31+ Sample Thought Process
-
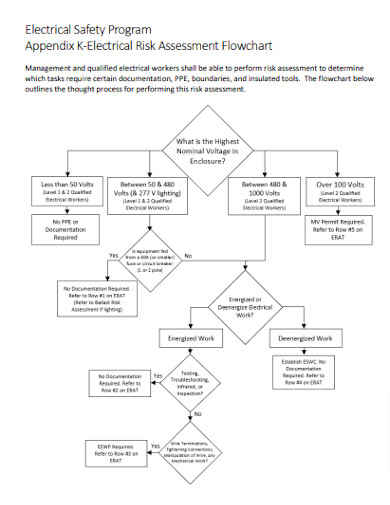
Flowchart Thought Process
download now -
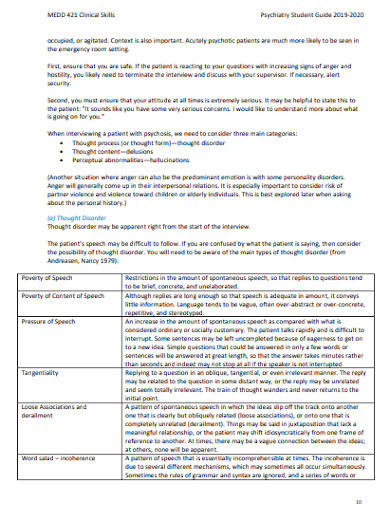
Psychiatry Thought Process
download now -

Mind Map Thought Process
download now -

Human Thought Process
download now -
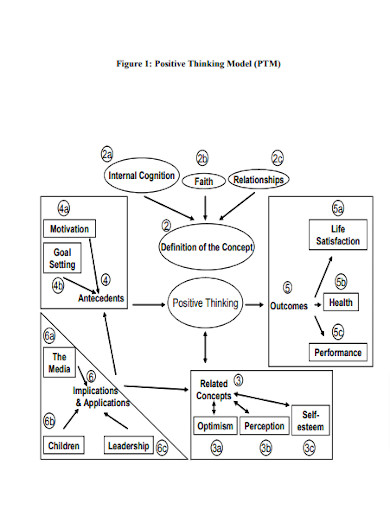
Positive Thought Process
download now -

Cognitive Thought Process
download now -

Tangential Speech Thought Process
download now -

Writing Thought Process
download now -

Re-engineering Thought Process
download now -

Critical Thought Process
download now -

Thought Process Diagram
download now -

PowerPoint Thought Process
download now -

Goal Thought Process
download now -

Object Thought Process
download now -

Student Thought Process
download now -
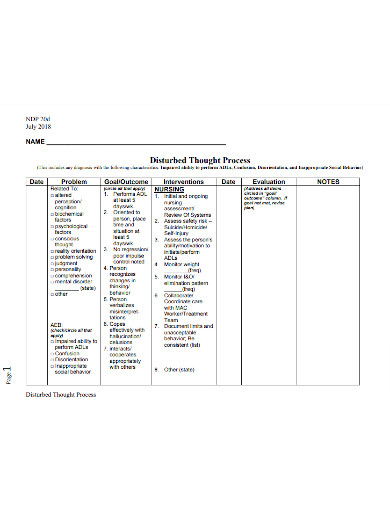
Disturbed Thought Process
download now -

Psychological Thought Process
download now -

Nursing Thought Process
download now -

Object-Oriented Thought Process
download now -

Assessment Thought Process
download now -

Nursing Diagnosis Disturbed Thought Processes
download now -

Thought Process Layout
download now -

Individual Thought Process
download now -
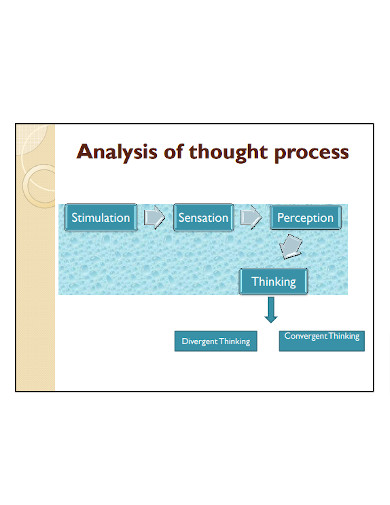
Thought Process Analysis
download now -

Sample Thought Process
download now -

Perspective Thought Process
download now -

Leadership Thought Process
download now -

Thought Process Format
download now -

Thought Process Review
download now -
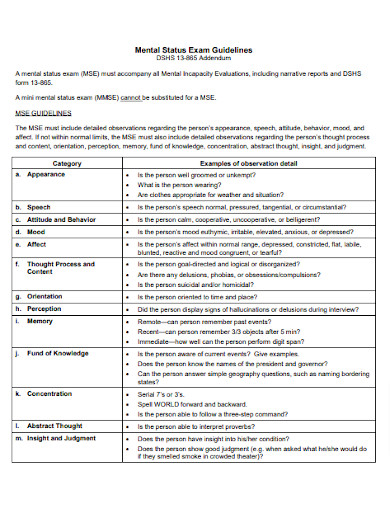
Basic Thought Process
download now -

Editable Thought Process
download now -

Management Thought Process
download now
FREE Thought Process s to Download
31+ Sample Thought Process
What is Thought Process?
Types of Thought Processes
How to Construct a Thought Process
FAQs
How can visual diagrams and illustrations aid in improving mental clarity and productivity?
What is the importance of mental status and mental health assessment in optimizing cognitive abilities?
What are some practical exercises or activities that can be used to unlock the power of your thought process?
What are the key factors that influence the brain’s ability to facilitate creative thinking and decision-making?
What is Thought Process?
The thought process refers to the intricate sequence of cognitive operations that occur within the brain, shaping our perceptions, interpretations, and reasoning. It encompasses the systematic progression of thoughts and the manner in which information is processed, analyzed, and synthesized. A dynamic interplay of conscious and unconscious mental activities, the thought process involves the integration of sensory inputs, memories, emotions, and logical reasoning. It is influenced by various factors such as personal experiences, cultural background, and individual perspectives. The thought process encompasses creative thinking, decision-making, problem-solving, and the formulation of beliefs and attitudes. By using visual diagrams, illustrations, and mind maps such as fishbone diagrams and Venn diagram templates, we can enhance our thought processes, facilitating mental clarity, creativity, and effective communication. Understanding and optimizing our thought processes empowers us to navigate complexities, solve challenges, and unlock the full potential of our cognitive abilities.
The thought process in PDF holds significant importance for individuals, students, and professionals alike. According to recent studies, 90% of the information transmitted to the brain is visual, making visual aids in PDFs crucial for comprehension and retention. For individuals, visual diagrams and illustrations in PDFs enhance mental clarity by organizing complex ideas into digestible formats, aiding in decision-making and problem-solving. For students, research shows that visual learning improves retention by 400% compared to text-only learning, making PDFs with visual elements indispensable for academic success. Professionals benefit from PDFs with visual aids as they enhance communication and collaboration, increasing productivity by 36%. The thought process in PDFs empowers individuals, students, and professionals by maximizing understanding, knowledge retention, and overall efficiency in their respective domains.
Types of Thought Processes
The thought process is the cognitive journey our minds take to analyze, reason, and make decisions. It involves various mental activities such as perception, memory, problem-solving, and creative thinking. Explore different types of thought processes as understanding and improving our thought processes can enhance our ability to think critically and make informed choices.
How to Construct a Thought Process
Constructing a thought process involves a systematic approach to organizing and developing ideas. Follow these four steps to effectively construct a thought process:
Step 1: Define the Objective
Clearly identify the purpose and objective of your thought process. Whether it’s making a decision, solving a problem, or generating creative ideas, a well-defined objective sets the foundation. Consider using visual tools like mind maps or diagrams to visually represent the objective and associated components.
Step 2: Gather Information
Gather relevant information and data related to the objective. Conduct research, seek diverse perspectives, and collect pertinent facts and insights. Visualize the gathered information using diagrams or illustrations to facilitate comprehension and recall. This visual representation aids in identifying patterns, connections, and potential solutions.
Step 3: Analyze and Evaluate
Analyze the gathered information critically. Break down complex ideas into manageable parts and assess their relevance to the objective. Apply analytical thinking techniques to identify strengths, weaknesses, and potential alternatives. Use decision-making frameworks, such as pros and cons lists or decision trees, to evaluate options and their potential outcomes.
Step 4: Synthesize and Iterate
Synthesize the analyzed information and generate new ideas or solutions. Employ divergent thinking techniques to explore multiple possibilities. Refine and iterate the thought process, incorporating feedback and adjustments as needed. Visualize the synthesized ideas and solutions using diagrams or mind maps to identify relationships and enhance understanding.
FAQs
Visual diagrams and illustrations play a significant role in improving mental clarity and productivity. They provide a tangible representation of complex ideas, making information more accessible and understandable. By organizing thoughts into visual formats, such as mind maps or flowcharts like project management workflow charts and process maps, the brain can process and retain information more efficiently. Visuals also enhance memory recall, allowing for quicker retrieval of information when needed. Additionally, visual stimuli engage multiple senses, promoting active learning and deeper understanding. The use of diagrams and illustrations encourages creative thinking, enabling connections between concepts and fostering innovative problem-solving.
Mental status and mental health assessment play a crucial role in optimizing cognitive abilities. Understanding one’s mental status using a mental health progress note and a mental wellness planner provides insights into cognitive functioning, emotional well-being, and overall mental health. By assessing factors such as attention, memory, problem-solving, and mood, individuals can identify areas of strength and areas that may require improvement. Detecting and addressing mental health issues, such as anxiety or depression, is vital as these conditions can significantly impact cognitive abilities. Effective assessment allows for early intervention, personalized treatment plans, and access to appropriate support resources.
There are several practical exercises and activities that can unlock the power of your thought process. One effective exercise is brainstorming, where you generate ideas without judgment or limitation. Mind mapping is another valuable tool, allowing you to visually organize and connect thoughts and concepts. Engaging in creative activities like drawing, writing, or playing musical instruments stimulates the mind and promotes divergent thinking. Solving puzzles and engaging in problem-solving activities sharpen analytical skills. Journaling helps clarify thoughts and emotions, fostering self-reflection and insight. Engaging in physical exercise boosts cognitive function by increasing blood flow to the brain. Finally, mindfulness and meditation practices cultivate focus, attention, and mental clarity.
Several key factors influence the brain’s ability to facilitate creative thinking and decision-making. Firstly, a conducive environment that encourages exploration, risk-taking, and open-mindedness stimulates creativity. Secondly, diverse and rich experiences, such as exposure to different cultures, disciplines, and perspectives, broaden the neural networks and foster innovative thinking. Thirdly, maintaining optimal cognitive health through regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate sleep supports cognitive processes necessary for creative thinking and decision-making. Additionally, managing stress levels is crucial as chronic stress hinders creative problem-solving and impairs decision-making abilities. Finally, cultivating a growth mindset, embracing failure as a learning opportunity, and nurturing curiosity fuel the brain’s capacity for creative thinking and effective decision-making.
How can visual diagrams and illustrations aid in improving mental clarity and productivity?
What is the importance of mental status and mental health assessment in optimizing cognitive abilities?
What are some practical exercises or activities that can be used to unlock the power of your thought process?
What are the key factors that influence the brain’s ability to facilitate creative thinking and decision-making?
Understanding and harnessing these thought processes, using brain-friendly visual tools like diagrams and illustrations, can lead to enhanced creative thinking, improved decision-making, and optimized mental health assessment. They promote effective problem-solving, innovative ideation, and holistic understanding of complex concepts, supporting individuals, students, and professionals in various domains. By following the aforementioned steps and leveraging visual aids, you can construct a comprehensive and effective thought process. This approach promotes clarity, creativity, and efficient decision-making, empowering individuals in various contexts, from problem-solving to design and mental health assessment. So, download and use our sample document templates for creative thinking, decision-making, and mental health assessment such as concept notes and self-assessment plans.
