratory is in good working order. It contributes to the prevention of any type of property and equipment damage. It contributes to the proper organization of the laboratory and the preservation of a safe working environment.
What Is the Goal of a Laboratory Audit Checklist?
The audit checklist is intended to be used to review the process in order to determine its overall success. Auditors conduct laboratory audits to determine whether or not the lab’s processes are performing as intended. They make use of checklists to track down evidence of compliance. As Clause 8 says, in the event of insufficient process documentation, an auditor will go to general standards for advice. One important element to emphasize is that while using an audit checklist in a laboratory, the goal is to examine the process and ensure that problems are not introduced into the environment. The purpose of the audit checklist is to explore the laboratory rather than only to look for nonconformities as the name implies. The audit is intended to review the process in order to ensure that the records provide evidence that the process complies with the company’s specifications. The auditor only requires the process owner to make adjustments when the procedure does not meet the requirements set forth by the auditor.
Guidelines in Laboratory Maintenance
Norms and guidelines have been set in order to ensure the safety of laboratory employees as well as any other individuals who may be participating in the research. Observing the following principles will aid in the maintenance of a safe laboratory environment for workers to operate in, hence protecting them from chemical exposure and unanticipated disasters. Here are some guidelines in laboratory maintenance:
How to Prepare a Laboratory Audit Checklist Preparation
The audit is a procedure that is based on systematic actions that are carried out in order to analyze or measure the conformance of a certain process. Any process can be audited by using a checklist, which the auditor uses to gather evidence to demonstrate that the process complies with the standards outlined in the criteria. Labs are typically organized around one or more of the following working principles: either they work within an organization to perform tests and analyses on specific products, manufacturing processes, or operations, or they work independently as a third party to perform tests and analyses on samples provided by clients/customers. It does not matter whatever criteria are used in a laboratory; the following process flow phases are always followed:
1. Receiving Test Samples Is the First Step
Identification and traceability, handling and storage, and receiving records are only a few of the activities and data that should be scrutinized.
2. Identification and Classification of Test Samples
Traceability and marking documentation, for example, should be checked, as should other activities and records. Samples that are not in compliance
3. Preparation for the Examination (Conditioning, Apparatus Preparation, or Other Pre-Requisites)
Process documentation, testing requirements, and preparation criteria are only a few examples of activities and documents that should be reviewed.
4. Carrying Out a Test-Analysis Procedure
Process documentation, machine fitness (calibration), personnel competency (qualification), and process records are only a few of the activities and records that should be scrutinized throughout the audit.
5. Preparation of Test Results Reports
Records, for example, should be verified on a regular basis, as should other activities. Control of nonconforming samples and the preservation of records are all important considerations.
There are various considerations that must be taken into consideration when completing these five fundamental processes in order to obtain effective test findings. They can comprise documentation of test methods, the competency of persons doing tests, the fitness of testing equipment, the environment in which tests are performed, the measurement traceability of test results, and input/output criteria for completing test analysis, amongst other things.
FAQs
What Is the Purpose of an Audit Checklist?
What should be clearly recognized is that the goal of employing an audit checklist for a laboratory is to examine the effectiveness of the process and to guarantee that non-conformities do not occur throughout the auditing.
What Are the Areas of Audit in the Laboratory?
The preanalytical, analytical, and post-analytical phases of the laboratory’s operations are all subject to audit. Following a thorough examination of the theoretical foundations of clinical audits in the laboratory, this paper describes in detail how a laboratory-based clinical audit should be done and monitored, with particular emphasis on the chemical pathology lab.
What Should be Included in an Internal Audit?
It is the responsibility of the laboratory to document its policies, systems, plans, processes, and instructions, to the extent that this is required to ensure the quality of the test and/or calibration results. The documentation for the system must be conveyed to, understood by, and made available to the necessary employees before it can be implemented.
The audit is a procedure that is based on systematic actions that are carried out in order to analyze or measure the conformance of a certain process. Any process can be audited by using a checklist, which the auditor uses to gather evidence to demonstrate that the process complies with the standards outlined in the criteria. The example checklist shown above is tailored to a single laboratory. During the course of conducting a laboratory audit, the audit criteria will include two primary components.
The first will be the process requirements that have been specified for that particular laboratory, and the second will be the standard process requirements. As long as the laboratory does not have a documented process that is specific to its operations, the auditor will examine process activities in accordance with standard requirements. Because the criterion for documented information has not been met, there will be a non-conformity in the process as a result of the audit’s findings. The absence of documentation indicates that a corrective action plan by the process owner will be required, and this will be included in the audit’s final report.
