38+ SAMPLE Food Safety Checklist
-

Restaurant Food Safety Checklist Template
download now -
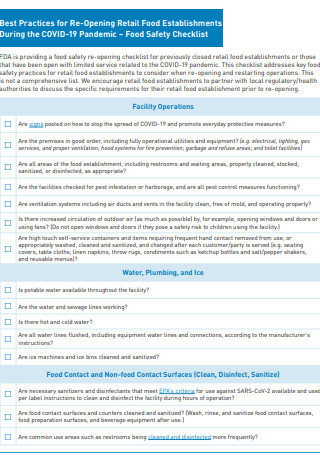
Kitchen Food Safety Checklist During Covid 19
download now -
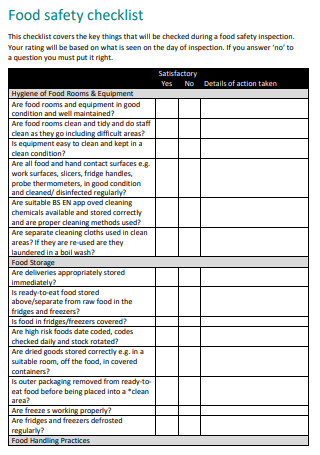
Sample Personal Hygiene Food Safety Checklist
download now -

Daily HACCAP Food Safety Checklist
download now -

Cooking Food Safety Checklist
download now -
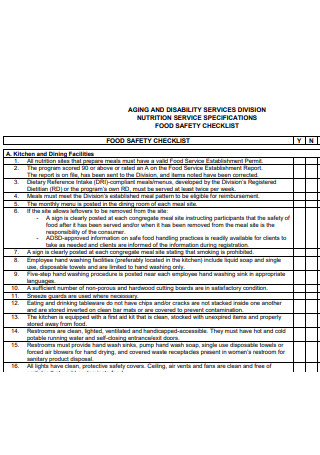
Nutrition Service Specification Food Safety Checklist
download now -

Printable Food Safety Checklist at Home
download now -

Basic Food Safety Self-Inspection Checklist for Food Processors
download now -
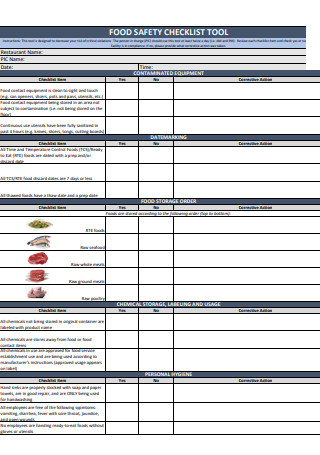
Food Safety Internal Audit Checklist Tool
download now -
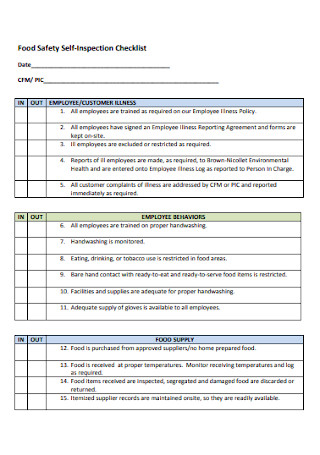
Food Safety Warehouse Self-Inspection Checklist
download now -
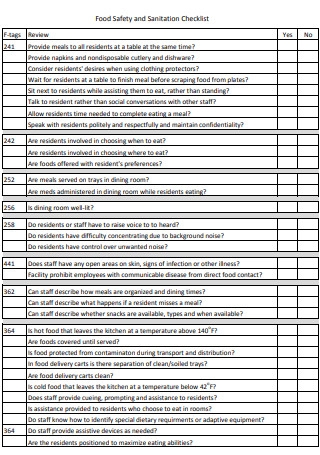
Food Safety and Warehouse Sanitation Checklist
download now -
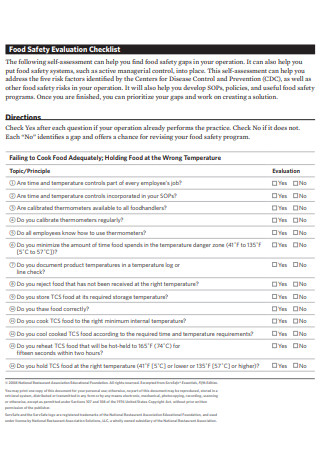
Food Safety Transportation Evaluation Checklist
download now -
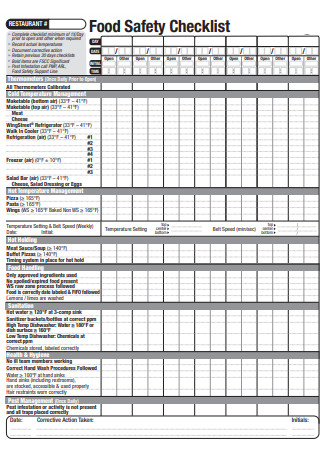
Weekly Restaurant Food Safety Checklist
download now -

Food Safety Checklist for Food Handler Hygiene
download now -
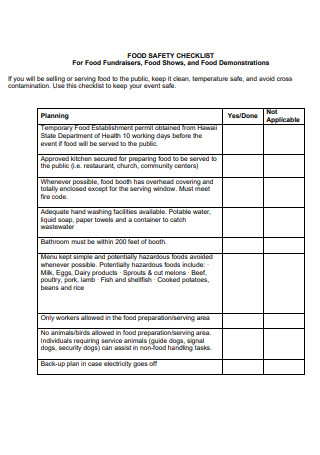
Food Safety Equipment Checklist For Food Fundraisers
download now -
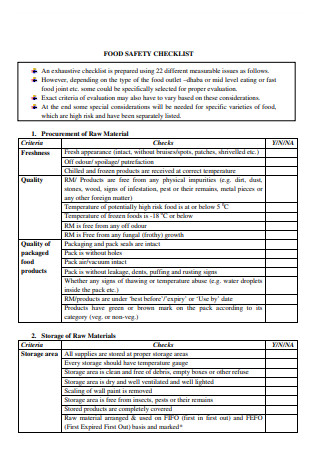
Preventive Maintenance Checklist Food Safety
download now -

Food Industry Safety Policy Checklist
download now -

Food Handler Cleaning Food Safety Training Checklist
download now -
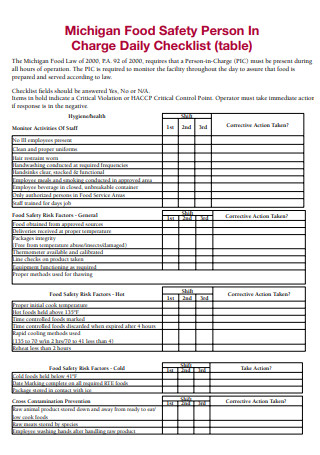
Food Safety Person In Charge Daily Checklist
download now -

Home Food Safety Checklist
download now -

Food Safety Preventive Control Plan Checklist
download now -
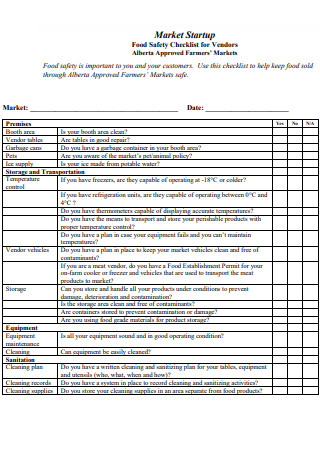
Employee Food Safety Checklist for Vendors
download now -
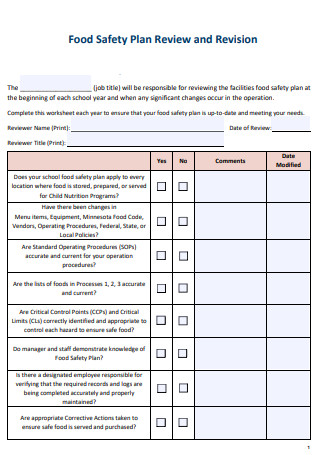
Food Safety Plan Review and Revision Checklist
download now -

Food Safety at the Hazard Farmers Market Checklist
download now -
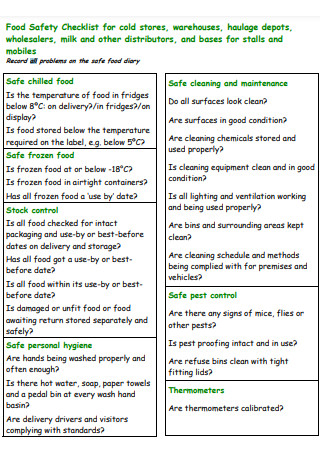
Food Safety Checklist for Standard Operating Cold Stores
download now -

Food Service Health and Safety Checklist
download now -
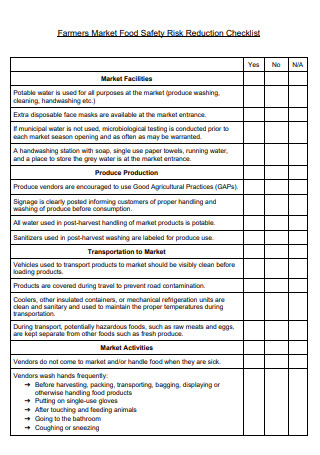
Farmers Market Food Safety Risk Reduction Checklist
download now -
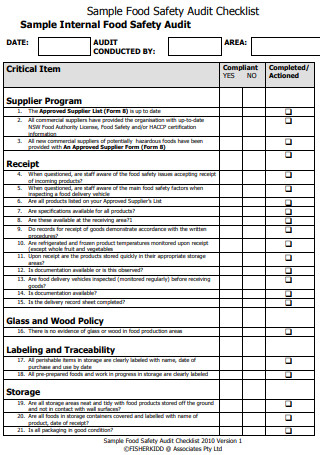
Sample Food Safety Audit Checklist
download now -

Food Safety Checklist For Planned-over Foods
download now -
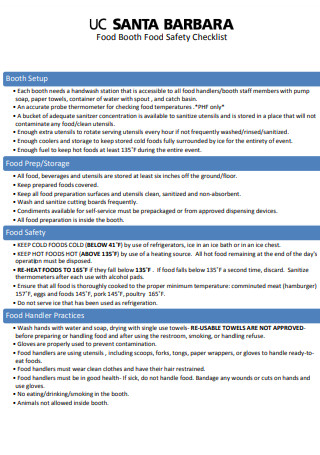
Food Booth Food Safety Checklist
download now -

Checklist for Food Safety
download now -
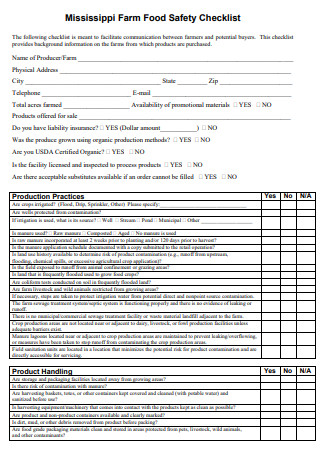
Mississippi Farm Food Safety Checklist
download now -

Food Safety Checklist for Meal Distribution
download now -

Food Safety Culture Checklist
download now -

Food Safety Backgrounder Checklist
download now -
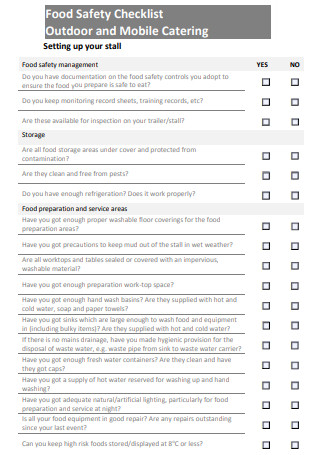
Food Safety Checklist Outdoor and Mobile Catering
download now -
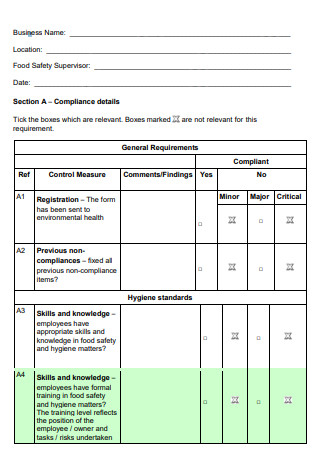
Formal Food Safety Checklist
download now -
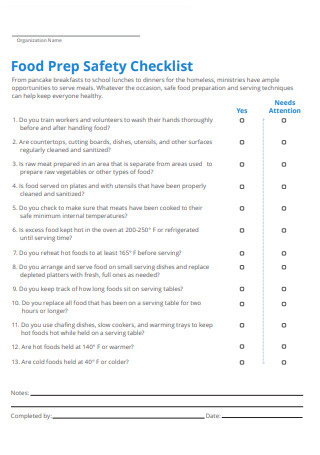
Food Prep Safety Checklist
download now -
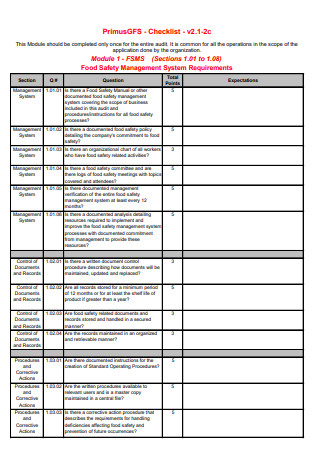
Food Safety Management System Requirements Checklist
download now
FREE Food Safety Checklist s to Download
38+ SAMPLE Food Safety Checklist
a Food Safety Checklist?
Benefits of Food Safety Regulations
Principles of Food Safety
How To Keep a Food Safe
FAQs
What is the definition of a health and safety checklist?
Why are eggs considered a high-risk food?
Is turmeric good for a fever?
What Is a Food Safety Checklist?
A food safety checklist is used to determine whether a food establishment adheres to safe food handling and good hygiene practices. It can assist in ensuring that food-related activities adhere to established standards. Food safety is critical because it helps protect consumers from food-borne illnesses. Additionally, it assists consumers in avoiding health-related risks such as allergy and even death. Also, it safeguards food processing establishments against product recalls that result in financial hardship due to unsafe products. Other issues that may arise due to hazardous products include rejected products, potential lawsuits, and business closure by public health authorities in response to reports of unsafe products being sold to the general public. According to a poll, up to 60% of people globally are concerned that their food will cause them to harm in the next two years. Additionally, more than half anticipate being significantly damaged in the next couple of years due to eating contaminated food.
Benefits of Food Safety Regulations
Families adore traditional gatherings centered on overflowing lunch tables piled high with every imaginable dish prepared and shared according to their personal preferences. A recent food poisoning incident that nearly resulted in a family death brought the family’s relationship with food safety into sharp focus. It led them on a journey of food safety discovery throughout the food processing and manufacturing reports. They realized that they all bear significant responsibility for food safety, particularly during the packaging, transportation, storage, cleaning, preparation, cooking, and food. Here are some of the advantages of food safety regulation.
Principles of Food Safety
Food safety is a concern that affects everyone, not just restaurant owners and cooks. Safe food habits begin at home. Maintaining them can help you and your family avoid potentially fatal foodborne infections. These can occur as a result of eating food that has been contaminated with poisonous substances and microbial pathogens that can cause harm to the body. The necessity of ensuring food safety cannot be overstated as our food supply becomes more global. Its principles are as follows:
Water and raw resources that are safe
When preparing healthy meal plans, it is critical to use safe water and basic materials. If you live in a country where tap water is not chemically treated to ensure its safety, it is preferable to drink only filtered or bottled water. It is advisable to wash raw materials such as fruit and vegetables before preparing and cooking them. Fruits and vegetables that are not sanitized may contain Listeria, a bacteria that can cause food poisoning and other serious illnesses.
Storage
Food storage is essential. Once cooked, many food products must be stored in a dry location away from direct sunlight or a refrigerator with precise temperature requirements. When preserving these products in their proper conditions, it’s critical to consider how long we may store and consume them before they become unsafe to drink. Another vital point to consider is the storage location. To avoid cross-contamination, it is advisable to keep meat and other food items that could potentially spill and contaminate other food items on the bottom shelf.
Cooking
Cooking is a crucial food hygiene principle. While this may seem self-evident, it is more about how you cook than remembering to cook the raw chicken. It is critical to prepare chicken and other foods that may contain microorganisms fully. Once the meat has been adequately cooked, never return to the same chopping board or plate on which the raw meat was first placed. Additionally, food separation is a way to avoid infection. This may entail storing raw meat in leak-proof packaging to prevent fluids from spreading to other food products.
Contamination
Contamination is an essential concept in food hygiene. Contamination of food occurs in three distinct ways:
- Chemical Contamination- Contamination of this type results in disease and food poisoning. Chemical contamination is frequently caused by pesticides that remain in fruits and vegetables. Chemical contamination can also occur due to kitchen cleaning chemicals, pest control agents, or food containers made of hazardous plastic.
- Physical Contamination- Physical contamination is caused by objects such as hair, glass, jewelry, or any other material containing bacteria that could contaminate food. This is a simple contaminant to prevent, but it is critical. It could be as simple as removing jewelry before working with food, pulling back your hair, and thoroughly washing your hands.
- Cross-Contamination- It is critical to avoid cross-contamination when preparing and cooking food. For example, raw poultry can induce campylobacter and salmonella food poisoning.
How To Keep a Food Safe
Bacteria from improperly kept, prepared, handled, or cooked foods frequently cause food poisoning. Food tainted with microorganisms that cause food poisoning may seem, smell, and taste normal. If food is not properly preserved, bacteria can grow to deadly levels. If you’re interested, here are some things to take to ensure the safety of your food.
Step 1: Food should be frozen safely.
When shopping, buy refrigerated and frozen items at the end of your journey and store them as soon as feasible at home. Take an insulated cooler bag or an icepack with you on hot days or for excursions longer than 30 minutes to keep frozen foods chilled. When transporting hot and cold foods, keep them separate. When you get home, immediately place refrigerated and frozen meals in the refrigerator or freezer. Check to see if foods in the freezer have frozen solid.
Step 2: Refreezing thawed food is not recommended.
While frozen food is thawing, bacteria that cause food poisoning can increase, therefore avoid melting frozen food in the temperature danger zone. Refrigerate defrosted food until ready to cook. If defrosting food in a microwave oven, cook it soon after defrosting. Avoid refreezing thawed food as a general rule. When frozen and handled between melting and refreezing, the risk varies according to the food’s condition, but fresh food should never be refrozen once thawed.
Step 3: Separate raw and cooked foods.
Refrigerate raw and cooked foods separately. Germs from raw food can contaminate cold cooked food, and if the meal is not properly cooked again, the bacteria can spread to deadly levels. Raw foods should always be stored in sealed or covered containers at the bottom of the refrigerator. Maintain a layer of raw foods beneath cooked meals to prevent liquids such as meat juices from trickling down and contaminating the cooked food.
Step 4: Choose food storage containers that are durable and non-toxic.
Ensure that your food storage containers are clean, good shape, and solely used for food storage. To avoid infection, cover them with tight-fitting lids, foil, or plastic film—empty opened cans into proper containers. Throw out high-risk food that has been left in the danger zone for more than four hours – do not refrigerate or save it for the next day. Check the expiration periods on food products and discard expired items. If you are unsure of the expiration day, discard it.
Step 5: Cook the dish completely and keep it refrigerated.
You cannot rely solely on color and texture to determine whether your food is cooked and safe to consume. Utilize this flow chart in conjunction with a food thermometer to determine whether your food has achieved a safe minimum internal temperature. Refrigerate perishable items at or below 40 degrees F within two hours of purchase. Raw meat packaged in its original packaging should be stored on the bottom shelf to avoid fluids from spilling and contaminating other foods.
Step 6: Select carefully.
Choose unbruised and undamaged food. Ascertain that no eggs have been cracked. Keep an eye out for a spotless meat or fish counter and a spotless salad bar. Avoid purchasing cans that are bulging or damaged, fractured jars, or jars with loose or bulging lids. If you’re shopping for fresh-cut produce, consider those that are chilled. Keep fresh fruits and vegetables individually from meat, poultry, and fish products at the grocery store, and always check your grocery list. Bring an ice chest to store frozen or perishable items if the journey home will take more than an hour. If it’s hot outdoors, keep your groceries in the air-conditioned passenger compartment of your car rather than the trunk, which may be uncooled.
FAQs
What is the definition of a health and safety checklist?
A health and safety checklist is a valuable tool for reinforcing best practices and ensuring that you comply with applicable safety standards. Conducting routine inspections using health and safety checklists helps prevent workplace accidents reports and prepares your firm for an EHO inspection. It is also advisable to create your own food plan.
Why are eggs considered a high-risk food?
When eggs are uncooked or undercooked, they pose a high risk of food illness. The most prevalent contaminants are salmonella, and salmonella can also be found in chicken.
Is turmeric good for a fever?
Turmeric is a powerful antioxidant that has long been employed in traditional Ayurvedic therapy. It is thought to be a herb that cleanses the entire body, particularly the liver. It aids metabolism and is used to treat fevers, infections, and inflammations.
Food safety is best achieved when everyone engaged with food, from the expert to the consumer, takes responsibility. Various procedures and good practices are adopted along the food chain to ensure that the food that reaches the consumer’s table is suitable for eating, that contamination risks are minimized, and that the population benefits from safe, high-quality food. However, food safety should not be solely the responsibility of food industry professionals. Policy and procedures guide professionals, but consumers are also responsible for ensuring food safety in their homes. The best method to practice food safety is to be well-versed on the fundamentals of nutrition: natural processes and, in particular, the threats to food posed by chemicals, both naturally occurring and those introduced by the environment. In the end, having more information regarding food safety benefits everyone.
