23+Sample Nonprofit Bylaws
-

Bylaws Not for Profit Corporation
download now -

Non Profit Corporate Bylaws
download now -

Sample Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Church Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Nonprofit Association Bylaws
download now -

Corporation Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Charitable Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Form Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Business Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -
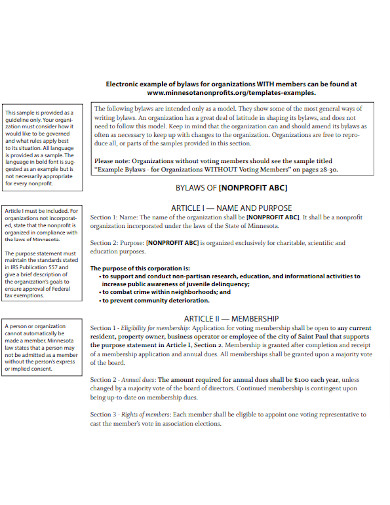
Policy Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Foundation Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Corp Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Constitution Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Editable Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Company Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Agreement Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Simple Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Basic Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Printable Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Membership Organization Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Board Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Free Nonprofit Bylaws
download now -

Nonprofit Bylaws in PDF
download now -

Private Foundation Nonprofit Bylaws
download now
FREE Non Profit Bylaws s to Download
23+Sample Nonprofit Bylaws
What are Nonprofit Bylaws?
1. Purpose and Essence of Nonprofit Bylaws
2. Distinction from Articles of Incorporation
3. Key Elements in Nonprofit Bylaws
4. Crafting the Bylaws
5. Fluidity and Flexibility
6. Legal Implications
FAQ’S
Can our nonprofit operate without bylaws?
Do bylaws have to be complicated or lengthy?
What happens if we don’t follow our bylaws?
What are Nonprofit Bylaws?
Nonprofit bylaws serve as the constitution for the organization, laying the foundation for its governance, operations, and decision-making processes. They are critical, legally-required documents that provide guidelines for nonprofits, ensuring they function within both their stated mission and the confines of the law. Here’s a detailed look at nonprofit bylaws and their significance.
1. Purpose and Essence of Nonprofit Bylaws
Bylaws act as an internal training manual. They define:
The organization’s purpose and mission.
The structure and function of the board of directors.
The rules and procedures for decision-making and conflict resolution.
2. Distinction from Articles of Incorporation
While bylaws are internal documents, the articles of incorporation are public and filed with the state to legally establish the organization. The articles often contain basic information about the nonprofit, while bylaws delve into the details of its operations.
3. Key Elements in Nonprofit Bylaws
A comprehensive set of bylaws typically includes:
Organization’s Name and Purpose
Clearly states the official name and the core mission the nonprofit aims to fulfill.
Board Structure
Defines the size, duties, roles, and powers of the board of directors.
Membership
If applicable, details about membership types, rights, dues, and processes for admission and termination.
Meetings
Specifies when, where, and how meetings (annual, board meeting, and special) are held, and what constitutes a quorum.
Officers and Committees
Describes roles, election procedures, tenure, and responsibilities.
Conflict of Interest Policy
Aims to protect the organization’s interest when contemplating entering into a transaction that might benefit the private interest of a board member.
Amendment Procedures
Explains how the bylaws can be changed or revised in the future.
Dissolution Clause
Outlines how assets will be distributed if the nonprofit closes its operations.
4. Crafting the Bylaws
Developing bylaws requires careful thought and consultation. It’s often a collaborative process involving board members, stakeholders, and legal counsel to ensure legal compliance and alignment with best practices.
5. Fluidity and Flexibility
Over time, the needs and operations of a nonprofit may change. It’s crucial that bylaws are not static but reviewed periodically. The process for amending bylaws should be streamlined yet thorough, ensuring the organization remains relevant and effective.
6. Legal Implications
While bylaws are an internal document, they carry significant legal weight. They can be used in court to determine whether the nonprofit is acting consistently with its stated rules and procedures. Therefore, adhering to the bylaws is not just a best practice but a legal necessity.
FAQ’S
Can our nonprofit operate without bylaws?
While it might be possible for a very short period after formation, operating without bylaws is risky. They are typically a legal requirement, and without them, governance and decision-making processes can become chaotic and legally questionable.
Do bylaws have to be complicated or lengthy?
Not necessarily. Bylaws should be comprehensive enough to guide the organization’s operations but tailored to the nonprofit’s size and complexity. Small nonprofits might have simpler bylaws compared to large, multi-tiered organizations.
What happens if we don’t follow our bylaws?
Failure to adhere to bylaws can have legal ramifications. It may also jeopardize the organization’s tax-exempt status and can lead to mistrust among stakeholders.
Nonprofit bylaws are essential for ensuring an organization operates smoothly, transparently, and within the law. They bring clarity to decision-making processes, protect the organization’s mission and vision, and build confidence among stakeholders and the public. Crafting them with precision and foresight, and regularly updating them, is crucial for the long-term success and sustainability of any nonprofit organization.
