Soil Sample Testing
-

Testing Roster Template
download now -

Automation Testing Test Case Template
download now -
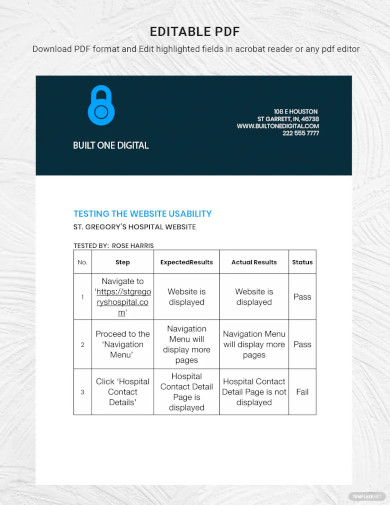
Manual Testing Test Case Template
download now -

Security Testing White Paper Template
download now -

SQL Server Integration Services Testing Test Case Template
download now -

Benefits of Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing for Nutrient Availability
download now -

Soil Testing Project
download now -

Soil Health Testing
download now -

Basic Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing Technicians
download now -
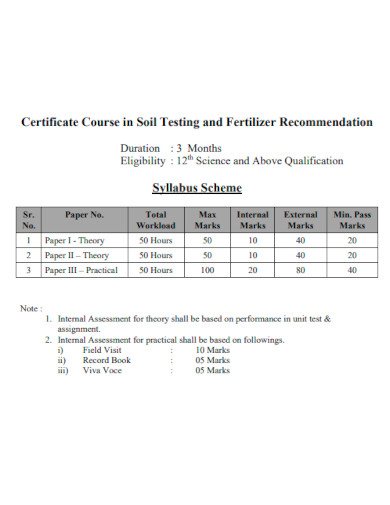
Certificate Course in Soil Testing and Fertilizer
download now -

Soil Testing Activities
download now -

Soil Testing Method
download now -

Soil Testing Program
download now -

Importance of Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Biology Testing
download now -
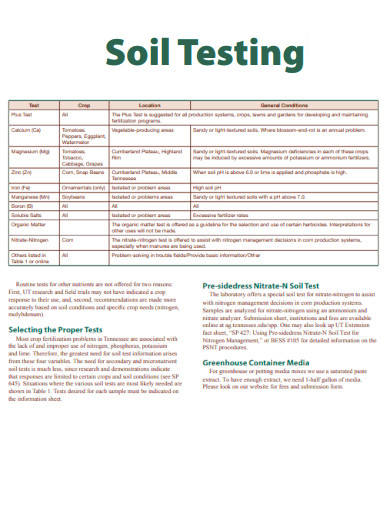
Editable Soil Testing
download now -

Laboratory Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing Lecture
download now -

Enabled Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing Collection
download now -
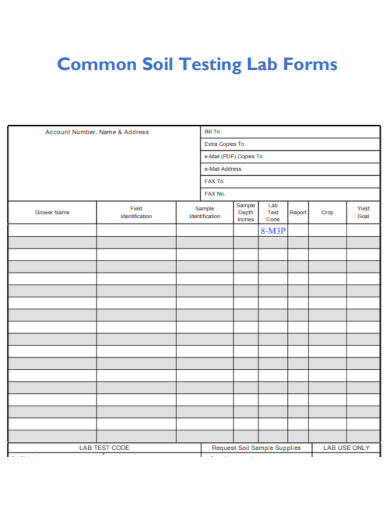
Common Soil Testing Lab Form
download now -

Smart Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing Procedure
download now -

Accurate Soil Testing Laboratory
download now -

General Soil Testing
download now -
Soil Testing Sampling and Analysis
download now -

Soil Testing in Urban Gardens
download now -

Choosing a Soil Testing Laboratory
download now -

Routine Soil Testing Analysis Form
download now -
Soil Testing in PDF
download now -

Soil Testing and Crop Technician
download now -

Soil Testing Kit
download now -

Soil Testing for Field Crops
download now -

Request Proposal for Soil Testing
download now -

Small Scale Solutions Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing Scenario
download now -

Soil Nutrient Testing
download now -

Testing Your Soil
download now -

Testing Soil Acidity
download now -

Sampling Soil for Testing
download now -

Soil Testing Lesson Plan
download now -

Soil Testing Brochure
download now -
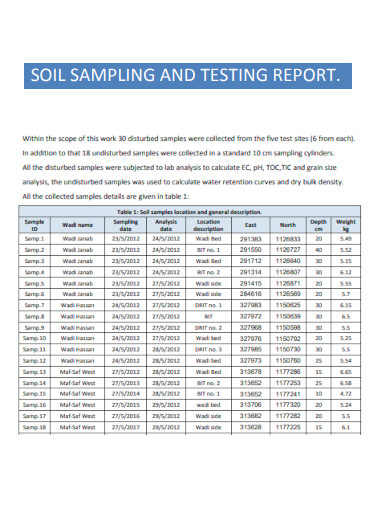
Soil Sampling and Testing Report
download now -

Soil Testing System
download now -

Soil Testing Diagnostic Tool
download now -

Soil Testing and Interpreting Results
download now -

Site Assessment and Soil Testing
download now -

Homeowner Soil Testing
download now -

Easy Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing More Important Than Fertilizer Use
download now -

Soil Sampling Testing for Home Landscape
download now -

Testing Soil Health
download now -

Soil Testing Programme
download now -

Principles of Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing Information
download now -

Soil Testing for Lawns
download now -

Formal Soil Testing
download now -

Identification of Soil Testing Laboratories
download now -

Soil Testing and Field Setting
download now -

Extension Soil Testing Laboratory
download now -

Testing Your Soil for Contaminants
download now -
Soil Testing Application Form
download now -

Printable Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing and Plant Analysis
download now -

Overview of Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing in India
download now -

Soil Testing Handbook
download now -

Soil Sampling Testing
download now -

Component of Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing Leads to Decision Making
download now -

Soil Testing Resources
download now -

Soil Testing and Assessing Soil Texture
download now -

Adoption of Soil Testing
download now -

Certificate Course in Soil Testing
download now -

Garden Soil Testing
download now -

Considerations Soil Testing in Turfgrass
download now -

Interpretation of Soil Testing Result
download now -

Testing Soils for Organic Matter
download now -

Soil Testing for Fruit Corps
download now -

Soil Testing Example
download now -

Soil Testing Record Sheet
download now -
Soil Water and Plant Testing
download now -

Soil Testing for Vegetable Crops
download now -
Soil Testing Service
download now -

Improving Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing Fact Sheet
download now -

Soil Plant and Feed Testing
download now -

Annual Soil Testing
download now -

Multiple Advantages of Soil Testing
download now -

What is Soil Testing
download now -
Topsoil Testing Report
download now -

Home Soil Testing
download now -

Variability In Soil Testing
download now -
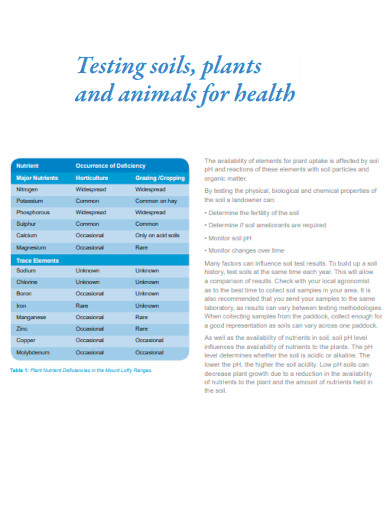
Testing Soils Plants and Animals for Health
download now -

Soil Testing and Handling
download now -
Soil Testing Excellent Investment for Garden
download now -

Advanced Soil Testing
download now -

Procedures for Soil Testing
download now -

Development of Low Cost Soil Testing
download now -

Soil pH Testing
download now -

Advanced Level Training in Soil Testing
download now -

Simple Soil Testing
download now -

History of Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing for Manure Management
download now -

Empower Innovations in Routine Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing For Survey
download now -

Testing Soil Quality Indicator
download now -

Virtual Training on Soil Testing
download now -

Soil Testing Checklist
download now
What is Soil Sample Testing?
Soil sample testing is a process of analyzing the properties of soil to determine its nutrient content, pH level, and other factors affecting plant growth. Garden soil sample testing and lawn soil sample testing are two common types of soil testing that homeowners can conduct themselves. This procedure is essential because it enables you to examine the soil’s nutrient content, optimize the pH level for agricultural crops, spot potential problems like compaction of the soil, excessive salinity, or the presence of contaminants that could impede plant growth, and get a specialized recommendation for your specific plants or crops. It is also included in an agriculture business plan, a lawn care contract, and a landscaping request for proposal.
Because various plants require varying depths of soil nutrients, sampling depth is an important factor in soil sample testing. Collecting soil samples can be accomplished with a test kit or soil tester, and the type of information required will determine the soil testing technique being used. Once the samples are analyzed, a research analysis report is generated that indicates the soil nutrient content and its suitability for plant growth. Soil sample testing is an essential step towards addressing nutrient deficiencies and other soil-related issues and ensuring the health of plants and the success of a garden or lawn. Plus, you can save money in the long run as you avoid unnecessary or excessive fertilization.
Types of Soil Testing Methods
Various types of soil testing methods are used to assess soil characteristics and provide valuable insights for optimal plant growth. These methods include chemical analysis using chemical equations to balance templates, pH testing, nutrient extraction, texture analysis, and more. Each technique offers unique information crucial for effective soil management.
How to Test Your Soil
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), around 33% of global soils are estimated to be degraded due to erosion, nutrient depletion, and contamination. Soil sample testing helps identify and address these issues, promoting sustainable land management practices. Follow these five basic steps so that you can effectively test your soil, gather important information about its nutrient content, pH level, and overall health, and make informed decisions to optimize your garden or lawn’s growth and productivity.
Step 1: Determine the Sampling Depth
Decide the appropriate depth for collecting soil samples based on whether it is for garden soil sample testing or lawn soil sample testing. Typically, a depth of 6-8 inches is recommended for gardens, while 2-4 inches is suitable for lawns.
Step 2: Obtain a Test Kit or Soil Tester
Get a suitable soil test kit or soil tester from a reputable source. These kits often come with instructions and necessary components for collecting and analyzing soil samples.
Step 3: Collect Soil Samples
Follow the instructions provided with the test kit or soil tester to collect soil samples. Use a clean sampling tool to collect multiple soil samples from the designated area, ensuring representative sampling.
Step 4: Perform Soil Testing
Utilize the soil test kit or soil tester to conduct the recommended soil testing methods. This may include measuring pH, nutrient levels, organic matter content, or other relevant parameters. Follow the soil test kit’s instructions carefully for accurate results.
Step 5: Analyze the Results
Once the testing is complete, refer to the analysis report or instructions provided with the test kit to interpret the results. Identify any nutrient deficiencies, pH imbalances, or other soil issues highlighted in the report.
FAQs
Soil sample testing is a process of analyzing the nutrient content and overall health of soil samples. It aids landscapers and gardeners in determining what nutrients and soil enhancements their plants may need to develop effectively. Testing soil samples is vital for keeping a healthy garden or lawn since it offers valuable information about the soil’s quality, pH balance, and nutrient deficiencies.
While professional soil testing labs can provide more detailed analysis, it is possible to perform basic soil sample testing at home using a soil test kit or soil tester. These kits are generally accessible and, when used properly, can yield credible findings. But, it would be advisable to consult with a professional soil testing firm if you have specific soil concerns or need a more in-depth examination.
The recommended sampling depth for soil samples depends on whether you are testing garden soil or lawn soil. A depth of 6 to 8 inches is suggested for gardens, while 2-4 inches is suitable for lawns. To account for any variability, make sure to collect several samples from different locations within the region.
The information provided in a soil sample testing analysis report will depend on the type of testing performed. However, analysis reports typically include information on soil pH, nutrient levels (such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium), and organic matter content. The report may also provide recommendations for amendments or treatments to improve soil health and promote plant growth.
Soil sample testing can range in cost depending on the level of analysis required. While more in-depth testing can be more expensive, some professional testing laboratories offer basic soil testing services for free or at a reasonable cost. Simple soil test kits are also offered for purchase and are often affordable.
What is soil sample testing, and why is it important for gardens and lawns?
Can I perform soil sample testing myself, or do I need professional help?
How deep should I collect soil samples for testing?
What information can I expect to receive in a soil sample testing analysis report?
Is soil sample testing expensive?
A study published in the Journal of Environmental Quality found that accurate soil testing and nutrient management can improve crop productivity by 10-20% while reducing fertilizer costs and minimizing environmental impacts. Thus, understanding soil sample testing, the types of soil testing methods available, and the basic steps to test your soil are all critical for those in the agriculture industry, including farmers, agriculturists, and gardeners. Soil sample testing is vital for maintaining healthy crops, maximizing yields, and protecting the environment. By using appropriate testing methods and following recommended steps, individuals can obtain accurate soil nutrient information, which can inform optimal nutrient management practices and lead to sustainable land management practices. Sample.net provides an eclectic collection of test samples and other documents that you can easily use including sampling methods PDF, testing checklists, and test PDF templates.
