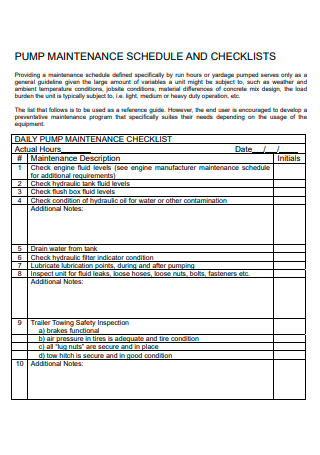
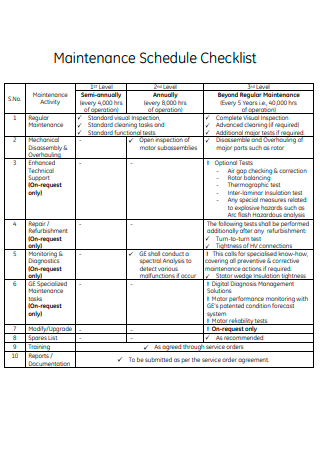
3+ Sample Maintenance Schedule Checklist
FREE Maintenance Schedule Checklist s to Download
3+ Sample Maintenance Schedule Checklist
What Is a Maintenance Schedule Checklist?
Benefits of Scheduled Maintenance
Tips for Optimizing Maintenance Scheduling
How to Begin a Program of Preventive Maintenance
FAQs
What is a scheduled maintenance activity?
Is scheduled maintenance necessary?
Which type of maintenance is most effective?
What Is a Maintenance Schedule Checklist?
Any task given a deadline and assigned to a technician is scheduled maintenance. It may be a recurring task performed at regular intervals or a one-time occurrence. Planned maintenance consists of inspections, adjustments, routine service, and shutdowns. Altering the bearings on a conveyor belt every 30 days or inspecting the condition of a motor every 90 days are examples of maintenance performed at regular intervals. In addition to recurring work orders, scheduled maintenance can take the form of a one-time work order. If a problem is identified with an asset, a time is scheduled to inspect and repair the asset. Scheduled maintenance’s primary objectives are to reduce reactive maintenance, equipment failure, and maintenance backlog. Standard inspections extend the life of assets and decrease the frequency of equipment repairs and replacements. Scheduling tasks also allows for more cost-effective and productive resource allocation. According to the statistics, the maintenance costs range between 15% and 40% of total production costs.
Benefits of Scheduled Maintenance
Commercial facilities require regular maintenance. This is because their moving parts are susceptible to wear and tear. It would be best if you opt for the scheduled maintenance plans for safety. With such strategies, you can guarantee the security of your system. Additionally, you can certify that you comply with safety standards. After doing so, you will gain these benefits. Here are eight reasons why scheduled maintenance is a good idea.
Tips for Optimizing Maintenance Scheduling
Your delivery schedule will likely be disrupted if your truck experiences last-minute mechanical problems. And if you have to pull a car from duty, there’s a chance that some orders won’t be delivered, which can harm customer satisfaction and revenue. These five maintenance planning principles and maintenance scheduling suggestions will assist you in being proactive and keeping your trucks operating with minimal downtime.
1. Have a distinct position for planning and scheduling
Do not overburden your fleet manager or delivery manager with the responsibilities of planning all routes, addressing delivery delays, and attempting to find time for maintenance. If you do, they will likely be unable to perform optimally and may prioritize ways over care, leading to mechanical issues. Instead, create a maintenance management position responsible for fleet maintenance and let your fleet manager focus on meeting delivery targets. Hiring a maintenance manager will alleviate the workload of your fleet manager and permit more frequent routine inspections of all trucks. Your maintenance manager transforms your company’s approach to truck problems from reactive to proactive, reducing vehicle downtime and saving money.
2. Use a CMMS
A CMMS, or computerized maintenance management system, keeps track of each truck’s mileage and upcoming required and optional maintenance. In addition, CMMS software keeps track of vehicle information, equipment logs, asset management, and work requests or orders. A CMMS software keeps each truck up-to-date on required preventative maintenance. It automatically tracks optional or last-minute maintenance, preventing these issues from being lost in translation during busy days. Although this can be accomplished with wipe boards or tracking spreadsheets, you should utilize maintenance organization software because it can track this data in greater detail by VIN, thereby increasing accuracy and leaving a detailed paper trail after maintenance has been completed.
3. Prioritize tasks and projects
Prioritize preventive maintenance over delivery routes to avoid long-term delays caused by extensive repairs. Prioritize routine maintenance to prevent future more significant problems. If you do not prioritize essential maintenance over deliveries, you risk a breakdown resulting in days of costly and preventable downtime per truck. According to research, preventative maintenance can save businesses money by reducing downtime, increasing efficiency, decreasing the risk of expensive reactive repairs, extending equipment lifespans, and enhancing customer service.
4. Plan weeks ahead
Plan your delivery orders and maintenance schedules several weeks in advance to identify potential delays or scheduling conflicts. Look for slow periods during which you can bring your trucks in for routine maintenance and ensure you have sufficient lorries on the road. Planned maintenance saves money and time because it allows you to work around busy or slow periods.
5. Concentrate on route planning and optimization as a value generator
Regular maintenance is a necessary expense because it is the only way to prevent your truck from developing significant problems. However, it is based on miles driven; therefore, reducing mileage will reduce costs. With route optimization, you can be confident that the distances between stops are always optimal. Planning and optimizing your routes will reduce the operational expenses of your business over time. In addition, the individual responsible for creating your delivery routes and schedules will increase delivery efficiency, resulting in increased revenue and customer satisfaction.
How to Begin a Program of Preventive Maintenance
Before we get started, let’s review the distinction between reactive and preventive maintenance. Reactive maintenance refers to repairs performed on broken equipment. Due to the unplanned qualities of these repairs, reactive maintenance is ideal for assets that are either non-essential to operations or inexpensive enough to be repaired frequently. Alternately, preventive maintenance involves performing maintenance tasks regularly to prevent unscheduled breakdowns and associated costs.
Step 1: Establish Clear Goals
Remember, not every asset requires scheduled maintenance. Equipment essential to production, quality, safety, and service delivery is an excellent candidate for preventive maintenance programs. Leave everything else to routine reactive maintenance. In addition, you do not need a substantial budget to develop a system that supports consistent results. For these reasons, it is crucial to begin the process by outlining the program’s objectives. Potential program objectives include reduced equipment downtime, improved work completion rates, maximum production time, and increased asset reliability. Request early input from your organization’s machine operators, maintenance technicians, and other key stakeholders. Their information will be essential for establishing practical priorities, making future hires, outlining standard operating procedures (SOPs), and establishing a successful preventive maintenance program.
Step 2: Inventory Your Assets
Once everyone is on board, conduct an inventory of the assets you wish to include in your preventive maintenance program. Regular asset history tracking will play a vital role in your PM strategy. Monitoring asset data will ensure that your team does not perform excessive preventive maintenance on one asset relative to others. Refining your program will also reveal maintenance spending patterns, worker inefficiencies, and optimal asset replacement intervals. Also, consider the asset’s current condition, productivity, and workplace safety. You can organize your data using an excel spreadsheet or a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS).
Step 3: Perform a Critical Analysis
Criticality analysis is the process of evaluating the significance of assets about their potential risks. In this context, the risk is defined as all possible failure occurrences and their potential effects on organizational productivity, expenses, and safety. Taking the time to rank the importance of your assets will assist in determining which routine maintenance tasks should be scheduled first, based on the availability of resources. High-priority assignments are crucial to production/safety AND have high repair/replacement costs. Alternatively, equipment maintenance that is not essential to production or safety and has low repair/replacement costs should be deprioritized. Assets that are non-essential, inexpensive, and worn-out are typically better for reactive maintenance. The procedure appears straightforward until competing priorities are weighed against one another.
Step 4: Identify Optimal PM Ratios
The financial benefits of preventive maintenance and unproductive worker hours are overshadowed by excessive maintenance. Determining the optimal preventive maintenance ratios for your unique assets and work environment is crucial. First, consult your equipment manufacturer’s manuals. These manuals contain valuable information regarding recommended maintenance schedules, work instructions, and essential spare parts. Next, examine your organization’s maintenance data from the past to gain unique insights into asset failure patterns. In addition, machine operators and maintenance technicians who work with the assets can provide insightful information regarding their behaviors.
Step 5: Schedule Your PMs
It is time to plan your preventive maintenance activities. Do not attempt to tackle everything simultaneously. Before breaking down high-priority tasks into short-term schedules, we advise developing a long-term maintenance plan. A user-friendly Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) will make assigning, monitoring, and modifying your PM program a breeze.
Step 6: Train Your Team
Up to 12% of unplanned downtimes can be attributed to operator error. If you do not want to onboard the employees responsible for maintaining your assets, your preventive maintenance program will likely fail, regardless of how meticulously you plan it. Organize training sessions for employees who will be holding the assets. Also, ensure that work instructions are written in clear, simple language. You should also provide additional learning resources for employees’ reference. Ensure that they are aware of when and how to perform preventive maintenance.
Step 7: Track the Success of the Preventive Maintenance Program
Monitor your chosen KPIs, solicit team member feedback, and make appropriate adjustments. Remember that you can never eliminate downtime. Instead, focus on progress by determining the number of PMs performed on critical assets and the number of times these assets have failed since the program’s inception. Based on this information, you should be able to determine whether you should reduce or increase your PM activities. If your team is not achieving its objectives, conduct a root cause analysis to determine where inefficiencies are occurring and make the necessary course corrections.
FAQs
What is a scheduled maintenance activity?
Predetermined maintenance tasks are those that are planned. They ensure that assets remain operational for as long as possible without unscheduled downtime. Maintenance triggers, such as time, usage, event, and condition, determine the timing of scheduled maintenance.
Is scheduled maintenance necessary?
Every vehicle requires routine maintenance to function correctly. Following your car’s manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedule will protect your investment, help ensure the vehicle’s durability and dependability, and even save you money.
Which type of maintenance is most effective?
Predictive maintenance is superior to preventive maintenance in detecting potential failures and determining required actions. Examine our comparative article on these two maintenance types to better understand their distinctions.
Executing a scheduled maintenance plan should be preceded by a comprehensive review of all assets, including their relative importance to the organization and anticipated maintenance needs. The time spent creating a new scheduled maintenance plan is also the optimal time to question any preconceived intervals or tasks that may have been applied arbitrarily or without adequate data. Are you prepared to create a Maintenance Schedule Checklist? We are cheering you on!