Healthcare Business Plan Samples
-

Healthcare Agency Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Marketing Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Company Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Consulting Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Business Plan Template
download now -

Health Care Social Care Business Plan Template
download now -

Healthcare Business Plan Template
download now -

Healthcare Clinic Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Environment Strategic Business Planning
download now -

Integrative Healthcare Business Plan
download now -

International Healthcare System Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Services Business Plan
download now -

Basic Healthcare Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Medical Center Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Business Plan Example
download now -

Healthcare System Business Plan
download now -

Powering Healthcare Business Plan
download now -
Healthcare Business Plan For Clinical Facilities
download now -

Healthcare Business Plan in PDF
download now -

Sample Healthcare Business Plan
download now -

Standard Healthcare Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Reduces Business Planning
download now -

Modernizing Healthcare Business Plan Operations
download now -

Healthcare Services Strategic Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Organization Management Business Plan
download now -

Printable Healthcare Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare and Wellness Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Business Sustainability Plan
download now -
Healthcare Integrated Business Plan
download now -

Formal Healthcare Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Foundation Business Plan
download now -

Healthcare Business Plan in DOC
download now
FREE Healthcare Business Plan s to Download
Healthcare Business Plan Format
Healthcare Business Plan Samples
What is a Healthcare Business Plan?
Purpose of a Healthcare Business Plan
How to Write a Healthcare Business Plan
FAQs
How does the healthcare industry operate?
What are the four major healthcare industries?
What is the healthcare sector?
How can compliance be ensured in a Healthcare Business Plan?
What role does financial planning play in a Healthcare Business Plan?
What makes a Healthcare Business Plan attractive to investors?

Download Healthcare Business Plan Bundle
Healthcare Business Plan Format
1. Executive Summary
- Brief overview of the healthcare business (clinic, hospital, telemedicine service, etc.)
- Mission and vision statements
- Summary of key objectives
- Overview of services or products offered
- Funding requirements and potential return on investment (ROI)
2. Business Description
- Description of the business and its unique value proposition
- Legal structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, etc.)
- Location and facilities overview
- Industry overview and market trends
- Description of the target audience (e.g., demographics, health conditions)
3. Market Analysis
- Industry analysis and market size
- Key market trends and drivers
- Target market segmentation
- Geographic, demographic, psychographic, or behavioral segmentation
- Competitor analysis:
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Market position comparison
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
4. Services or Product Line
- Detailed description of the healthcare services or products provided
- General practice, specialized care, home health services, telehealth, etc.
- Unique selling points (USPs)
- Compliance with healthcare regulations and standards
- Research and development (if applicable)
5. Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Marketing objectives and goals
- Branding strategy
- Marketing channels (digital marketing, local advertising, partnerships, etc.)
- Pricing strategy
- Sales strategy and patient acquisition tactics
- Patient retention programs and loyalty plans
6. Operational Plan
- Day-to-day operations plan
- Facility requirements and management
- Technology and tools used (e.g., EMR/EHR systems)
- Inventory management (for pharmaceuticals, medical supplies, etc.)
- Licensing, permits, and healthcare compliance requirements
- Quality assurance processes
7. Management and Organization
- Organizational structure
- Bios of founders and key team members
- Roles and responsibilities
- Recruitment and training plans
- Advisory board or consultants (if any)
8. Financial Plan
- Start-up costs and capital requirements
- Revenue model and pricing structure
- Projected income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets (3-5 years)
- Break-even analysis
- Funding requirements and strategy (e.g., loans, investors, grants)
- Financial risks and contingency plans
9. Impact Analysis
- Contribution to the community (e.g., job creation, improved health outcomes)
- Healthcare accessibility and affordability goals
- Compliance with sustainability and environmental standards
- Social responsibility initiatives
10. Appendix
- Supporting documents (e.g., licenses, certifications, legal documents)
- Resumes of key personnel
- Detailed financial projections
- Additional charts, graphs, or tables
- Market research reports or references
What is a Healthcare Business Plan?
A Healthcare business plan entails creating a document that explains the services you aim to offer as well as how you intend to operate your company. Reimbursement, fee schedules, billing systems, managed care contracts, and operational challenges are all common issues in the health care industry. You may persuade potential investors that your business plan is sound and deserving of their investment by outlining how your firm solves these obstacles. There are available templates that you can use as a basis. Otherwise, there are healthcare business plan examples you can check out for references as you write your business plan. You can also see more on Coaching Business Plan.
Purpose of a Healthcare Business Plan
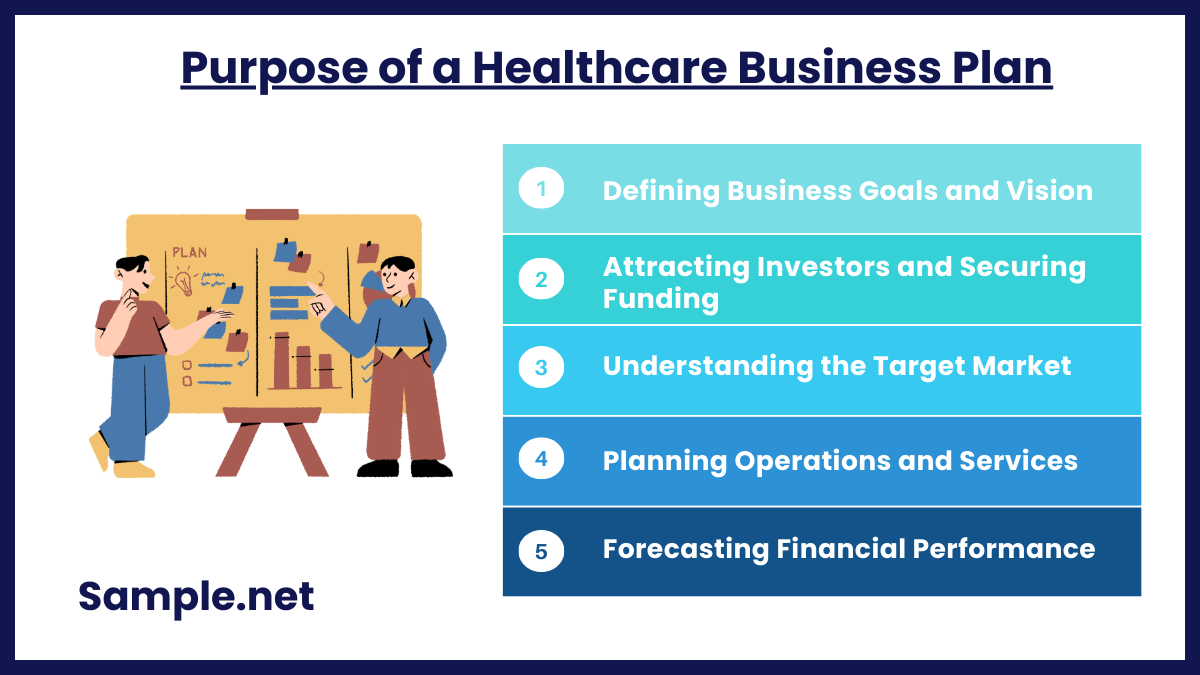
1. Defining Business Goals and Vision
A healthcare business plan helps in clearly defining the mission, vision, and objectives of the organization. This clarity ensures that all stakeholders understand the business’s purpose and direction. It also provides a benchmark for measuring progress and success over time. A well-defined vision fosters focus and alignment across teams. It serves as a guide for making strategic decisions and navigating challenges.
2. Attracting Investors and Securing Funding
Investors need to see a clear and convincing plan before committing to a healthcare business. A business plan demonstrates the potential profitability of the venture, backed by market research and financial projections. It also highlights the business’s competitive edge and growth opportunities. By showcasing a well-thought-out plan, entrepreneurs increase their chances of securing funding and partnerships. A solid business plan builds investor confidence in the organization’s ability to succeed. You can also see more on Business Sales Plan.
3. Understanding the Target Market
Market analysis is a key component of a healthcare business plan. It identifies the demographics, needs, and preferences of the target audience. Understanding the market helps businesses tailor their services to meet patient needs effectively. This ensures higher patient satisfaction and loyalty, contributing to sustainable growth. A detailed analysis also helps in identifying gaps in the market that the business can address.
4. Planning Operations and Services
A healthcare business plan outlines the operational framework, including staffing, equipment, and facility needs. It specifies the services to be offered and the processes for delivering them efficiently. This detailed planning ensures smooth operations and high-quality patient care. Additionally, it highlights compliance with healthcare regulations and standards. A robust operational plan minimizes risks and enhances service delivery.
5. Forecasting Financial Performance
Financial planning is a critical purpose of a healthcare business plan. It includes budgeting, revenue projections, and cost analysis to ensure financial stability. Entrepreneurs can anticipate expenses, calculate profitability, and plan for future investments. A clear financial forecast helps in managing resources effectively and preparing for challenges. It also reassures stakeholders of the business’s financial viability. You can also see more on Annual Business Plans.
How to Write a Healthcare Business Plan

Writing a healthcare business plan without knowing the steps will prove to be difficult and challenging. Even if you are aware of what it is, without a complete guide, you may be confused about what to do. The purpose of a healthcare business plan is to assist you in defining and identifying your target audience as well as your key prospects. It can also help you evaluate and compare your practice’s statistics to those of your competitors. With that being said, you are more than ready to proceed to the steps outlined in this article. Keep on reading to know more. You can also see more on Executive Business Plan.
Step 1: Search for internet resources that are available
To begin drafting your healthcare business plan, use the resources given by websites such as this Article and other similar sites where templates are provided. Use this site’s provided templates for an easier method to create the business plan. Through the use of a template, you won’t have to worry about starting from scratch which may take valuable time off of your day which could have been spent doing other more important responsibilities. Do remember that you can put your own unique spin to the template. The beauty of templates is that you are able to customize them as much as you want.
Step 2: Define the healthcare company’s description
Make a brief description of your healthcare company. List how your service provides non-medical care to elderly or handicapped clients at home, for example. Urgent care centers, for example, usually offer certified physician treatment, on-site lab tests, prescription services, and extended hours. Describe the abilities and expertise of your technicians and other members of your team. If you want to buy and manage a franchise, the parent company will usually offer you information and training about the business. Be sure to thoroughly explain what is the particular focus or practice of your healthcare business to avoid misconceptions. You can also see more on Quality Assurance Business Plan.
Step 3: Create a competitive analysis and marketing strategy
This step is where you will need to determine who your competition are. Examine their advantages and disadvantages. Prepare your marketing initiatives, which might include detailing your intentions to create a website to offer your services or running an email marketing campaign to attract new consumers. Describe your area and how you plan to get referrals, such as via networking with doctors and hospital administrators. Patients in need of home health care are typically referred to local respected organizations that provide high-quality assistance to discharged patients by these health care specialists.
Step 4: Clarifying the management and organization
For this step, you should include a section that explains how you plan to run your healthcare business. Make a list of the charting and billing applications you plan to utilize. Create a system for accepting money and reimbursing you for your services. Using the materials offered by a Budget Marketing Plan, make a list of the licenses necessary to operate a health care business in your community. Make sure you follow the criteria for delivering health care services and that your local hospital and private insurance will compensate you for your services.
Step 5: Set up financial as well as strategic objectives
Describe how you intend to fund your business and provide a multi-year strategy. It is important to think ahead to project the expected outcome of the healthcare business in the long. Declare the number of patients you hope to treat by the end of the first year, for example. Sort these patients into groups based on their needs, such as home healthcare or personal injury cases. Set success criteria, such as achieving an average of a specific percentage of customer satisfaction based on client feedback from follow-up Surveys form.
FAQs
How does the healthcare industry operate?
Companies that provide clinical services, manufacture medications, and medical equipment, and provide healthcare-related support services such as medical insurance make up the Healthcare Industry. In the diagnosis, treatment, nursing, and management of illness, disease, and accident, these businesses play a critical role.
What are the four major healthcare industries?
The four major healthcare industries include pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, equipment, distribution, facilities, and managed health care. Knowing these major healthcare industries is essential to figure out which healthcare business you will get yourself into. If you have already chosen or are aware of what your healthcare business falls under, you can proceed to check out the example of a healthcare business plan to get a clearer understanding of how it is formatted. You can also see more on Investment Company Business Plan.
What is the healthcare sector?
According to Investopedia, the healthcare sector is a business that offers medical services, produces medical equipment or medications, provides medical insurance, or otherwise enables the provision of healthcare to patients to make up the healthcare industry. Think over how to write out your healthcare agency business plan as you are now more aware of the healthcare sector.
How can compliance be ensured in a Healthcare Business Plan?
The plan should address healthcare regulations, licensing requirements, and patient data protection laws. Highlighting compliance builds trust and avoids legal complications.
What role does financial planning play in a Healthcare Business Plan?
Financial planning ensures that the business remains profitable and sustainable. It outlines startup costs, revenue projections, and funding requirements while preparing for potential challenges. You can also see more on Business Action Plan.
What makes a Healthcare Business Plan attractive to investors?
A strong plan includes clear goals, competitive analysis, financial sustainability, and growth strategies. It assures investors of the business’s potential for long-term success.
