17+ SAMPLE Product Management
-
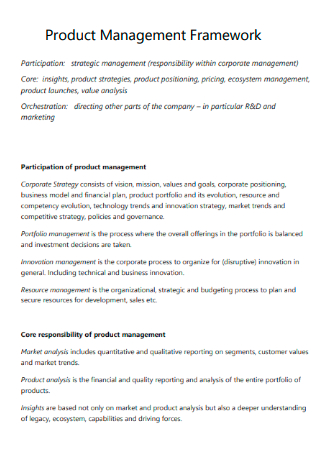
Product Management Framework
download now -

Sample Product Management
download now -

Strategic Product Management
download now -

Health Product Management
download now -
Software Product Management Form
download now -

New Product Management
download now -

Digital Product Management
download now -

Product and Brand Management
download now -

Discipline of Product Management
download now -

Product Portfolio Management
download now -

Basic Product Management
download now -
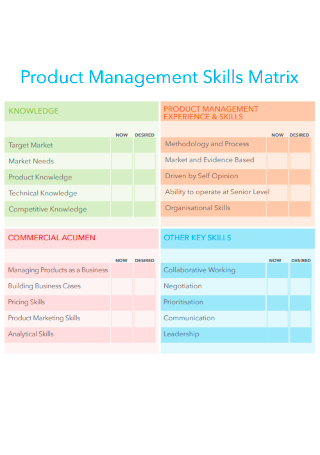
Product Management Skills Matrix
download now -

Product Management & Knowledge Management
download now -

Fashion Product Management
download now -

Product Manager View on Practical Assumption Management
download now -

Clinical Study Product Management
download now -
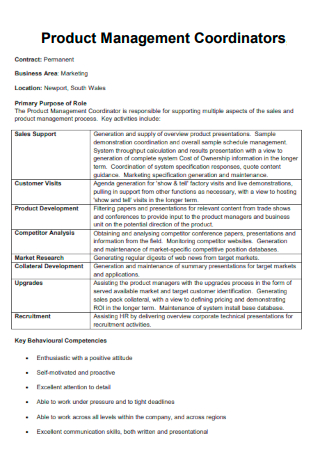
Product Management Coordinators
download now -

Product Security Risk Management
download now
What Is Product Management?
Product management is an organizational function that guides each step of the product lifecycle, starting from the product development stage to the positioning of the product until the product pricing stage. To do this, organizations must focus on the product itself and its consumers. For an organization to build the best possible product for the public, product managers must advocate for the target consumers within the organization and to make sure that the business listens to and heeds the voices of its customers. By putting the customers first and foremost in the product management process, product teams and members routinely produce products that are better-designed and have high performance. In industries that need to produce better and improved versions of products like technology, there is a heavier need to have an intimate understanding of the customers and the ability to create tailored and accurate solutions through the products. Product management is a role within product development teams focusing on the successful execution of the product lifecycle. Product management is also a cross-functional role. It means that there is cross-functional communication with stakeholders, C-level executives, and the marketing and sales departments.
According to a survey coming from Pragmatic Marketing Inc. in 2016 that surveyed 2,500 product managers and product marketers, about 28 percent of the time focuses on the strategizing production while 72 percent of the time concentrates on the tactics and execution of products.
Types of Product Managers in Product Management
Pursuing a career in product management is interesting for many individuals and many reasons. Product managers come from various kinds of backgrounds and industries, and the variety constitutes different types of product management processes and procedures. The section below covers the various types of product managers that operate in different sectors that companies implement in their businesses.
Terms Related to Product Management
When working with product management, there are terms and phrases that individuals must be familiar with to understand the field better. There are different vocabularies that product management teams use when communicating with one another, and persons functioning in product management must have a better grasp and understanding of what these terms mean. The section below covers different terminologies that are present in product management.
A Guide To a Product Management Process
There is no standardized process for product management. Processes evolve and adapt to the changes that the company implements. The processes also depend on the product lifecycle stages and the personal preferences of product team members and company executives. The section below provides a helpful guide for individuals and teams about the process of product management.
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step of the product management process is to identify the high-value pain point of customers. Many individuals want something better or something that they do not currently have. Product management teams turn these abstract customer complaints and wants into a problem statement to find the most plausible solutions. Solving customer problems and easing the pain that they feel ignites the spark and motivation of the team for the next steps to come. Without a clear and set goal that directly impacts the identified pain points of consumers, the product will have a difficult time gaining traction and gaining the attention of customers.
Step 2: Quantify the Various Opportunities
There are many problems and pain points associated with customers. However, not all of them are worth solving. To justify the investment to be put into constructing and developing products, product managers must build a business case according to the total addressable market, the severity of the problem, and the willingness to purchase or pay for alternative solutions. After product management evaluates the potential market, they can then start trying to address the problem.
Step 3: Research About Potential Solutions
With a clear target in mind, product management can investigate customer problems and pain points. The team must be able to identify all the plausible solutions to address the problem and not rule out any answers. Product managers must first validate candidates according to the target market, going through various ideas from the technical team to guarantee that these are feasible. Product managers also start to develop customer personas to gauge if there is interest in the identified solutions.
Step 4: Developing an MVP
After validating the appeal and viability of a solution, the product development team can take full charge. The first thing to do is to define a standard functionality for the product so the team can begin building toward a working product that the company can test. Creating a minimum viable product (MVP) is to guarantee that the core function of the product meets the market needs. MVPs can test how well the product performs and the overall message and position in the value proposition with product marketing.
Step 5: Create a feedback loop
Customer feedback is one of the essential parts of the product life cycle. It is during this step of the product management process that the team receives feedback about what customers think, say, and feel about the product since they have first-hand experience. Product management must also make it easy for customers to leave constructive feedback. Consequently, they must also process, synthesize, and react to feedback and create action plans in the product roadmap and backlog.
Step 6: Set the Strategy and Execute
Assuming that customers receive the product well, the next step is to create a product strategy. Establish goals and objectives to improve the product, get it into the market, expand its reach, and align with the overall organizational strategy for desired outcomes. The strategy must be reasonable, progress towards goals, and contains defined key performance indicators. The strategy must secure stakeholder alignments and buy-ins. After having a plausible product concept, an established feedback system, and a rational strategy, the next step is to execute the strategy. There are various prioritization frameworks available for product management to decide on the activities and actions to take. Make sure to base the decision-making process on the items that have the greatest impact on the objective. When all is this set, product management teams can create the product roadmap to visualize the lifecycle of the product.
FAQs
What are the three major areas of project management?
The three primary areas that project management focuses on consist of product discovery, product planning, and product development.
How do you become a product manager?
There are certain requirements for individuals who are planning to endeavor in project management. As a project manager, a person needs an undergraduate degree, years of experience, and specialized training.
Is product management part of marketing?
Many companies and organizations put product management in other departments. However, traditional businesses consider product management plays a marketing role.
Product management is an essential procedure for many organizations, especially for those that provide products for consumer markets. Product managers are vital to the production of goods to target and cater to specific markets according to their pain points, needs, and problems. Product management focuses on the product life cycle, ensuring that the products the company produces address the problems of purchasing consumers while performing efficiently. Familiarize yourself with the product management process and download the templates available in the article. Get yours today from Sample.net.
