9+ SAMPLE Equipment Maintenance Checklist
-
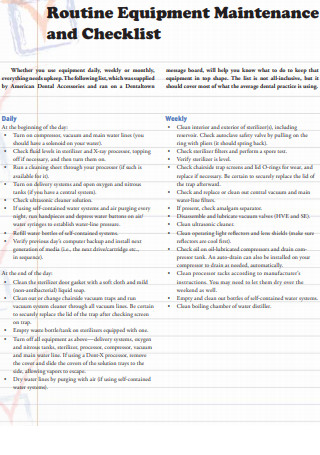
Routine Equipment Maintenance Checklist
download now -

Cooling Equipment Maintenance Checklist
download now -

Equipment Maintenance Checklist
download now -

Sample Equipment Maintenance Checklist
download now -
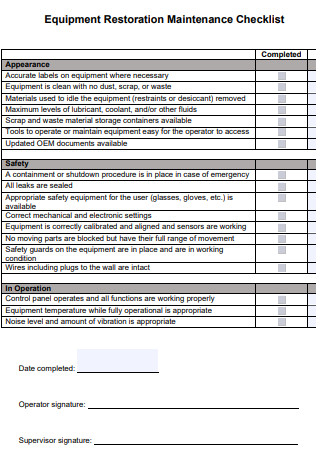
Equipment Restoration Maintenance Checklist
download now -

Dental Equipment Maintenance Checklist
download now -
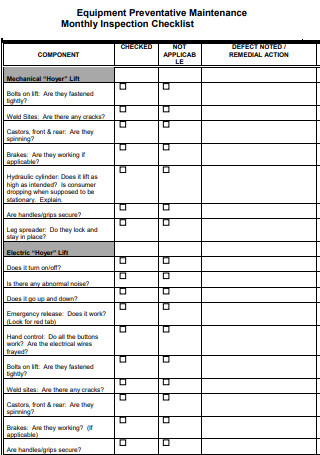
Equipment Preventative Maintenance Monthly Inspection Checklist
download now -
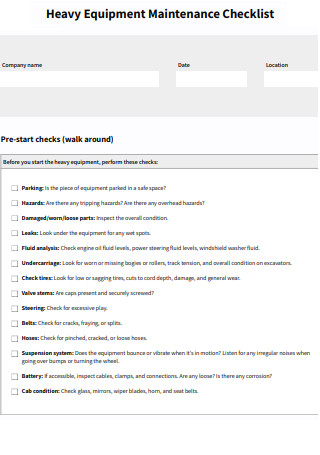
Heavy Equipment Maintenance Checklist
download now -
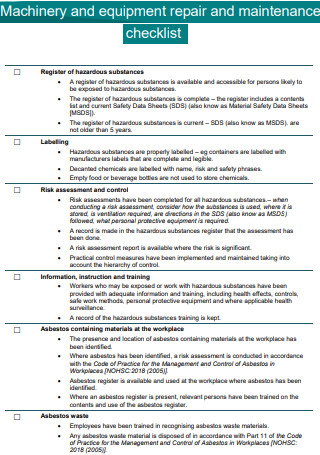
Machinery and Equipment Repair And Maintenance Checklist
download now -
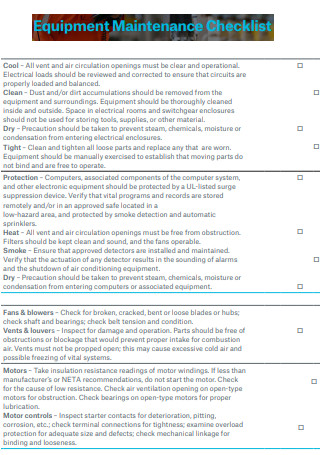
Standard Equipment Maintenance Checklist
download now
What Is an Equipment Maintenance?
Any procedure required to keep a company’s equipment in dependable functioning order is known as equipment maintenance. It could involve both preventative maintenance and corrective maintenance. Each type will require different resources to keep it all in good condition. For instance, repairs made to automated food processing equipment won’t appear the same as those made to heavy construction equipment. According to statistics, 39% of facilities still keep maintenance reports on paper.
Benefits of Equipment Maintenance
In a commercial context, the adage “if it’s not broken, don’t fix it” does not apply to equipment maintenance. However, why would you pay for equipment service if it is in perfect condition? Here are six reasons why this practice is essential and how it can benefit you and your organization.
How to Obtain Preventive Maintenance
Although it may not sound thrilling, doing essential maintenance on the manufacturing machinery that businesses depend on to produce items and fulfill the strict deadlines of their clients could mean the difference between meeting and missing a delivery date. Regular preventive maintenance can identify potential safety issues, improve product quality by keeping materials clean, angles squared, and blades sharp, save money by extending the equipment‘s life, and enable discounted service.
Step 1: Schedule equipment maintenance based on consumption
Even though some machines tell the operator when to do maintenance, waiting for this can slow production. If tasks are planned ahead of time, they are less likely to be put off and then forgotten so that a production deadline can be met. The more you use a machine, the more abuse it can take, so think about how often it needs to be fixed. If you use a small edge bander for eight hours a day, once every six months is probably enough to keep it in good shape. But if you run three shifts on the same machine, you might need to do maintenance on it every three months or even more often if you don’t have a qualified maintenance crew.
Step 2: Employees should be held responsible for maintenance
After determining what preventative maintenance tasks must be conducted and when they should be performed, assign responsibility for their completion to a maintenance coordinator, machine operator, or other relevant employees. Use a sheet affixed to each machine, a software application, or daily, weekly, and monthly cards submitted to supervisors for these selected staff to sign off on maintenance operations. Regardless of the approach you choose for tracking, regularly adhere to the preventative maintenance schedule you’ve developed.
Step 3: Ensure preventive equipment maintenance is helpful and plan for seasonality.
For example, greasing the rack and pinion of a beam saw can cause oil and sawdust to harden within the gears over time, preventing the loads from turning. Ask your equipment representative which jobs each piece of equipment is best suited for if you are uncertain. Additionally, production does not need to be impacted by preventive maintenance. Plan projects that necessitate downtime for slower seasons. This investment can prevent 36 to 48 hours of unanticipated “corrective” maintenance if something breaks.
Step 4: Request a maintenance plan from the manufacturer of your equipment.
Some machinery manufacturers offer preventative maintenance visits for a set annual fee or discounted labor and part prices. If your service provider does not offer service agreements, suggest one. In addition to ensuring that maintenance is completed on your equipment, service contracts also help you budget for it. Consider at least the manufacturer service programs for these machines, as maintenance programs are especially crucial for frequently used equipment.
Step 5: Document service visits
When you plan a maintenance visit with an equipment manufacturer, ensure the service technician will document the inspection. It is essential to document the service date and the parts of the equipment that were inspected and the work conducted. Request from the representative a copy of the inspection report. This checklist will serve as a record for the manufacturer and assist you in identifying items that your personnel should inspect independently.
Step 6: Keep service manuals handy
Manuals are frequently misplaced, but machine operators must have access to them. The manuals include vital information such as electrical schematics, part identification, operational instructions, safety standards, and maintenance suggestions. Most manuals provide a maintenance section that specifies what should be performed and how frequently. This information is especially crucial for operators who were not there for the original training session conducted by the machinery manufacturer.
Step 7: Ensure management supports preventive maintenance
Failure to schedule preventative maintenance, overriding scheduled maintenance to meet production demands and requesting that employees reduce maintenance expenditures can send the wrong message and ultimately cost an organization more in machine downtime and repair fees. Consider maintaining the equipment during off-hours if production demands do not allow for planned maintenance activities. When evaluating budgetary requirements, remember that failing to execute preventative maintenance may result in substantially greater expenses if equipment breaks down, especially during peak production periods.
FAQs
What is an equipment maintenance plan?
A strategy for equipment maintenance is the proactive servicing of assets by their maintenance schedules. By implementing a planned maintenance program in your organization, you can ensure that routine equipment inspections are performed accurately.
What is basic equipment care?
Primary care refers to the housekeeping, cleaning, informal monitoring, preservation, and simple ad hoc maintenance of equipment, which is usually performed by operators but can also be performed by maintenance technicians.
What are maintenance skills?
Maintenance skills involve inspecting, diagnosing, and resolving problems with machines or structures. In addition, they are utilized to do basic repairs or preventive maintenance on various equipment to ensure its longevity and functionality.
What is the significance of a maintenance checklist? Indeed, maintenance checklists are vitally important. Those who employ such a checklist are a testament to how long they can maintain their equipment or machinery in operational order. These items are not inexpensive, but proper care and maintenance are undoubtedly budget-friendly.
