53+ Sample Teacher Evaluation Forms
-
Substitute Teacher Evaluation Form Template
download now -
Student Teacher Evaluation Form Template
download now -

Teachers Evaluation Form Template
download now -

Printable University Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -

Teacher PreSchool Evaluation Annual Form
download now -
Preservice Middle School Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -
Mentor Teacher Assessment Evaluation Form
download now -
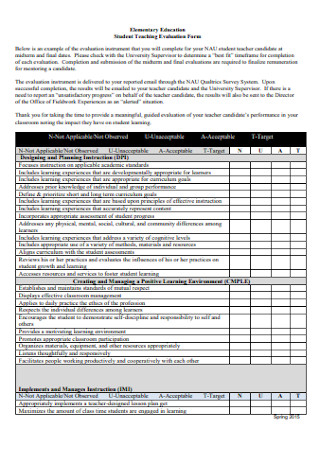
Education Teaching Evaluation Feedback Form
download now -

Public School Teacher Principal Evaluation Form
download now -

Free Printable School Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -

Primary School Student Teacher Evaluation Form for Applicants
download now -
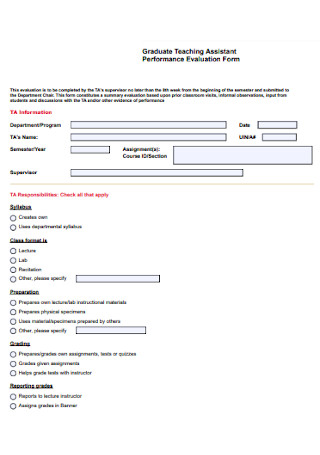
Graduate Teaching Assistant Evaluation Form
download now -
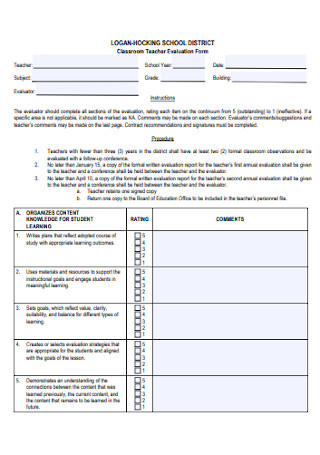
Kindergarten Classroom Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -
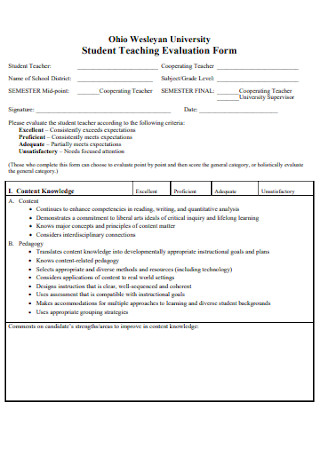
Student Cheerleading Teaching Evaluation Form
download now -

Confidential Elementary Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -
English Teacher Child Care Evaluation Form
download now -
Substitute Teacher Survey Evaluation Form
download now -
Art Teacher Approval Evaluation Form
download now -
Formal Teacher Training Evaluation Form Format
download now -

Teaching Observation Self Assessment and Evaluation Form
download now -

Blank English Teacher Evaluation Form Example
download now -

Childhood Staff Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -
Science Education Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -
Confidential Math Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -

Faculty Teaching Evaluation Form
download now -
Teacher Effectiveness Evaluation Form
download now -

Postgraduate Training Evaluation Form
download now -
Simple Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -

Teacher Meeting Evaluation Form
download now -
Teacher Participant Evaluation Form
download now -
Teacher and Supervisor Evaluation Form
download now -

Medical Program Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -

Academy Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -

Senior Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -

Teaching Summative Evaluation Form
download now -
Lecturer Evaluation Form
download now -

Techaer Training Evaluation Form
download now -
Teacher Conference Evaluation Form
download now -
Lecture Evaluation Form Template
download now -
Teacher Performance Evaluation Form
download now -
Lesson Evaluation Form for Teachers
download now -
Student Teacher Final Evaluation Form
download now -

Teacher Self Evaluation Form
download now -
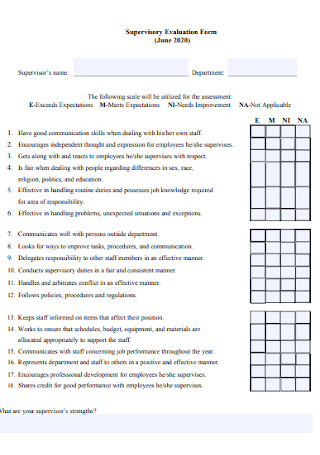
Teacher and Supervisory Evaluation Form
download now -
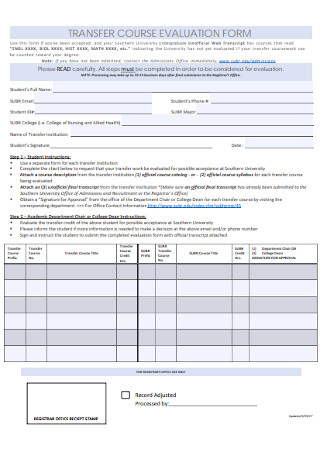
Teacher Transfer Course Evaluation Form
download now -
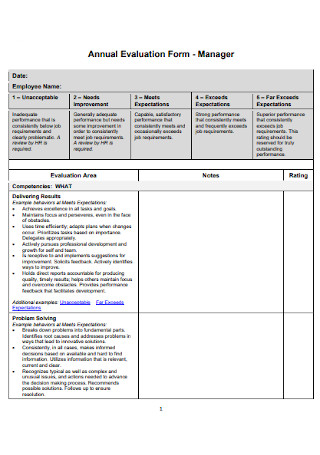
Teacher Annual Evaluation Form
download now -

Teacher Apprentice Training Evaluation Form
download now -
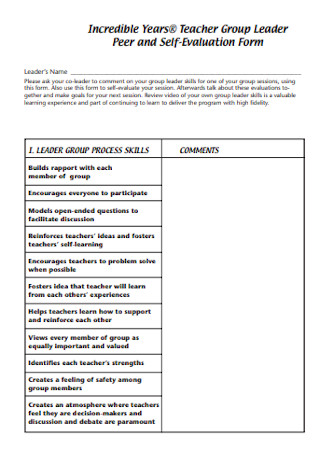
Teacher Peer and Self-Evaluation Form
download now -
Employee Performance Evaluation Form
download now -
Student Council Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -

Cooperating Teacher Evaluation Form
download now -
Teacher Performance Evaluation Form
download now -

Master Teacher Evaluation Form
download now
FREE Teacher Evaluation Form s to Download
53+ Sample Teacher Evaluation Forms
What Is a Teacher Evaluation Form?
Who Can Rate a Teacher?
Other Ways to Evaluate a Teacher
Areas of Assessment in a Teacher Evaluation Form
Parts of a Teacher Evaluation Form
How to Create a Teacher Evaluation Form
FAQs
What is the purpose of a teacher evaluation form?
What should teachers be evaluated on?
Which is the best method of teacher evaluation?
Can teacher evaluation improve teaching?
What Is a Teacher Evaluation Form?
A teacher evaluation form is a form used to evaluate a teacher’s performance in the classroom. It covers several aspects of a teacher’s classroom duties; and normally uses a standard criteria as a basis for grading.
According to a post published by UNICEF, teachers are bearing the brunt of online and remote learning caused by the global COVID-19 pandemic. The world has had to shift and adapt to digital solutions, with education one of the most impacted sectors of all. Children’s lives were upended due to the health crisis and many schools have, or are still struggling to adapt to the changes. The article urges all education stakeholders to help address the problems faced by teachers, who are carrying much of the burden. Teachers, more than ever, need the necessary support, training, preparation, and tools to tackle this new phase of virtual education.
Who Can Rate a Teacher?
Other Ways to Evaluate a Teacher
Before heading into the usual method of rating a teacher’s performance through standard rubric or via a grading system, there are also other ways to complement the method:
Areas of Assessment in a Teacher Evaluation Form
A teacher evaluation form can contain several aspects. It is usually divided into categories. Each category then lists specific instances or describes a situation. Each item is then assigned a rating. The following are some major areas in the assessment of a teacher’s performance:
Parts of a Teacher Evaluation Form
The format of a teacher evaluation form would depend on the school or administration. This can be long or short, generic or course-specific. However, there are basic parts of an evaluation form that should be present.
How to Create a Teacher Evaluation Form
Creating a teacher evaluation form requires keen attention to detail. With the ideas presented above, you can now begin customizing your form. Keep these important steps in mind:
Step 1: Finalize the Format
When creating your evaluation form, choose a layout that will best enable the evaluator or student to grade effectively. Feel free to create a table or a survey-type layout, depending on your objectives and needs. Be sure to aim for clarity and simplicity when providing instructions.
Step 2: Decide on the Criteria
A teacher’s classroom performance needs to be quantified and measured. Evaluation forms are one way to determine how effective a teacher is. Decide on your chosen rubric, whether that be in numerals, checkboxes or descriptions.
Step 3: Fill in Item Descriptions
Using the tips above as a guide, list each item under every category accordingly. Each category may contain several descriptions. Make sure to number these properly. For instance, under the category of ‘Relationship to Students’, be straightforward and indicate the instances where this might be observed. It’s best to state it clearly and declaratively like, ‘The teacher encourages class participation and respects students’ opinions’. Another example would be, ‘The professor communicates effectively and has a firm grip on language and fluency’, under the category of ‘Attitude’.
Step 4: Add Extra Sections
Leave adequate space for evaluators to note down their own personal views and comments. You can add other sections like suggestions for improvement, or teacher’s strengths and weaknesses.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a teacher evaluation form?
A teacher evaluation form is important in measuring a teacher’s effectiveness in the classroom, and how well or poorly the teacher relates to the students. In this way, administrators, parents and even the students themselves can be sure that they are learning something valuable, and are receiving quality education. Teacher evaluation forms are systematically put in place in order to promote constant improvement and aid better learning.
What should teachers be evaluated on?
Teachers should be evaluated on their knowledge and mastery of a subject, in the preparation and execution of their lesson plan, and in their classroom management and day-to-day lessons. How a teacher relates to and engages his or her students is also an important point to evaluate. Lastly, the teacher’s ability to help the students learn in a relevant and impactful way should also be reviewed and evaluated.
Which is the best method of teacher evaluation?
The best way to find out if a teacher is effective in the classroom is by employing a combination of objective assessment (using standard evaluation forms), regular classroom observations, and genuine student feedback. The student’s views and opinions are critical because they are at the receiving end of the teacher’s instruction; and it is ultimately their education and learning that is on the line. The impact a teacher has on a student should be justly taken into consideration.
Can teacher evaluation improve teaching?
Yes, in some ways. Improvement in a teacher’s classroom instruction is one of the main smart goals of teacher evaluations. The reason behind evaluating a teacher’s performance in the classroom is to not only help the teacher gain an understanding and awareness of his abilities and impact, but to help him work on areas that need improvement.
Regardless if a teacher is a first-time instructor, teaching assistant, probationary lecturer, regular faculty, or a substitute teacher, the potential impact they have on young students can sometimes go beyond ordinary comprehension. When Jack Black, in the film ‘School of Rock’, falsely assumed the identity of a substitute teacher, he could not have known the impact he was about to create on his unknowing and passionate students. Browse through the editable templates above and start making a teacher evaluation form now!
