7+ SAMPLE Workplace Safety Checklist
-

Workplace Safety Inspection Checklist Template
download now -
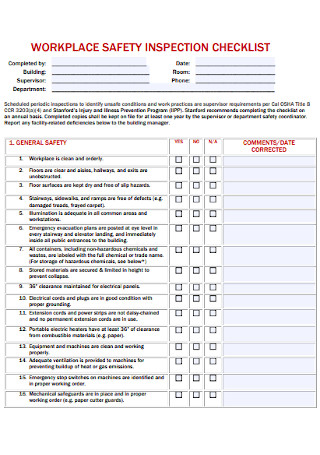
Workplace Safety Inspection Checklist
download now -
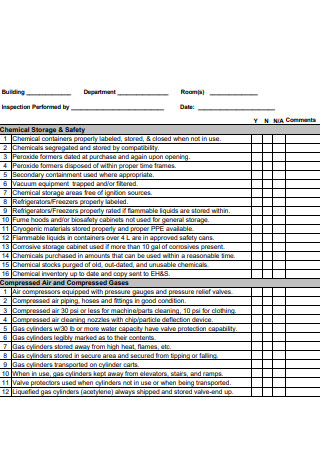
Workplace Safety Audit Checklist
download now -

Workplace Safety Checklist
download now -

Remote Workplace Safety Checklist
download now -

COVID-19 Workplace Safety Planning Checklist
download now -

COVID-19 Workplace Safety And Health Checklist
download now -
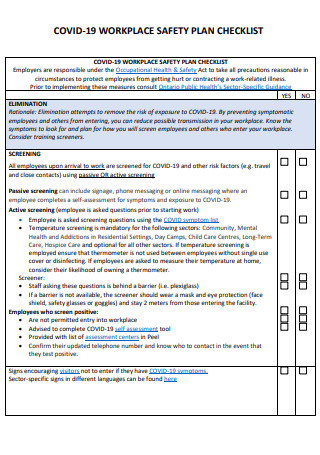
COVID-19 Workplace Safety Plan Checklist
download now
FREE Workplace Safety Checklist s to Download
7+ SAMPLE Workplace Safety Checklist
What Is a Workplace Safety Checklist?
Aspects of Checklist Design That Should Be Considered
How do you plan for inspections?
How to Write a Workplace Safety Checklist
The Benefits of a Workplace Safety Checklist
Types of Hazards in the Workplace
Issues with Checklists that Could Occur
FAQs
Who should be in charge of safety inspections?
What are the objectives of an inspection?
Is it possible to utilize different types of inspection reports?
When should safety inspections be performed, and how often should they be done?
What Is a Workplace Safety Checklist?
Safety Checklists are records that are used to identify possible dangers during safety inspections. Each workplace and sector has its unique set of risks, and health and safety experts must be able to determine which checklists are appropriate for individual workplaces and procedures in order to guarantee that all safety requirements are met. Safety checklists are a useful tool for identifying potential workplace dangers. They should be completed during inspections, reported on, and used as the basis for safety recommendations, as well as being recorded for record-keeping purposes. This article has an available workplace safety inspection checklist that you can use as a reference in making one that suits your office.
Aspects of Checklist Design That Should Be Considered
It’s vital to remember that authorities will not take inspection checklists seriously if they are badly prepared. Lists that aren’t thorough enough or aren’t asset-specific are typically seen as extra paperwork that must be completed only for regulatory purposes.
Furthermore, many of the advantages listed will not be available with these weaker inspection checklists. As a result, while designing an effective worksite Inspection Checklist, be careful to include the following features:
How do you plan for inspections?
Strategic Planning is essential for an effective inspection. These are additional reminders in planning before conducting a thorough inspection within your workplace.
How to Write a Workplace Safety Checklist
Some companies task authorities or experienced individuals to walk around the building and search for issues. Others have sit-down sessions to address potential job risks. In the meantime, many utilize checklists to ensure that inspections include relevant points and that they are recorded for future reference. These checklists can be a simple method to make inspections more tangible, which can enhance operations and safety in many situations. Check out the various workplace safety checklist examples that have been provided in this article for you to use as a reference. You may not have the time to start from scratch which is where a template will be important to utilize. But of course, you can’t just use a generic checklist, you must take the time to observe what your own company has and match your checklist with your company.
Step 1: Check on the Tools and Machinery
Equipment within the company be it used by employees themselves or guests and visitors need to be checked for any mishandles that can lead to it harming users of the said machine in the future. For larger and smaller types of machinery alike, machine guards should be present and prepared beforehand to avoid accidents. Otherwise, a Work Accident Report may be filed. If a machine creates excessive noises or an increasing sound level, be sure that it isn’t faulty as well.
Step 2: Review Employee Facilities
The next step, a suggestion for the checklist is to proceed to where employees may be staying most of the time. Make sure there are no confined spaces that can trap an employee when emergencies ring out, this goes with floor and wall openings to be wide enough for passage. Platforms, stairs, and ladders should also be wide and strong enough to handle a certain capacity or amount of weight. Lastly, update and locate a medical first aid as well to keep track that it can be easily accessible if necessary.
Step 3: Survey Electrical Outlets
Electricity should never be underestimated even if they are covered up because certain wirings may have been mishandled or move in certain situations. Make sure to survey the lighting and related electronic devices found within the company.
Step 4: Scan Storage Spaces
This step may only apply to a company with an available warehouse or deals with shipping systems. Some employees may be handling certain materials and have loading or unloading storages that can be dangerous if left unattended or un-updated. This may be where personal protective equipment comes in handy.
The Benefits of a Workplace Safety Checklist
When a complete inspection checklist is created, it will include all of the required information for each asset. In the field, it must be basic and easy to use, but not to the point of being too general. Inspection checklists can be completed on paper or digitally, utilizing mobile devices and cloud-based applications if they are properly constructed. The numerous functions of a digital checklist are a benefit. All of these advantages contribute to a company’s bottom line while also promoting employee well-being. A decent inspection checklist should be able to do the following:
Types of Hazards in the Workplace
Dangers in the workplace are uncommon and in order to avoid and address them, then you would need to know the different types between them. In knowing the different types of dangers and hazards, you can come up with a better Risk Management Action Plan for the benefit of the company and even the employees.
Issues with Checklists that Could Occur
As previously said, as people become accustomed to utilizing checklists, they may tend to run through them rapidly and without giving them much consideration. When checklists aren’t suited to your company or aren’t precise enough, this problem becomes even more prevalent. Encourage staff by leaving encouraging comments, promptly following up on concerns discovered during inspections, and making inspections a subject of conversation. Health and Safety Checklist, in order to be used appropriately for your company, adjust it to suit your company.
Another issue with checklists is that, while they can aid in identifying existing issues, they may not be as effective in identifying new risks. People may miss anything not on the checklist since they are accustomed to checking for certain concerns. This is especially problematic when procedures or machinery change. If a new chemical is introduced to a work process, for example, the checklist may not include information regarding any new equipment that is necessary for the task. As a result, if anything in the workplace changes that might affect safety, checklists should be updated.
FAQs
Who should be in charge of safety inspections?
Engineers, maintenance staff, occupational hygienists, health and safety specialists, as well as supervisors and managers, can form a safety inspection team to assist create and monitor action controls. A safety inspection squad should be made up of qualified and certified health and safety personnel who are familiar with rules and procedures, as well as possible risks and work processes.
What are the objectives of an inspection?
Inspections are essential because they allow you to listen to the concerns of employees and supervisors, get a better knowledge of occupations and activities, and detect current and prospective dangers. establish the root causes of risks, provide recommendations for remedial action, and keep account of the measures done to remove or control the risk.
Is it possible to utilize different types of inspection reports?
There are three more types of inspection Reports namely an ongoing, pre-operation, and periodic. As part of their job obligations, supervisors and staff perform ongoing inspections. Hazardous situations are identified during these inspections, which are either corrected promptly or reported for further action. The frequency of these inspections varies depending on the quantity of equipment used and the conditions in which it is used. Regular, scheduled examinations of key components of equipment or systems that have a high potential for inflicting significant harm or disease are known as periodic inspections. Inspections are frequently performed as part of preventative maintenance or hazard management programs. A qualified or competent person may be required to check particular types of equipment, such as elevators, boilers, pressure vessels, scaffolding, and fire extinguishers, at certain points in the work process and at regular intervals, according to laws and regulations.
When should safety inspections be performed, and how often should they be done?
The frequency of safety inspections is determined by a number of criteria, including your organization’s previous incident records, The size and quantity of work activities, as well as the risk quotient that might emerge due to the equipment and work procedures used, are all factors to consider. Even incorporating new processes or technology might introduce new or unexpected risks. Hazardous zone as a result of the environment or other underlying risks. In an ideal world, safety inspections would occur as often as regular safety meetings. Safety inspections and meetings should be separated by at least a week to allow teams to take control measures and focus on concerns that require further attention.
Safety checks can be done in a variety of methods at work. In order to ensure the safety of the company, you need to have a workplace inspection form ready in case there are certain areas of the company building that needs assessing. If so, a safety orientation checklist can also function in a similar manner in order to cater to the safety requirements of the company. Now that the article has defined and showed you the steps in writing a workplace security checklist, you should come up with a checklist for your workplace to ensure that the employees and everyone within the company are safe and far from danger.
