20+ SAMPLE Project Estimate
-
Project Fee Estimate Request
download now -

Project Cost Estimate Worksheet
download now -
Project Estimate Request Form
download now -

Project Estimate Example
download now -
Project Estimate Worksheet
download now -
Project Budget Estimate
download now -
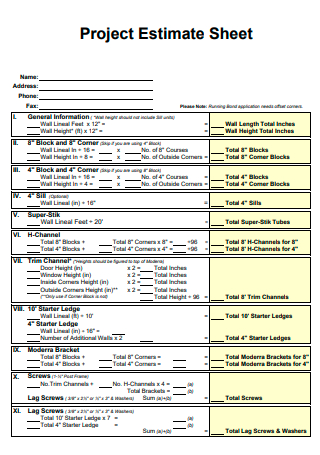
Project Estimate Sheet
download now -
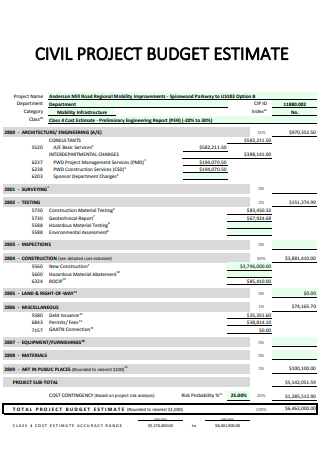
Civil Project Budget Estimate
download now -

Project Cost Estimate Sheet
download now -

Contractors Certification of Project Cost Estimate
download now -
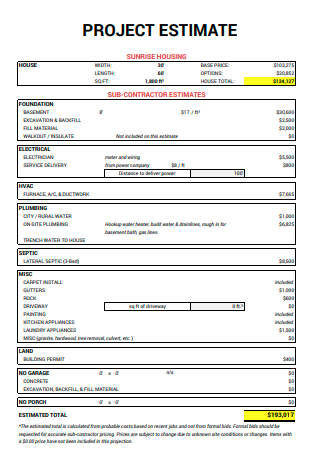
Basic Project Estimate
download now -
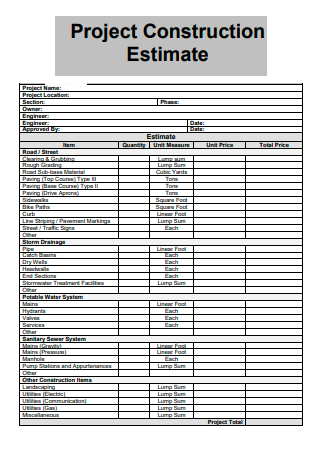
Project Construction Estimate
download now -

Project Cost Estimate
download now -
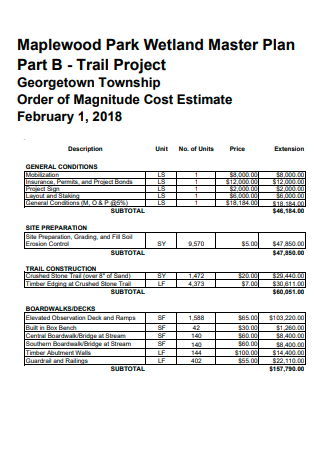
Trail Project Cost Estimate
download now -
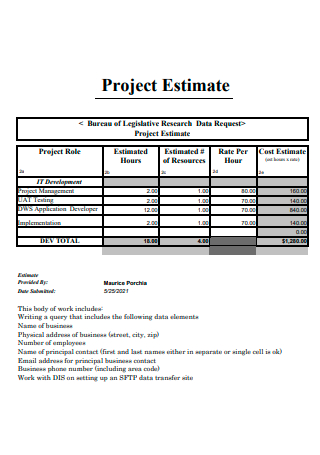
Printable Project Estimate
download now -

Project Estimate Request
download now -

Sample Project Estimate
download now -

Project Management Estimate
download now -

Capital Project Cost Estimate
download now -
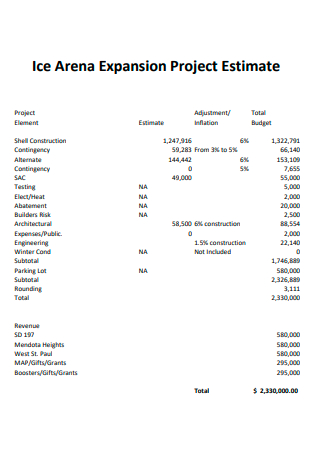
Expansion Project Estimate
download now -

Project Estimate Approval
download now
FREE Project Estimate s to Download
20+ SAMPLE Project Estimate
What Is a Project Estimate?
Components of a Project Estimate
How To Construct a Project Estimate Involving Time and Costs
FAQs
What are the different types of project estimating?
What is the need for project estimates?
How do you make accurate estimations?
What Is a Project Estimate?
Project estimates or project estimations is a process of forecasting the time, costs, and resources that a team or organization requires to deliver a project. It is when a business or a group of people predict the overall cost of a proposed project through an outline of the scope of work. The closer the estimate is to the actual prices and costs of the project, the more likely that the budget and spending will stay on the positive end, enabling a smooth transition of tasks and activities in the project. Although project estimation is not the most exciting part when planning for a project, getting the budget planning right from the beginning can make a difference when it comes to the project being a success. Many projects are prone to scope creep situations, with cases rising from year to year. Team leaders must be diligent in the process of budget planning and price forecasting to ensure that the project cost estimates remain accurate and that the tasks and activities they perform are viably profitable in the end. Since project cost estimates rely on price forecasting from the scope of work, the entire process must provide an outline of the duration of tasks and the individuals responsible for accomplishing these tasks. As such, project estimates do not stop when the project begins. Instead, there must be continuous monitoring and adjustments throughout the project duration.
Project estimates are essential to every organization pushing for new projects and programs, and there are cost estimators that can cover the job of making these estimates. According to the United States Bureau of Labor and Statistics, there are over 199 thousand cost estimators in the United States in 2020, with the median pay ranging at 65 thousand dollars per year in 2021.
Components of a Project Estimate
Project estimations are necessary for different projects in many industries. Estimating is the process of analyzing all available data that a company can use to predict the cost, time, and resources that teams require to complete a project. There are six key areas that project estimates must touch or go over during its construction and implementation. These six factors are interrelated, and the prediction of one can easily influence the others. As such, using similar project techniques for each one improves the accuracy of the project estimate. The section below details these components together with helpful information through their descriptions to help readers understand their significance to the document.
How To Construct a Project Estimate Involving Time and Costs
Estimating the costs of a project requires breaking it down into different tasks to figure out the team members that will be responsible for each activity. Once the project begins its implementation phase, the key goal is to not overspend and stay within the budget. The section below covers the essential steps to develop a project estimate that guarantees a team to complete the project on time and within a budget.
-
1. Identify the Responsibilities and Expertise of the Team Members
For an accurate project estimate, project managers must focus more on the involved parties in the project instead of solely focusing on numbers. Project estimation techniques start with establishing positive working relationships. The more the manager knows about the working habits and processes of an individual, the easier it is to estimate their work. Building a stronger understanding and collaboration with members keeps project tasks in line with the proposed budget. As a project manager, it is vital to show honesty. It’s better to admit what you know and what you don’t know. It gives the project manager to associate and communicate more with their team members to understand the workings of different projects.
-
2. Understand the Project Management Processes of the Company
After knowing the expertise and responsibilities of team members, the next step is to understand how the organization completes or accomplishes its projects. If the company fosters singular methods for its projects, study the process, identify all possible dependencies, and run them with the estimates. It is the mission of the project manager to understand the processes for getting work done and the things that can happen when making adjustments to the project schedule. Do everything to understand the process. Ask individuals who know and have experience with the how, when, and why. Knowing more about them allows a project manager to strategize with the team and its clients to find alternatives to make the project work while saving time and money. Be sure to talk about the project vision with team members as it impacts the effort and scope put into the project.
-
3. Familiarize Yourself with Several Project Estimation Techniques and Trends
The flow of the business world changes more at a quick rate. In project management, a team manager must always be on top of trends, changes, and deliverables in the industry. To improve the skills of a manager when it comes to project estimates, read relevant publications, websites, and blogs. Make sure to attend training and networking events, joint meetups, and conventions that focus on project management and estimations. A project manager must also understand the different approaches to estimate projects that work best. Different estimation techniques include top-down estimating, bottom-up estimating, analogous estimating, parametric model estimation, and three-point estimating.
-
4. Utilize Historical Data To Develop Better Project Estimates
Historical data helps with new projects by analyzing records and previous information to help create better estimates. Start by asking the team to keep track of their time and provide an accurate estimate of the overall level of effort. It determines what it takes to get the job done while being profitable. Seeing how the team spends on a particular task or deliverable provides estimates for similar projects in the future. Review project histories repeatedly to ensure there are no underestimates of project costs and hours. Underestimating produces stress and causes a disservice to clients, causing more harm than good. Utilize project baselines to compare estimates with actual costs. Note where there are discrepancies and provide a measurement of how it affects the level of effort. It helps determine whether there is still room to improve on estimates for project tasks.
-
5. Ask for Detailed Questions About Project Questions To Improve Estimations
Whether the project stems from a request for proposal (RFP), a discussion, a written letter, or an email, the project manager must know all the possible detail of the project before providing a realistic estimate. Three factors can affect overbudgeting, namely, time, cost, and scope. Using a Gantt chart helps estimate the RFP. Ask the appropriate questions that can build an accurate estimate according to the needs of a client. Be persistent and get the answers you need to form a good estimate and use judgment to determine what questions require answers.
-
6. Utilize a Work Breakdown Schedule for Granular Estimates
A work breakdown schedule (WBS) helps a project manager to separate a project into smaller components and helps to be more specific about the work that the team needs to complete. Provide a framework for a detailed cost estimate and a guided schedule for development and control procedures. Using a WBS helps the team to understand if the intended budget supports the project estimate. The team can easily map out the required tasks and deliverables that work with the amount to reach client goals. If a client comes back to the manager and tells them that they are not willing to spend the amount on the estimate, use the WBS to make the necessary adjustments. It allows the organization to create a project estimate that aligns with the budget of the client and work out a set of project requirements.
FAQs
What are the different types of project estimating?
The types and techniques that businesses use in project estimates include top-down estimates, bottom-up estimates, analogous estimations, parametric estimations, what-if analysis, and three-point estimations
What is the need for project estimates?
Constructing a project estimate gives the team, stakeholders, and project clients for them to have a general idea of the time, effort, and resources they need to complete a project.
How do you make accurate estimations?
There are different ways to accurately make estimates when trying to accomplish tasks and activities. To make accurate estimations, you can do the following:
- Time your tasks
- Overestimate the time requirements
- Check the schedule
- Utilize the three-point estimation
- Use time tracking apps
Writing project estimates takes skill and experience. If the person writing the project estimate is inexperienced, then the best move is to meet with team members and collaborate on writing accurate estimates. Aside from communicating with team members, an individual can derive their estimates from previous similar projects. To help you construct a comprehensive and accurate project estimate, check out the templates from Sample.net, selecting from the 20+ SAMPLE Project Estimate in PDF | MS Word.
