Graph Paper PDF
-
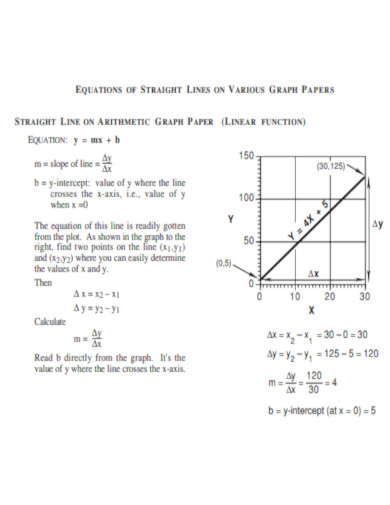
Equations Of Straight Lines on Various Graph Papers
download now -
M Step Graph Paper
download now -
Printable Graph Paper
download now -
Half Inch Grid Graph Paper
download now -
Editable Graph Paper
download now -
Student Sheet Graph Paper
download now -
Plain Graph Paper
download now -
Basic Graph Paper
download now -
Coordinate Plane Graph Paper
download now -
Super Teacher Worksheet
download now -
Mini 10 Graph Paper
download now -

Documentation of the Graph Paper
download now -
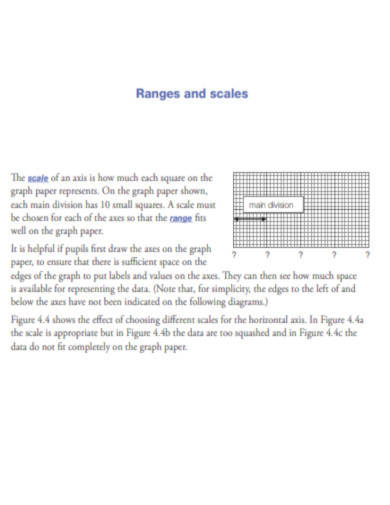
Ranges and Scales of Graph Paper
download now -
Set of Four 4 Quadrant Graph Paper
download now -

Artbeads Graph Paper
download now -
1 Centimeter Graph Paper
download now -
One Square Foot Graph Paper
download now -
Drawing Grid Graph Paper
download now -
0.5 cm Graph Paper
download now -
Sample Graph Paper
download now -
End of Grade Graph Paper
download now -
EOC Graph Paper
download now -
Missouri Botanical Garden Graph Paper
download now -

1/4 Inch Grid Graph Paper
download now -
Coordinate Graph Paper
download now -
Standard Graph Paper
download now -

One half Centimeter Grid Graph Paper
download now -
Medium Graph Paper
download now -

Graph Paper 20 X 20
download now -

0.75 cm Graph Paper
download now -
Isometric Graph Paper
download now -
Simple Graph Paper
download now -
Blank Lines Graph Paper
download now -
Slow the Flow Irrigation Plan Graph Paper
download now -

Graph Paper Programming Goal
download now -

Creating Graph Paper in MS Word
download now -
Graph Paper Programming
download now -
Graph Paper PDF
download now -
Count Graph Paper
download now -
Graph Paper Format
download now -

1.25 cm Graph Paper
download now -
Free Graph Paper
download now -
General Graph Paper
download now -
Scrap Graph Paper
download now -
Energy Challenge Graph Paper
download now -

Cornell Note-Taking Graph Paper
download now -

Small Dot Graph Paper
download now -

Maximum Usable Frequency Graph Paper
download now -
Regular Grid Graph Paper
download now -
Small Graph Paper
download now -
Creative Graph Paper
download now -
Square Dot Graph Paper
download now -
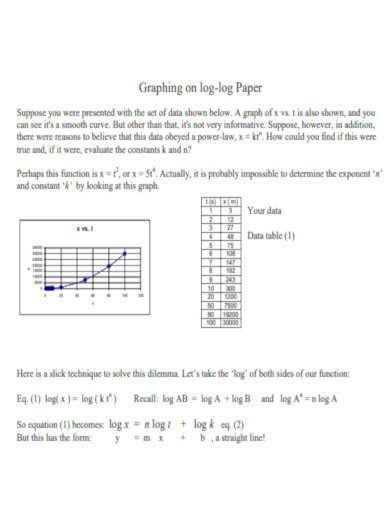
Graphing on Log-Log Paper
download now
What Is a Graph Paper?
In the most fundamental sense, graph paper is preprinted paper with thin lines that form a grid. There are numerous methods for achieving this, but the most prevalent is a square grid of parallel horizontal and vertical lines. You are likely already aware of ruled paper preprinted with horizontal lines that can be used for precise writing. A grid on graph paper anchors your work in two dimensions instead of one. However, graph paper can also be used for amusement. It is ideal for designing intricate patterns for interior design, quilting, beading, embroidery, and knitting. Graph paper is also an effective tool for games that contain maps or strategic divisions of space: for example, most role-playing games use it to depict where players are about the terrain, opponents, and other characters.
Benefits of Graph Paper
Graph paper is used for more than just math. As a result of its versatility, graph paper is one of the world’s most popular types of writing. Daily, this paper can be used for household projects and creative projects. When you have a large amount of excess paper, consider how it can be used. Most frequently, this paper is used initially. It can be used for charting mathematical data. Those enrolled in any mathematics course are aware of the significance of graphing. When taking courses such as statistics and calculus, you will use graph paper regularly to complete assignments. This paper can be printed from a computer or purchased from a local store. This paper is relatively easy to locate. Graph paper could also be utilized for artistic endeavors. In reality, most poster boards are graph-lined on one side so the project can be centered and completed quickly. This type of paper facilitates the completion of graphing projects. You can also customize the scale of the various art projects, as this paper can be purchased or printed with different grid sizes.
Types of Graph
Any competent financial analyst is aware of the significance of adequately presenting results, primarily dependent on understanding the various measurement charts and graphs and when and how to use them. This portion describes Excel’s top eight graph kinds and the optimal use cases for each. You may find this document or print it from the computer in various grid sizes, allowing you to learn how to create compelling presentations and clear takeaways using these chart types.
How to Make a Graph in Google Docs
You can develop data visualizations and models in Google Docs to enhance your presentations, resumes, and reports. Data visualization can aid in interpreting big or complex data sets by highlighting data disparities. Instead of writing enormous volumes of text, you can use a graph to summarize or model your information when making presentation slides and reports. You can also use graphs in your resume to illustrate your quantifiable achievements and qualifications for an employment application. Consider the following steps for constructing a graph in Google Docs:
1. Open Your Document
Go to Google Docs and open the record where you wish to create a graph, either selecting an existing form or making a new one by clicking the “+” symbol. The “Insert” button on your document will open a drop-down menu. Locate and click on the “Chart” tab in the drop-down menu to open a sidebar containing graphing choices.
2. Choose Your Graph Type
The menu in the sidebar allows you to build a bar, column, line, or pie graph. Selecting the desired graph type inserts a generic graph that can be edited in Google Sheets. Your graph with generic data sets is automatically linked to a Google spreadsheet where you can change its data.
3. Edit Your Graph
When you enter a graph, a pop-up menu with the option “Edit in Sheets” displays at the bottom left of the screen. Clicking this button or right-clicking the graph will display the link choices. Selecting the chain connection icon will provide a drop-down menu with options to “Unlink” your documents graph, “Open source” to the linked Google sheet, and view all “Linked objects” in your document. To alter a graph, choose “Open source,” which will open the associated sheet in a new tab. If you wish to build numerous graphs, you can also pick “Linked objects” to view and edit each linked sheet. Depending on the graph type, you can modify the graph’s title, labels, values, colors, and legends when modifying the graph in sheets.
4. Customize Your Graph
In Google Sheets, you may modify the graph’s background, colors, fonts, lines, opacity, and shapes, among other graphic features. In your spreadsheets, right-click the chart and select the “Customize” option. If you wish to add or modify your gridlines, click “Gridlines” and adjust their number and thickness. To alter the graph’s backdrop or font, pick “Customize” and click “Chart style.” Select the many components of your graph from the “Chart style” option to personalize and change them to your specifications. You can alter font styles, background color, and transparency.
5. Format Your Document
If you wish to change the placement of your graph within your document, you can open a menu of placement options by left-clicking on the graph. Your graph is automatically aligned with any text that was there before insertion. You can select to have your graph “In the line” with your text, “Wrap text” around your graph, “Break text” to have your graph on a different line, “Behind text” to display your text on the graph, or “In front of text” to hide it.
6. Insert a Graph from Sheets
If you already have a data set sheet that you wish to utilize for a graph in your document, you can select “From Sheets” from the “Insert” menu, “Chart” tab, and graph choices. This opens a menu containing the available spreadsheets that can be inserted into a chart. When you pick a spreadsheet, Google Docs automatically locates charts within it and links them to your document. Select the sheet graph you wish to insert and click “Import” in the bottom right corner. You can change your graph data or reformat your page after inserting a graph from a sheet. You can “unlink” the document graph from the spreadsheet chart to preserve the current data if you wish to retain the inserted version as-is in the document while modifying the originating spreadsheet.
FAQs
What kind of paper is graph paper?
Graph paper, also called coordinate paper, grid paper, or squared paper is a writing paper with fine lines that form a grid. Graphs of functions, experimental data, and curves are often made with lines as guides.
What is a graph in a research paper?
Graphs are a typical way to represent data relationships visually. A graph’s goal is to display too many or complex data to be described correctly in the text and within the available space. In addition, a research paper’s purpose is not simply to inform the reader of what others have said about a topic but to engage the sources to intelligently present a distinct viewpoint on the issue at hand. This is achieved through the writing of two sorts of research paper proposals.
Can I copy a graph from a research paper?
If you want to reuse a table, chart, graph, or image from a published text, you must obtain permission from the copyright holder (articles, books, websites). The publisher is the copyright owner; therefore, contact the journalist of the journal report, book publisher, or website owner for permission.
Once you discover the many uses of graph paper, you will realize how convenient it is in a lot of projects. It is a wonderful and effective tool for problem-solving, communicating ideas, and exploring creativity. Use them in various projects and ensure that your handwriting or sketches are aligned well.
