18+ Sample Field Inspection Checklist
-
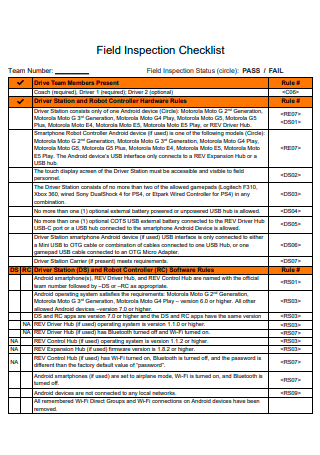
Field Inspection Checklist Template
download now -

Formal Field Inspection Checklist
download now -
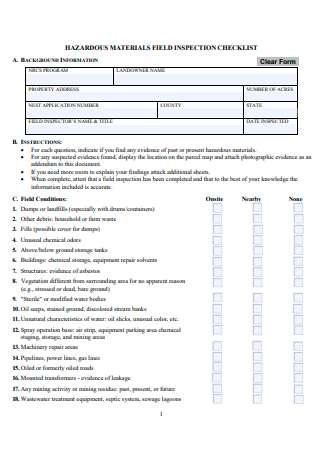
Materials Field Inspection Checklist
download now -
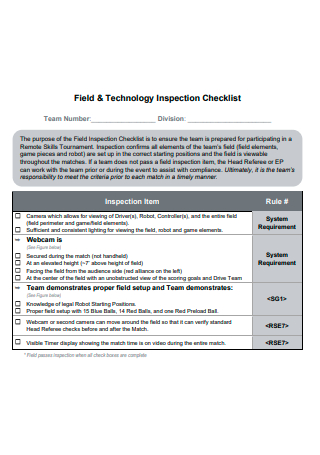
Field and Technology Inspection Checklist
download now -
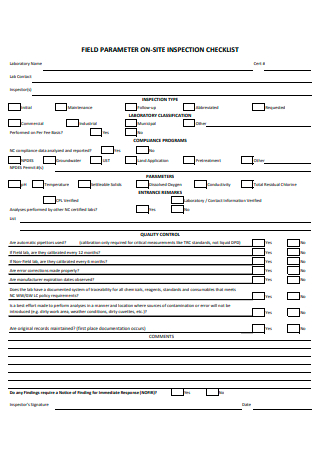
Field Parameter On-Site Inspection Checklist
download now -
Athletic Field Safety Inspection Checklist
download now -

Field Inspection Processor Checklist
download now -
Field Inspection Energy Checklist
download now -

Rooftop Field Inspection Checklist
download now -
Field Inspection Checklist in PDF
download now -
Fire Safety Field Inspection Checklist
download now -
Commercial Solar Thermal Field Inspection Checklist
download now -
Piping Field Inspection Checklist
download now -

Sports Facility and Field Inspection Checklist
download now -

Facility and Field Inspection Checklist
download now -

Field Inspection Checklist Example
download now -
Deck Field Inspection Checklist
download now -
Field Services Job Site Inspection Checklist
download now -
Field Maintenance Report Inspection Checklist
download now
FREE Field Inspection Checklist s to Download
18+ Sample Field Inspection Checklist
a Field Inspection Checklist?
Benefits of a Field Inspection Software
Types of Inspection Checklists
How To Create a Well- Designed Checklist
FAQs
What is a check list for inspections?
What is simple checklist?
What justifies inspection?
What Is a Field Inspection Checklist?
Safety officers or inspectors typically utilize inspection checklists in the field to conduct crucial safety exams. It encompasses all facets of the work environment present during and surrounding any work-related operation. A list ensures that inspections be completed efficiently and effectively by defining a guideline for each component that must be inspected. The checklist can be used to perform a full assessment of the environment’s safety and address hazards that could result in fatal but easily preventable work-related catastrophes. Safety inspectors and supervisors should use a well-written inspection checklist to assess all activities and variables that could potentially result in a safety hazard. Checklists for field inspections should be customized for the type of activity or operation being performed on-site. According to statistics, a 100% examination is approximately 87% effective. In other words, a 300% inspection will still overlook 0.3% of the defective goods.
Benefits of a Field Inspection Software
Inspection management software streamlined all checking, analyzing, recording, scheduling, and tracking papers, checklists, and web forms. It enables continual maintenance, repair, and organization at a fraction of the time formerly required by hand. So how does field inspection software aid you? Apart from enhancing profitability, equipment maintenance software helps prevent workplace injuries, protects against liability, and extends the life and productivity of the product.
Types of Inspection Checklists
Numerous safety inspection checklists are available for use in a variety of sectors. While specific sectors may have their own safety rules, most fields employ lists that adhere to OSHA guidelines. This is because widespread adoption of OSHA-compliant lists enables firms to remain compliant with industry standards and promote systematization of workplace health and safety activities. With this in mind, the following four OSHA checklists are frequently used to enhance safety across a variety of industries:
-
1. Self-inspection for construction
The self-inspection checklist for construction includes a thorough list of safety items that contribute to worker well-being. This checklist can assist construction site staff in effectively managing the large number of safety items they encounter daily. Not every item on the construction safety checklist will apply to every project site, as this list is exhaustive and applies to various task types.
2. Self-inspection for general industry
The general industry self-inspection checklist includes several safety measures designed to promote employee health in the workplace. Since experts can use this checklist to verify compliance with safety regulations in various industries, it may prove to be a widely valuable resource. This is especially beneficial for employees inside industries where safety standards are rarely followed due to a lack of regulation. While some of the elements on this checklist are identical to those on the construction self-inspection checklist, there are numerous additional things.
3. Housekeeping inspection
The housekeeping inspection checklist includes workplace cleanliness, sanitization, and personal protection measures. This checklist applies to various industries, and experts can use it to ensure that a certain degree of health regulation is maintained at their workplace. The housekeeping inspection checklist may be particularly beneficial for those working in the food service, healthcare, and manufacturing industries.
4. Personal protective equipment (PPE) inspection
The PPE safety inspection checklist includes topics that pertain to workplace compliance with the provision, maintenance, use, and upgrading of personal protective equipment (PPE) that protects personnel from occupational dangers. Professionals from various industries can use the PPE checklist to detect hazards and recommend protective equipment to ensure employee safety. Most sectors use this checklist in conjunction with others, as OSHA recommends that employers use personal protective equipment (PPE) as a supplementary risk control strategy.
How To Create a Well- Designed Checklist
Checklists are one of the most useful organizational tools in history, and when utilized properly, they may help you move quickly and effortlessly through activities. However, not all checklists are equal! If you want to use lists to become more organized and improve your life, you need more than just any checklist; you need the correct list. It makes no distinction whether you’re building a daily list or a situational index for a particular occasion; the procedure of constructing a list is identical. If you’re still interested in developing one, here are some things to take.
-
1. Carry out a “brain dump.”
The first step toward creating a practical checklist is to conduct a “brain dump” and write down every activity and to-do item bouncing around in your head. Take a seat and note down all tasks that need to be completed. For instance, suppose you’re constructing a wedding checklist. Everything from scheduling a tasting with the caterer to purchasing gifts for your wedding party to writing your vows should be written down. Alternatively, suppose you’re creating a daily checklist. In that case, you’ll want to note all of your repeating daily duties (such as bringing your child to soccer practice) as well as any forthcoming one-off tasks that you’ll need to incorporate into your daily routine. Don’t hold back when you’re performing your brain dump! You want to be transparent as possible with your list of probable tasks, and to- do’s.
2. Prioritize and organize chores
Once all of your tasks have been “dumped” onto the page, it’s time to begin categorizing and prioritizing them. First, you’ll want to organize and group your to-in do’s logically. Thus, you may manage chores according to their frequency (daily, weekly, or monthly), their type (such as scheduling appointments or to-for do’s school), or their relationship to your life. Once your tasks are sorted, it’s time to begin prioritizing them. To begin, evaluate each reading and assign it an A, B, or C grade. “A” jobs are critical and must be completed immediately. “B” tasks are necessary but less urgent, while “C” chores are something you want to keep on your radar for the future but are not required to complete immediately. As an illustration, suppose you’re designing a moving checklist. There are no correct or wrong responses when it comes to work prioritization. It’s simply a matter of determining which jobs are the most critical/urgent so you can complete them first.
3. Make a note of them on your to-do list.
After you’ve structured and prioritized your activities, it’s time to compile them into a physical checklist. Prioritize your tasks and, if applicable, include the date or time by which they must be completed. For instance, a daily list may have the duty, whereas a situational checklist may include the item.
4. As you finish each item, cross it off the list
Once you’ve organized your to-do list, it’s time to begin working your way through tasks, crossing off each thing on the checklist as you accomplish them. Not only will checking off items on your list motivate you to continue, but it will also help you maintain track of what you’ve accomplished and what still has to be done.
5. Continue to add things as they become available.
In an ideal world, you’d reach the bottom of your checklist and exclaim, “Excellent! I’m finished!” However, let’s face it—there is always more work to be done. However, the beauty of checklists is that if other chores (inevitably) arise, all you have to do is add them to your checklist and proceed!
FAQs
What is a check list for inspections?
A checklist is the fundamental inspection component used to document and record health and safety inspections. Each inspection checklist is tailored to a particular inspection process; for instance, a ladder inspection checklist will include instructions about examining a ladder.
What is simple checklist?
A simple checklist template is any procedure or list of tasks organized in the form of a checklist; in other words, it is a to-do list in which the order of the items is usually critical.
What justifies inspection?
Inspection and testing quantify and establish the product’s quality level. Inspection and testing are critical components of the manufacturing process because they aid in quality control, cost reduction, loss reduction, and determining the root cause of defective product creation.
Maintaining a safe and healthy workplace away from health risks and hazards is no easy undertaking. However, it is unquestionably gratifying. Assuring the safety of your workplace enables your staff to perform freely and confidently without concern for their lives. In general, this is a sound and ethical corporate practice.
