20+ SAMPLE Process Map
-
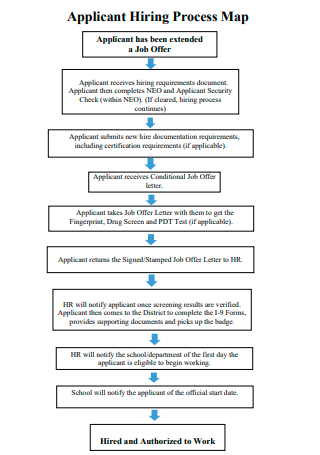
Applicant Hiring Process Map
download now -

Processing Map For Hot Working of Metals
download now -
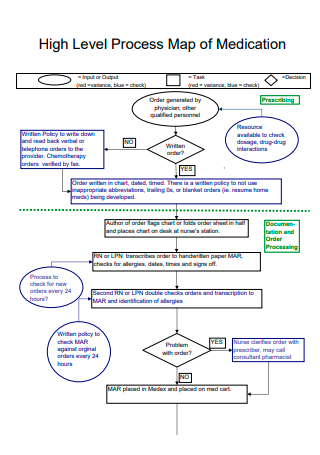
High-Level Process Map of Medication
download now -

Maximizing Enrollment Process Ma
download now -

Strategic Planning Process Map
download now -

Developing Process Maps for Oil and Gas
download now -

Process Map in PDF
download now -
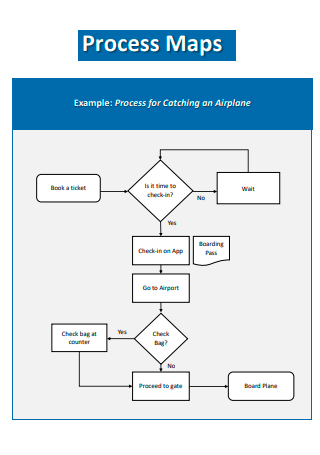
Process Map Example
download now -

Implementation Process Map
download now -

Research Process Map
download now -
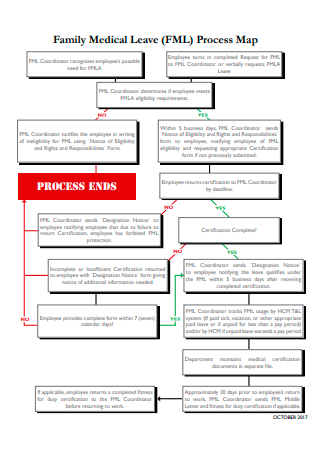
Family Medical Leave Process Map
download now -
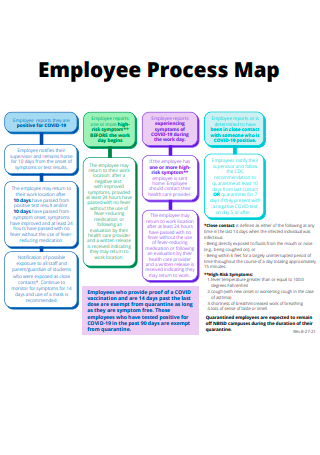
Employee Process Map
download now -
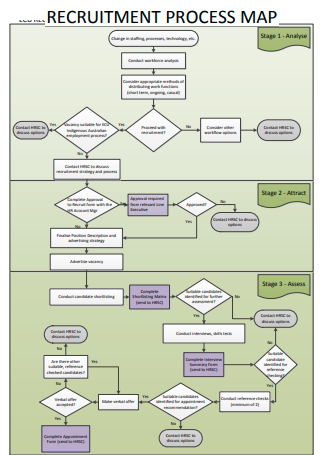
Recruitment Process Map
download now -

Printable Process Map
download now -
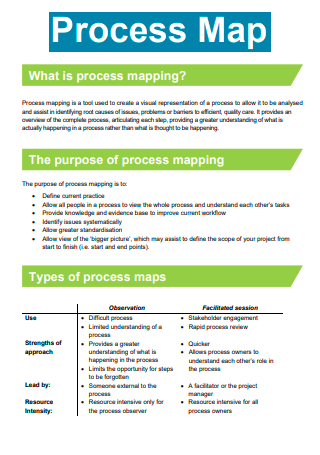
Formal Process Map
download now -

Claims Process Map
download now -
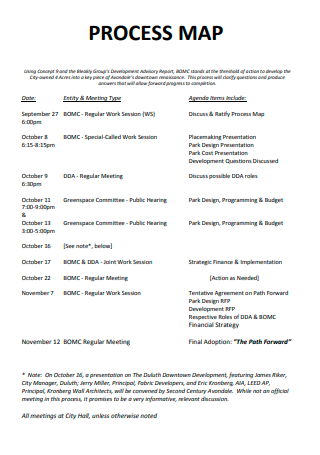
Simple Process Map
download now -
Interview Process Map
download now -

Process Map Viewer
download now -
E-Travel Process Map
download now -
Process Map Format
download now
What Is a Process Map?
A process map is a planning and management tool that businesses use to provide a visual representation of a workflow. It shows a series of steps, instructions, or sequences of events to produce an end product or deliverable. A process map is also known as a flowchart, process flowchart, process chart, functional process chart, process model, workflow diagram, functional flowchart, process flow diagram, and business flow diagram. The document shows the people and the procedures involved in a work process that any business or organization can use while revealing areas for improvement. The purpose of process mapping is to disseminate how particular processes and procedures work concisely and clearly. It enables team members to understand the methods of completing a task or activity without long verbal instructions. By mapping a process from beginning to end, the organization and its employees possess a comprehension of how the entire procedure happens, so there is room to identify inefficiencies and make improvements. Companies can also utilize process mapping for any type of process. However, process maps are far more common in process analysis, training, process improvement, and integration. They are valuable for describing and communicating complex processes, addressing recurring problems, and coordinating the responsibilities of team members for a project, program, or event.
According to a 2015 BPTrends survey, about 96 percent of companies record some kind of documented process. However, processes and procedures are what make companies run. Therefore, all processes must have a record because employees perform these activities more than once, running them repeatedly. Setting up a process map also helps to disseminate the procedure efficiently and effectively.
Symbols Used In Process Mapping
Specific symbols represent each element of process mapping. These symbols go by many names, including flowchart symbols, flowchart shapes, and flow diagram symbols. The symbols that people observe in a process map stem from the Unified Modeling Language or UML. UML is an international standard for drawing or creating process maps. The process symbols that organizations use fall into different categories, including process or operation, branching and control of flow, input and output, file and information storage, and data processing. The section below describes the various symbols that are present in process maps.
Types of Process Maps
Process maps vary in shape and size. Despite serving the same function or purpose, there are particular types of process maps that are more suitable for specific projects or programs. The section below covers the most common types of process maps that organizations use to represent their procedures.
How To Write a Process Map
Creating process maps is now a streamlined process as it uses workflow management software that provides a better understanding of process mapping. Process maps are also available to individuals using Microsoft applications, including Word, Excel, and Powerpoint. The essence of process mapping is to communicate a certain process to others to achieve organizational objectives. Having an idea of how to create a process map build stronger communication and understanding in the company. The section below covers the steps in developing a process map.
1. Identify a Procedure that Requires Mapping
The first step is to determine a process that requires a map. Ask whether there is an inefficiency in the steps that requires improvement. Is there a new process that needs relaying to all the team members for a project? Is there a process that raises many questions about a specific procedure? Identify the process that the organization needs to map out and start from there.
2. Identify the Necessary Activities for the Process
Make sure to record all the critical tasks that complete the procedure. Create a list of all the activities and the people responsible for performing them. Collaborate with team members and other stakeholders that are part of the process to account for all the required steps accurately and determine the required level of detail when executing tasks. The team must establish a where the start and end of the process to know which tasks to include to produce the desired results.
3. Write Out the Correct Sequence of Steps
After completing a list that lists all the necessary activities the team needs to complete a process, the next step is to sequence the activities into a step-by-step procedure until the entire process is complete from start to finish. It is also during this step that the team conducts a gap analysis to check for any gaps in the process, making the necessary adjustments after.
4. Begin Drawing the Base Flowchart Using the Process Map Symbols
Select the most appropriate type of process map to accommodate the steps and procedures. Draw out the necessary processes and represent the steps with the appropriate mapping symbols. The two previous sections help to identify which type of process map a team can use, along with the different process map symbols.
5. Finalize and Share the Process Map with Stakeholders
After the team finishes setting up and completing the process map, review it with the stakeholders that are with the team members during the process to make sure that everyone is on the same page and is in agreement with the information on the process map. Guarantee that no steps are left out or incomplete, and check for any inconsistencies and redundancies in the process map.
6. Analyze the Map To Check for Areas of Improvement
Once the process map accurately describes the process workflow, the comprehensive process map serves as a management tool that the team can analyze to discover various ways of improving the process. Take the team members and the stakeholders and gather all the feedback to identify the bottlenecks and inefficiencies present in the process. After identifying all the areas of improvement, take the initiative to resolve them and rework and perform the necessary adjustments to reflect these improvements.
FAQs
What are the main components of a process map?
Three principal components that make up a process map include inputs, outputs, and the necessary steps in the process.
What is a Six Sigma process map?
Six Sigma process mapping focuses on a flowchart illustrating all the steps of a process that documents all the inputs and outputs of an event, activity, or process in an easy-to-read manner using a step-by-step format.
What is the purpose of constructing a process map?
The purpose of working on a process map is to illustrate the sequenced flow of a process, activity, or event for organizations and businesses to improve their efficiency. It also provides the necessary insights into a specific procedure that enables teams to brainstorm ideas to improve the steps in a process, increase communication, and create a process document.
Process maps are essential to describe complex processes that are essential to keep a business running smoothly and efficiently. Business mapping provides different benefits to organizations that utilize them. Process mapping documents various business processes and procedures. It also enables knowledge transfer, produces an agreement for best practices, shows that all the processes are compliant with standards, and enables opportunities for improvement and continuous improvement. Write a process map for the organization today by selecting from the provided templates above, selecting from 20+ SAMPLE Process Map in PDF, only from Sample.net.
