Construction Cost Estimate Samples
-
House Construction Cost Estimate
download now -
Road Construction Cost Estimate
download now -
Construction Labor Cost Estimate
download now -
Dam Construction Cost Estimate
download now -
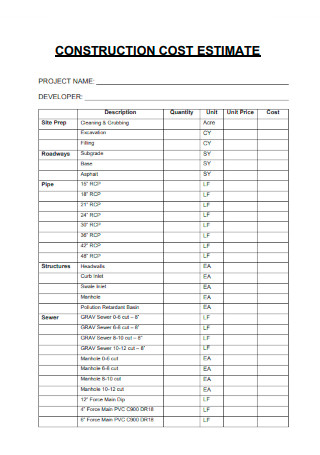
Construction Cost Estimate
download now -

Construction Plan and Cost Estimate
download now -
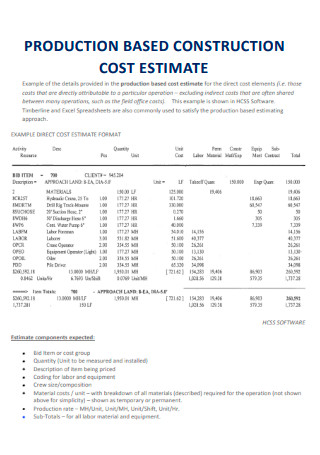
Production Based Construction Cost Estimate
download now -

Estimate of Facility Construction and Operating Costs
download now -
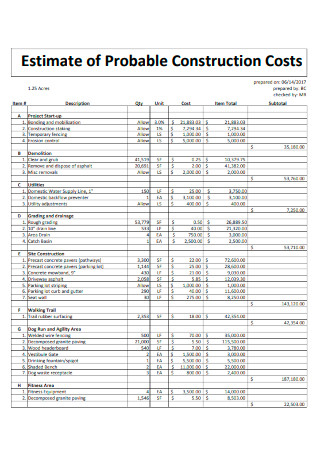
Estimate of Probable Construction Costs
download now -
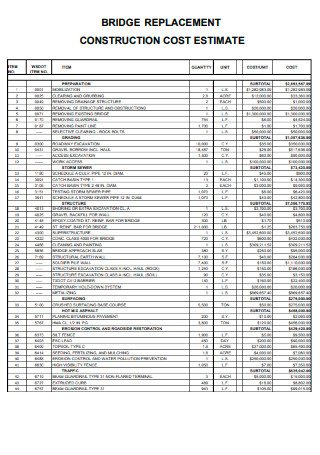
Bridge Replacement Construction Cost Estimate
download now -
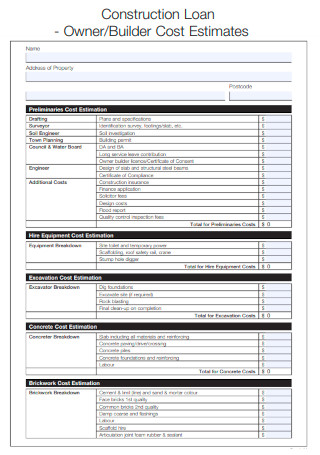
Construction Loan Owner & Builder Cost Estimates
download now -
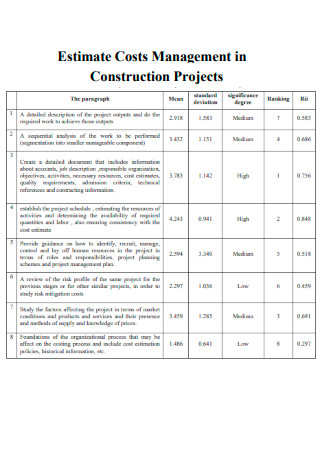
Estimate Costs Management in Construction Projects
download now -
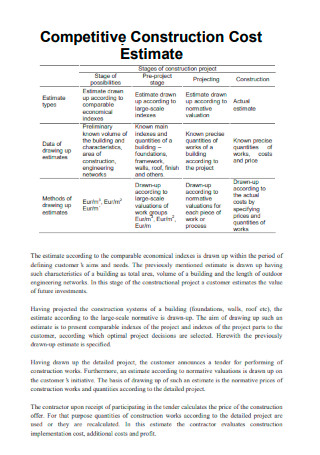
Competitive Construction Cost Estimate
download now -
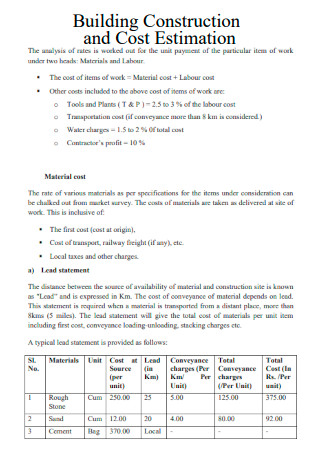
Building Construction and Cost Estimation
download now -
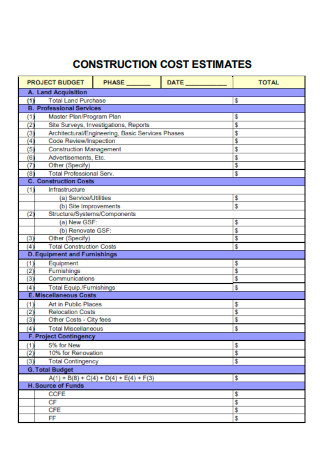
Construction Cost Estimate Project Budget
download now -
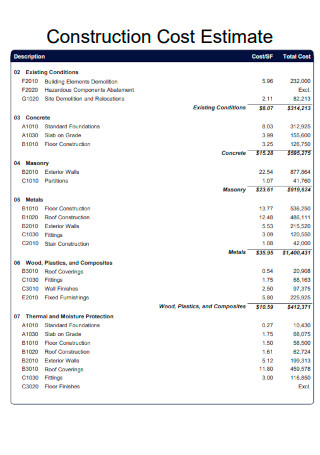
Sample Construction Cost Estimate
download now -
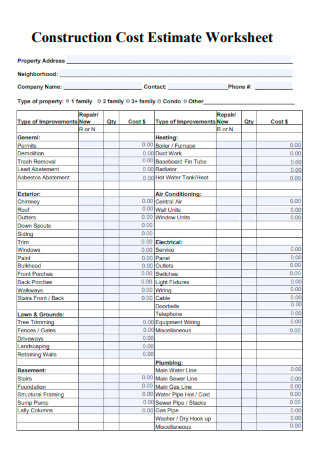
Construction Cost Estimate Worksheet
download now -
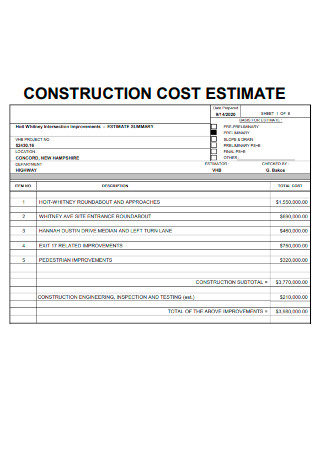
Basic Construction Cost Estimate
download now -

Preparation of the Official Construction Cost Estimate
download now -
Cost Estimate for Network Construction
download now -

Preliminary Cost Estimate Update for Construction and Maintenance
download now -

Report for Construction Cost Estimate
download now -
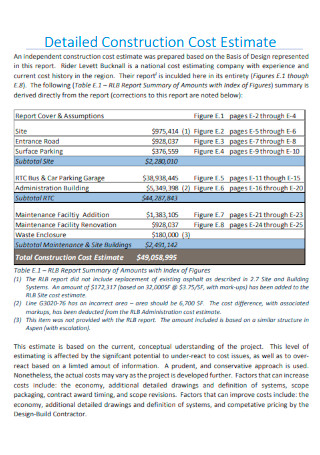
Detailed Construction Cost Estimate
download now -
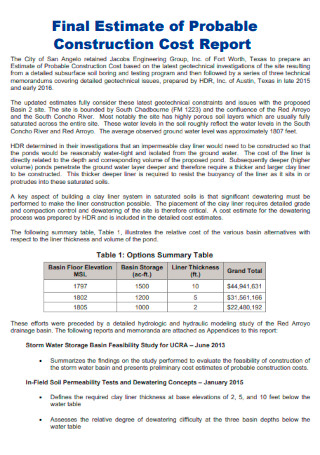
Final Estimate of Probable Construction Cost Report
download now -
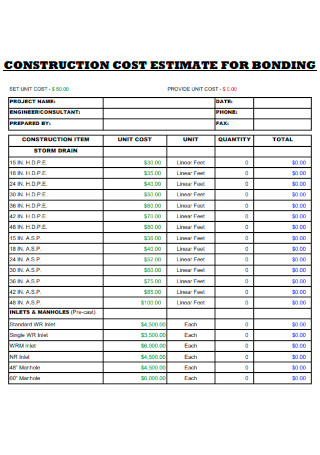
Construction Cost Estimate for Bonding
download now
FREE Construction Cost Estimate s to Download
Construction Cost Estimate Format
Construction Cost Estimate Samples
What is a Construction Cost Estimate?
Purposes of a Construction Cost Estimate
How to Make a Construction Cost Estimate?
FAQs
What Goes Into Your Estimate?
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid?
What Is Improper Estimation of Labor Costs?
How can errors in construction cost estimates be avoided?
How do changes in market conditions affect cost estimates?
When is a construction cost estimate prepared?

Download Construction Cost Estimate Bundle
Construction Cost Estimate Format
1. Project Details
- Project Name: [Insert Project Name]
- Client Name: [Insert Client Name]
- Location: [Insert Project Location]
- Project Number/ID: [Insert Project ID]
- Date of Estimate: [Insert Date]
- Estimated By: [Insert Name/Title]
2. Scope of Work
- Description: [Provide a summary of the work to be completed, key activities, and project objectives.]
- Duration: [Insert project duration in weeks or months.]
- Key Milestones:
- [Milestone 1: Description and expected completion date]
- [Milestone 2: Description and expected completion date]
- [Milestone 3: Description and expected completion date]
3. Cost Breakdown
A. Direct Costs
| Category | Item Description | Unit | Quantity | Unit Rate (Currency) | Total Cost (Currency) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Materials | [List materials] | [e.g., m2, kg, pcs] | [e.g., 100, 50] | [Unit rate] | [Total cost] |
| 2. Labor | [List labor roles] | [e.g., hours, days] | [Quantity] | [Rate per unit] | [Total cost] |
| 3. Equipment | [List equipment] | [e.g., hours, days] | [Quantity] | [Rate per unit] | [Total cost] |
| 4. Subcontractor | [List subcontractors] | [Type] | [Quantity] | [Rate per unit] | [Total cost] |
| 5. Other Direct Costs | [List additional direct costs] | [Unit] | [Quantity] | [Unit Rate] | [Total Cost] |
| Total Direct Costs | [Sum of Total Costs] |
B. Indirect Costs
| Category | Item Description | Unit | Quantity | Unit Rate (Currency) | Total Cost (Currency) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Overheads | [E.g., Office expenses, insurance] | [Unit] | [Quantity] | [Rate per unit] | [Total cost] |
| 2. Administrative Costs | [E.g., Supervision, legal fees] | [Unit] | [Quantity] | [Rate per unit] | [Total cost] |
| 3. Taxes and Permits | [List required permits and taxes] | [Unit] | [Quantity] | [Rate per unit] | [Total cost] |
| 4. Contingency | [Specify contingency %] | [Apply % to total direct costs] | [Amount] | [Total Cost] | |
| Total Indirect Costs | [Sum of Total Costs] |
4. Total Project Cost
| Category | Amount (Currency) |
|---|---|
| Total Direct Costs | [Insert Amount] |
| Total Indirect Costs | [Insert Amount] |
| Total Project Cost | [Sum of Direct + Indirect] |
5. Payment Terms
- Advance Payment: [e.g., 20% of total cost]
- Payment Schedule: [Provide payment schedule, e.g., 30% upon mobilization, 50% on milestone completion, 20% on project completion.]
- Payment Mode: [Bank transfer, check, etc.]
6. Notes and Assumptions
- [List important notes and assumptions about the estimate, such as currency used, material availability, price escalation considerations, etc.]
7. Terms and Conditions
- Validity: This estimate is valid for [X days] from the date of submission.
- Price Changes: Prices are subject to change due to [mention factors like inflation, labor strikes, supply issues, etc.].
- Exclusions: List any exclusions not included in the cost, such as land purchase, unexpected delays, etc.
- Force Majeure: Include a clause on events beyond the contractor’s control.
8. Authorization
| Prepared By | Approved By |
|---|---|
| [Name] | [Name] |
| [Position] | [Position] |
| [Signature] | [Signature] |
| [Date] | [Date] |
What is a Construction Cost Estimate?
A construction cost estimate is a financial projection of the total expenses involved in a construction project. It provides a breakdown of costs for materials, labor, equipment, overhead, and contingencies. This sample estimate serves as a roadmap for budgeting, bidding, and managing project costs from start to finish. Cost estimates are prepared by cost estimators, contractors, or project managers to ensure the project stays within budget. Accurate estimates are essential for minimizing financial risks and avoiding cost overruns.
Purposes of a Construction Cost Estimate

1. Accurate Budget Planning
A construction cost estimate provides a clear and accurate forecast of the total expenses involved in a project. This allows stakeholders, including project managers, investors, and clients, to establish a realistic budget before the project begins. Budget planning ensures that adequate funds are allocated for each phase of construction, reducing the risk of project delays or funding shortages. It also helps to prevent financial mismanagement and allows for better financial control throughout the project’s lifecycle. You can also see more on Construction Price Proposal.
2. Project Feasibility Analysis
One of the key purposes of a construction cost estimate is to assess the financial viability of a project. Before launching a construction project, stakeholders must evaluate if the available resources and budget are sufficient to cover all associated costs. If the estimated costs exceed available funding, the project scope may need to be adjusted or postponed. Conducting a feasibility analysis early in the project life cycle ensures that only viable projects are pursued, thereby saving time, effort, and money.
3. Facilitates Bidding and Contracting
Cost estimates play a crucial role in the bidding process, where contractors submit competitive bids to win construction contracts. Contractors use cost estimates to calculate the total cost of labor, materials, equipment, and other expenses before submitting a bid. Accurate cost estimates ensure that contractors submit competitive yet profitable bids. On the client’s side, cost estimates enable them to compare multiple bids from contractors, assess their fairness, and select the best offer. You can also see more on Commercial Construction Estimate.
4. Risk Management and Cost Control
A well-prepared construction cost estimate identifies potential risks and uncertainties that may lead to cost overruns. These risks include unexpected price fluctuations, delays, or design changes. By incorporating a contingency fund within the cost estimate, stakeholders can prepare for unforeseen expenses and reduce the impact of cost overruns. Risk management through cost estimates also allows project managers to identify critical areas of concern, enabling them to implement control measures early in the project.
5. Resource Allocation and Scheduling
A construction cost estimate breaks down costs for each resource, such as labor, materials, equipment, and subcontractors. This breakdown helps project managers allocate resources more effectively and determine the exact quantity and timing of required inputs. With a clear understanding of when specific resources are needed, managers can avoid wastage, reduce idle time, and improve overall project efficiency. This process promotes optimal use of resources and prevents delays due to resource shortages. You can also see more on Estimate Proposal.
How to Make a Construction Cost Estimate?

Step 1: Define the Project Scope
The first step in creating a construction cost estimate is to clearly define the project’s scope. This involves outlining the project’s key elements, such as size, location, design, and materials to be used. A well-defined scope provides clarity on the objectives, specifications, and deliverables. It also sets the foundation for estimating labor, materials, and equipment costs. By having a clear understanding of the scope, stakeholders can avoid unexpected changes that could increase project expenses.
Step 2: Conduct a Quantity Takeoff
Once the project scope is defined, the next step is to perform a quantity takeoff. This process requires identifying and calculating the amount of materials needed for the project. Using blueprints, technical drawings, and design plans, estimators count and measure each material, including concrete, steel, wood, and finishes. Accurate quantity takeoff ensures that the right amount of materials is ordered, reducing waste and minimizing costs. It also provides a solid foundation for estimating material costs in the next step. You can
Step 3: Estimate Material, Labor, and Equipment Costs
With the quantity takeoff completed, the next step is to estimate the costs of materials, labor, and equipment. Material costs are calculated based on current market rates for raw materials like concrete, steel, and lumber. Labor costs are determined by assessing the number of workers required, their hourly rates, and the estimated time to complete the project. Equipment costs are also calculated, considering rental fees, transportation, and operational costs for machinery like bulldozers and cranes. These cost components make up the core of the total project cost.
Step 4: Include Overhead, Contingency, and Indirect Costs
In addition to direct costs, it is essential to account for overhead, contingency, and indirect expenses. Overhead costs include administrative expenses, insurance, permits, and office-related costs that support project execution. A contingency fund is added to handle unexpected expenses, like material price increases or design changes, and it typically ranges from 5% to 10% of the total project cost. Indirect costs, such as legal fees, inspection fees, and taxes, must also be included to ensure a comprehensive and accurate cost estimate. You can also see more on Work Estimate.
Step 5: Review, Validate, and Finalize the Estimate
The final step in creating a construction cost estimate is to review, validate, and finalize the calculations. It involves cross-checking all costs, including material prices, labor rates, and equipment fees, to ensure there are no errors or omissions. Cost estimation software or spreadsheets are often used to streamline the process and reduce human errors. Project managers and stakeholders review the estimate to confirm that it aligns with the project’s budget and goals. Once approved, the final cost estimate serves as a financial guide throughout the construction process.
A construction cost estimate plays a crucial role in project success by providing a clear financial framework. It reduces risks, ensures resource allocation, and supports informed decision-making. By understanding costs upfront, contractors, architects, and clients can maintain project timelines, avoid overspending, and achieve construction goals efficiently. You can also see more on Construction Budgets.
FAQs
What Goes Into Your Estimate?
There are many models in the industry that determine what goes into a construction estimate. However, at an abstract level, all estimates can be divided into three. These are labor, materials, and overheads and profits.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid?
Inaccuracy in cost estimation is often a very costly mistake that results in cost overruns and blowouts in the schedule.
What Is Improper Estimation of Labor Costs?
Labor costs are some of the most expensive yet the most difficult to estimate. Using a simple hourly rate in the labor rate can lead to huge variations. Therefore, you need to be as detailed as possible when calculating labor rates, factor in the overtime, and source data from similar projects for better accuracy. You can also see more on Contractor Estimate.
How can errors in construction cost estimates be avoided?
To avoid errors, ensure clear project scope definition, use accurate unit rates for materials and labor, perform quantity takeoffs meticulously, and utilize construction estimation software. Additionally, involving experienced cost estimators and double-checking the final estimate can significantly reduce errors.
How do changes in market conditions affect cost estimates?
Market fluctuations, such as inflation, supply chain issues, and labor shortages, can significantly impact cost estimates. Material prices may increase unexpectedly, leading to higher overall project costs. To counter this, estimators add a contingency fund to absorb unforeseen price hikes. You can also see more on Budget Estimate.
When is a construction cost estimate prepared?
Cost estimates are prepared at various stages of a project, from the initial feasibility phase to the detailed design and pre-construction stages.
