Sampling Frame, PDF
-

Sampling Frames Development
download now -

Sampling Frames Coverage
download now -

Analysis of Sampling Frames
download now -

Basic Sampling Frame
download now -

Nonresponse Errors of Sampling Frames
download now -

Sampling Frames Constructions
download now -

Sampling Frames Research
download now -

Sampling Frames PDF
download now -

Creating the Sampling Frame
download now -

Address-Based Sampling Frame Overview
download now -

Sampling Frame Type and Structure
download now -

Effects of Sampling Frames Designs
download now -
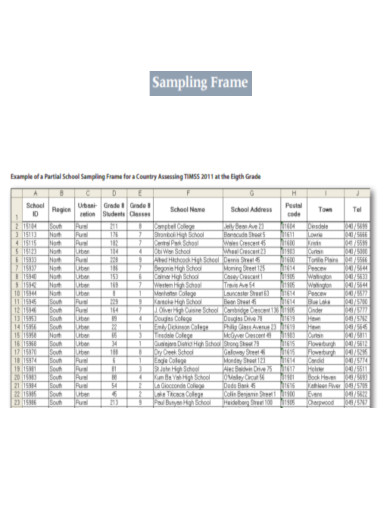
Standard Sampling Frame
download now -

Sampling Frame for Chemical Use
download now -

Conventional Sampling Frames
download now -

Case Review Sampling Frames
download now -

Purposive Sampling Frames
download now -

Sampling Frame Technique
download now -

Utilizing an Alternative Sampling Frame
download now -

Sampling Frame Example
download now -

Developing Sampling Frame
download now -

Editable Sampling Frame
download now -

Sampling Frame Monthly Trade Survey
download now -

Printable Sampling Frame
download now -

Voter Lists as Sampling Frames for Telephone
download now -

General Sampling Frame
download now -

Sampling Frame Random Sampling
download now -

Sampling Frame Data Collection
download now -

Building Master Sampling Frame
download now -

Facebook as a Sampling Frame
download now -

Facebook as a Sampling Frame
download now -
Temporal Sampling Frames Selection
download now -

Constructing the Sampling Frame
download now -

Sampling Frames Shape Induction
download now -

Pre Existing Sampling Frame
download now -

Two-Dimensional Sampling Frame
download now -

Sampling Frame Sample
download now -
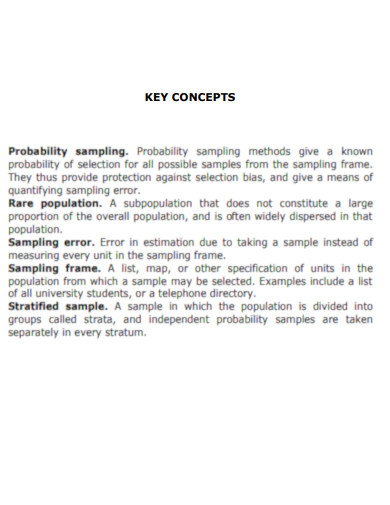
Sampling Frames Key Concept
download now -

Generate a Sampling Frames
download now -

Options for a Sampling Frame
download now -

Quality of Sampling Frames
download now -

Sampling Frame Assessment
download now -

Health Survey Sampling Frames
download now -

Use of Sampling Frames
download now -

Sampling Frames Issue
download now -

Sampling Frames for Improving Paddy Rice Statistics
download now -

Sampling Frames for Surveying Recreational Fisheries
download now -

Sampling Frames Project
download now -

Microbiological Sampling Frames Update Form
download now -

Suitable Sampling Frames for Household Surveys
download now -

Sampling Frames Investigation
download now -

Area-Based Sampling Frames
download now -

Sampling Frames for Surveying Emigrant
download now
FREE Sampling Frame s to Download
Sampling Frame, PDF
What Is a Sampling Frame?
Types of Sampling Frames
Structure and Properties of a Sampling Frame
How to Construct a Sampling Frame
FAQs
Why is a good sampling frame so essential in research?
What is the difference between the sampling frame and a sampling unit?
What is the difference between sampling frame, sample design, and sample survey?
What are the different types of sampling frames?
How to distinguish between a study population, a target population, and an external population?
What are the different types of sampling methods?
What Is a Sampling Frame?
A sampling frame is a list or material used to acquire observational access to the target population in a specific survey research or market research project. It is an integral sampling tool to identify and select a sample that follows a given probability sampling design and build contact with selected elements from the frame. In some cases, the sampling frame contains sampling units that are accumulated due to unknown individual elements. Typically, it is a physical listing of the population elements. However, it is also a procedure creating a result equivalent to a physical listing if such a listing is not available.
Moreover, a sampling frame provides details for locating and determining units. It brings out quantitative information for the estimation of population parameters according to the sample observations as the sampling frame includes any auxiliary information including measures of size and demographic details used for special sampling techniques like stratified sampling or special estimation techniques such as ratio or regression estimation.
Types of Sampling Frames
One of the extensively used sampling frames in statistics and survey research when it comes to sampling the human population is the telephone directory. But using this frame may lead to sampling error due to the exclusion of nonsubscribers, voluntarily unlisted subscribers, and involuntarily unlisted subscribers.
Structure and Properties of a Sampling Frame
Due to the lack of a credible sampling frame, there are very meaningful research investigations that are not undertaken at all. That’s why many survey planners use a good sampling frame because it is a crucial tool used for accuracy, being up-to-date, and completeness that can help them carry out their study efficiently and with definable reliability.
1. Identifiers
These components include primary identifiers and secondary identifiers. The primary identifier identifies the frame unit uniquely. On the other hand, the secondary identifiers guide in locating the sampling units. The structure of the master sampling frame (MSF) consists of primary identifiers, secondary identifiers, sampling particulars, and primary identifiers of the SSUs and USUs such as the identification particulars of the holder, type of holder, ID numbers of constituent plots, and many others.
2. Unit Characteristics
Stratification variables and measures of sample size are the basic unit characteristics. Stratification variables are used for the grouping of sampling units before the start of sample selection. While the measures of sample size are used for stratification, selection estimation, and many other sampling methods or techniques. In MSF, unit characteristics are diverse characteristics of the holdings that could be utilized for sample selection and estimation which include the operated area classified by agricultural and non-agricultural use, the number of plots and parcels in the holding, and agricultural activities of the holding, etc.
3. Operational Data
This aspect of the sampling frame consists of a sample selection indicator and a change indicator. A sample selection indicator has the purpose of showing which unit has been selected. A change indicator is a tool that keeps track of the nature and sources of changes.
4. Selection of Sampling Units
Researchers use a sampling frame when they select sampling units in various sampling designs and sampling methods. Usually, they consider stratification, size variable for probability-proportional-to-size (PPS) sampling, domain delineation, and variables for arranging the population for systematic sampling.
5. Estimation of Population Parameter
A sampling frame is carried out to estimate the parameter of the target population for the survey research study. Researchers determine the population size (N), the total size variable (Z), and the totals of variables for ratio estimation.
How to Construct a Sampling Frame
It is not always possible to come up with a perfect sampling frame in practice because of minor faults that are often tolerated and a good sampling frame is hard to get if you are within budget constraints. Avoid simple frames if they only provide incomplete access to the target population. Thus, it is fundamental to set aside sufficient resources so that you can construct a professional quality sampling frame for the target population in your survey planning work.
Step 1: Choose Sampling Frame Units
Consider the cost when you construct and maintain your sampling frame units. Check the type of information for sampling frame units available for your survey research. Think carefully about the stability of sampling frame units over time and the time necessary to construct the frame.
Step 2: Develop and Validate Sampling Frame
Include maps for the area-based frames while constructing the database for your sampling frame. Then, validate the sampling frame based on the achieved coverage and quality of information.
Step 3: Maintain the Sampling Frame
You need to clear up the duplicates and deaths such as closed business establishments, and burned down or demolished housing units. Add births that represent new building establishments and new housing units in enumeration areas. After that, revise the auxiliary information.
Step 4: Update Master Samples
Lastly, create updates on master samples when you prepare new lists of households using clustering samples to reflect any population changes so that it continues to be representative. Make sure that you update the whole sampling frame periodically to account for postcensal high-growth areas in your district, city, or region.
FAQs
A good sampling frame is very essential in research because it provides valuable implications on the cost and the quality of any survey in various types of populations. It must be complete so that the sample for your research work reflects your population accurately and precisely.
The sampling frame is the list of all the sampling units with the right identification. It may contain either a list of sampling units or a map of the area. On the contrary, a sampling unit consists of individuals that facilitate the process of sample selection. It can also be the study unit in a specific research study. Sampling units are generally a higher level or a group of units.
The sampling frame is a full list of all the units in a population. A sample design is an entire procedure involved in the research. While sample survey is a term used for a comprehensive study of the sample based on some real-world data.
The different types of sampling frames are list frames and area frames.
A study population is where the sample is selected for the study. A target population is an aim or major goal of the study in a specific area. While an external population could be the population of the whole district in which the city is located or even the city or the country’s population.
The different types of sampling methods are cluster sampling, simple random sampling, convenience sampling, purposive sampling, systematic sampling, and many others.
Why is a good sampling frame so essential in research?
What is the difference between the sampling frame and a sampling unit?
What is the difference between sampling frame, sample design, and sample survey?
What are the different types of sampling frames?
How to distinguish between a study population, a target population, and an external population?
What are the different types of sampling methods?
For successful marketing research and survey research purposes, researchers need to use an effective sampling frame to identify each population element once and not include unnecessary elements from the target population. They use direct sampling when selecting a sample from a frame that directly identifies each element of the defined population. Other researchers use indirect sampling as they choose a sampling frame indirectly related to their target population due to the unavailability of a sampling frame that corresponds directly to the preferred target population, for example, surveying business firms when they only have an incomplete sampling frame of those establishments. Feel free to use our templates for survey analysis reports, building surveys, market research scope of work, and market research proposals for your quantitative research, qualitative research, survey research, and market research projects.
