Snowball Sampling, PDF
-

Snowball Sampling PDF
download now -

Snowball Sampling Recruitment Method
download now -

Snowball Sampling Recruitment Guidelines
download now -

Snowball Sampling Example
download now -

Snowball Sampling to Recruit Participants
download now -

Enhancing the Diversity of Snowball Samples
download now -

Design-Based Estimators for Snowball Sampling
download now -

Concept of Snowball Sampling
download now -

Basic Snowball Sampling
download now -

Snowball Sampling Selection
download now -

Womanism and Snowball Sampling
download now -

Printable Snowball Sampling Completion
download now -

Snowball Sampling Survey
download now -

Snowball Sampling Study Design
download now -

Snowball Sampling Technique
download now -

Snowball Sampling in Qualitative Research
download now -

Editable Snowball Sampling
download now -

Snowball Sampling Method
download now -

Snowball Sampling Field Research
download now -

Snowball Sampling Large Graph
download now -

Snowball Sampling Comparision
download now -

Snowball Sampling Project
download now -

Snowball Sampling for Large Network
download now -

Non-Probability Snowball Sampling
download now -

Purposive and Snowball Sampling Techniques
download now -

Snowball Sampling for Language
download now -

Snowball Sampling Approach
download now -

Snowball Sampling Format
download now -

Snowball Sampling Category
download now -

Pros and Cons Snowball Sampling
download now -

Sampling Methods for Email Surveys
download now -

What is a Snowball Sampling
download now -

Snowball Sampling Assessment
download now -

Snowball Sampling Documentation
download now -

Snowball Sampling Definition
download now -

Referral Processes Snowball sampling
download now -

Structural Snowball Sampling
download now -

Snowball Sampling Strategies
download now -

Snowball Sampling Analysis
download now -

Convenience Snowball Sampling
download now -

Snowball Sampling Elements
download now -

Snowball Sampling Recruitment Strategies
download now -

Snowball Sampling Impact
download now -

Snowball Sampling Summary
download now -

Snowball Sampling Procedure
download now -
Snowball Sampling Types
download now -
Snowball Sampling Goal
download now -

Simple Snowball Sampling
download now -

Non-Representative Snowball Sampling
download now -

Standard Snowball Sampling
download now -
Snowball Sampling Learning Center
download now -

Snowball Sampling Use
download now -

Snowball Sampling Variation
download now
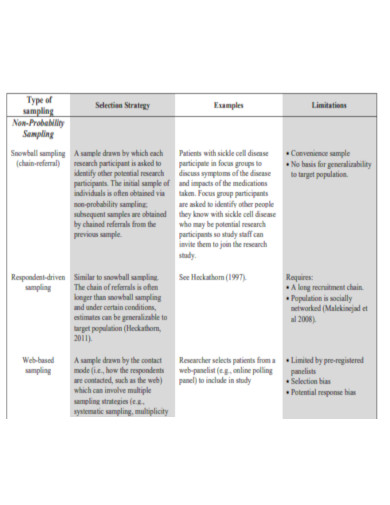
What Is a Snowball Sampling?
Snowball sampling is a non-probability method in which the samples have unique characteristics. Existing subjects offer referrals to recruit the samples necessary for a research study using this sampling technique. This sampling technique comprises a primary data source designating additional possible data sources that can participate in the research investigations. Using the snowball sampling method, a researcher can establish a sample based only on recommendations. Consequently, this technique is also known as the chain-reference sampling technique. Snowball sampling is a common technique for business research. The snowball sampling technique is frequently employed when a population is unknown or rare, and it is challenging to select participants to collect samples for analysis. According to studies, although market research can be expensive, it is sometimes more costly to make erroneous decisions based on inaccurate or insufficient information. Between 25 and 50 percent of the average company’s annual marketing expenditure is allocated to research operations.
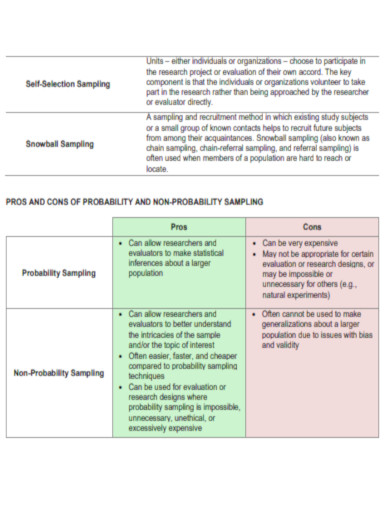
Benefits of Snowball Sampling
If you wish to examine a specific population, such as restaurant managers or crime victims, you must recruit volunteers for your study. Calling or mailing letters to random persons in the phone logs would take an interminable amount of time, as only some recipients would satisfy your requirements. The solution is snowball sampling, a method in which a small group of initial participants assists researchers in locating additional volunteers by tapping into their social networks. Snowball sampling is convenient, but it has numerous limits.
Types of Snowball Sampling
Snowball sampling commences with a convenience sample of one or more initial subjects. Following are multiple data collecting points. These “seed” participants are utilized to attract the first wave of participants. Depending on your study aims, you can pick between three distinct snowball sampling methods:
1. Linear Snowball Sampling
One referral per participant is required for linear snowball sampling. In other words, the researcher recruits a single subject, and that subject recruits a single topic. This procedure is repeated until there are sufficient individuals in the sample. When there are few limits on who can be included in a sample, linear snowball sampling is most effective.
2. Exponential Non-Discriminative Snowball Sampling
One referral per participant is required for linear snowball sampling. In other words, the researcher recruits a single subject, and that subject recruits a single topic. This procedure is repeated until there are sufficient individuals in the sample. When there are few limits on who can be included in a sample, linear snowball sampling is most effective.
3. Exponential Discriminative Snowball Sampling
Participants in this strategy provide many referrals. However, the researcher checks these referrals and selects only those who match specified inclusion requirements. Not all referrals are included in the sample, which is the primary difference between this and exponential non-discriminatory snowball sampling. Exponential discriminative snowball sampling is often employed when selecting participants based on specified criteria and is crucial to achieving research objectives.
How to Use Snowball Sampling in Research
To assess whether snowball sampling is the appropriate strategy, it is vital to analyze the constraints that may arise while employing these techniques. Although particular phases can vary based on the research topic and sampling approach, many snowball sampling techniques follow a similar pattern. Consider the following steps when implementing snowball sampling in your research.
1. Identify Possible Population Members
Finding a sample subject is the first step in efficiently employing snowball sampling. One or two sources may come from this phase to start your research. It’s crucial to confirm that these potential participants match the arbitrary criteria of your study, such as age employment application, to establish a representative sample.
2. Contact Potential Subjects
After identifying your sample subject or subjects, you can contact them to determine if they are willing to participate in your research. There are numerous ways to get with topics, including telephone and email memos. If people agree to participate, you can proceed with your sample procedures. If they decline to participate in the study, you may contact your second sample source or seek more sources.
3. Invite Subjects to Participate in Research
When recruiting participants for your study, you should inform them about the research and its intended outcomes. This explanation can assist participants in making informed decisions on participation. Even if people decline to participate, you can still ask for subject referrals to enhance your sample size.
4. Promote Topic Referrals
Once the initial subjects have been recruited for your study, you can encourage them to provide subject referrals. Instead of asking participants to indicate other potential issues, you may encourage them to suggest that others contact you directly. This strategy is beneficial when studying delicate topics, as it allows referred subjects to choose whether or not to contact you.
5. If Utilizing Discriminatory Sampling, Evaluate Referrals
Analyze the referral information you obtain if you are employing discriminative sampling methods. This analysis ensures that the most relevant participants for your research may be identified. You can use this analysis to discover respondents who meet the research objectives for your issue, such as those who complete a particular age or occupation criterion.
6. Repeat Until the Required Sample Size Is Reached
After contacting your initial referrals, you can request more referral information from them. You may repeat these procedures until the required population is reached or all referrals have been contacted. You may also cease collecting volunteers when you have amassed a large enough sample size to offer valuable data.
FAQs
Is snowball sampling biased?
Snowball sampling is dependent on recommendations. Here, the researcher recruits the initial participant or volunteers, who then recruit the subsequent subjects. Participants possess comparable qualities and are acquainted. This results in sampling bias, as only some people in the population have an equal probability of being included in the sample.
Is snowball sampling qualitative or quantitative?
Snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling technique in which only some population members are equally likely to be included in the sample. This means that you cannot utilize inferential statistics to draw broad conclusions, typically the objective of quantitative research. Consequently, a snowball sample is not representative of the target population and is more suitable for qualitative research.
Is snowball sampling random?
Snowball sampling is a type of nonprobability sampling. In contrast to probability sampling (which requires random selection), the initial study participants are responsible for recruiting additional volunteers. Snowball sampling is not unexpected because only some people in the target population have an equal probability of being drafted into the sample.
Many business leaders use Snowball sampling for high-level research because it helps them get answers from a specialized group. The results of snowball sampling are very relevant to the research situation and easily generalize to a larger group. This sampling method works best when there are few people to look at. If you have a big audience, choose probability sampling methods that ensure different subgroups are represented in your sample.
