48+ Sample Data Reports
-
Test Data Report
download now -
Employment Data Report
download now -

Government Data Report
download now -

Manufacturers Data Report
download now -

Monthly Suicide Data Report
download now -

Cultural Safety Baseline Data Report
download now -
Casting Data Report
download now -
Annual Data Report
download now -

Data Gap Analysis Report
download now -
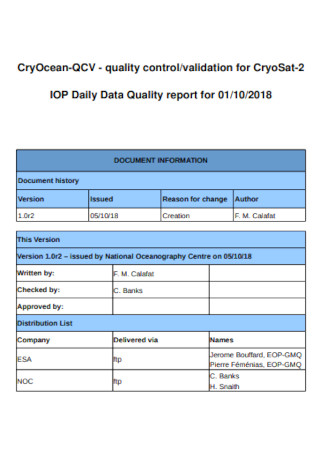
Data Quality Report
download now -
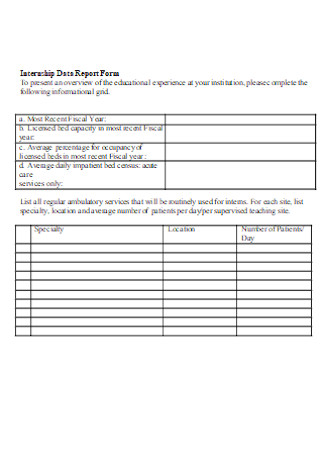
Internship Data Report
download now -

Qualitative Data Analysis Report
download now -

Structure of a Data Analysis Report
download now -
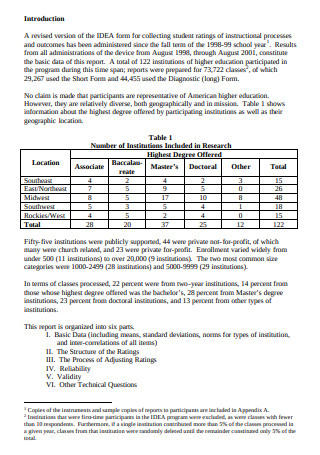
Data Technical Report
download now -

Basic Meter Data Report
download now -
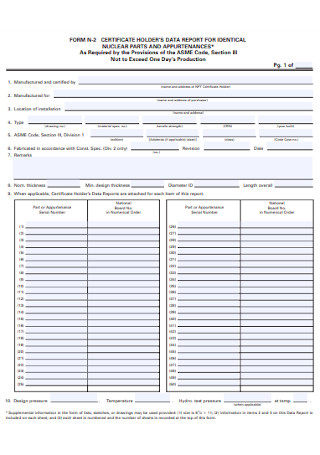
Holders Data Report for Indentical
download now -

Life Settlement Provider Data Report
download now -
Programme Data Report
download now -

Basic Data Report
download now -
Beneficiary Data Report
download now -

Applicant Data Report
download now -
Health Insurance Data Report
download now -

First National Waste Data Report
download now -
Data Report on Spouse
download now -
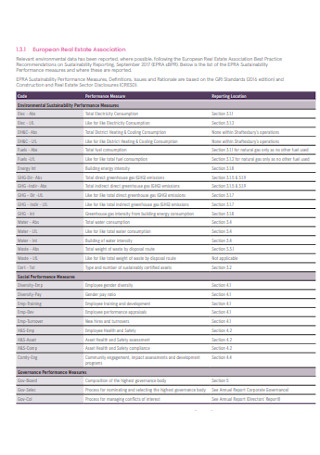
Sample Sustainability Data Report
download now -
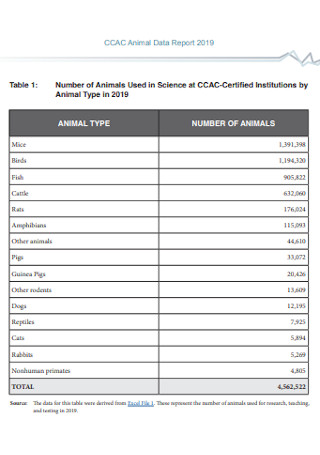
Animal Data Report
download now -

Strom Water Data Report
download now -
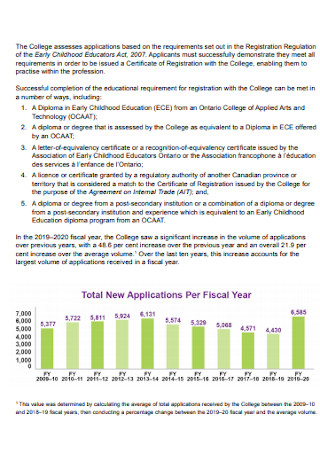
Membership Data Report
download now -
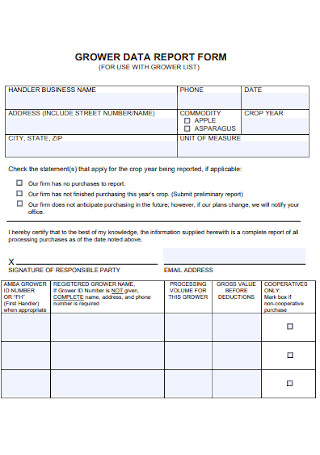
Grower Data Report Form
download now -
Site Data Report
download now -
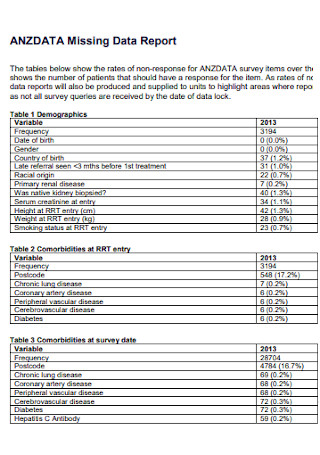
Missing Data Report
download now -

Data Analytics Center Report
download now -
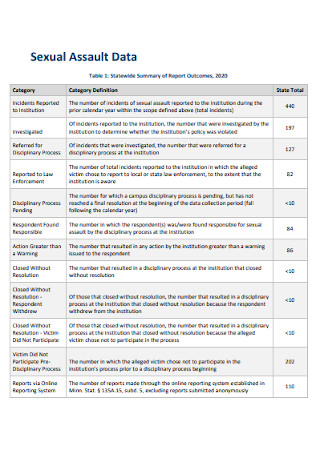
Sexual Assault Data Report
download now -

Childhood Experience Data Report
download now -
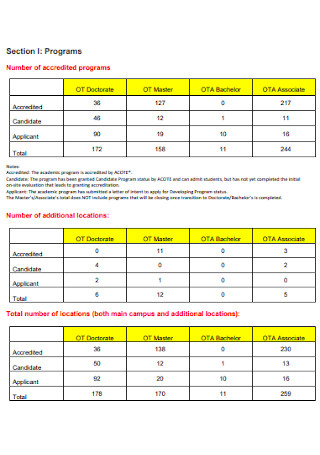
Program Annual Data Report
download now -

Individual State Aggregate Data Report
download now -
Data Report Request Form
download now -
Academic Data Report
download now -
Meter Data Reports
download now -
Data Report for Safety
download now -
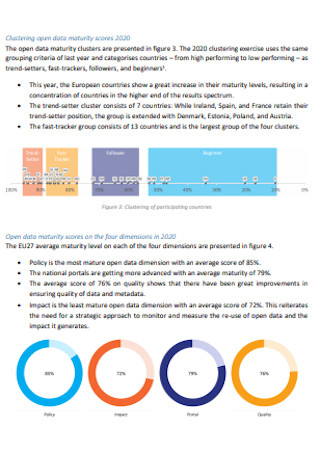
Open Data Marurity Report
download now -
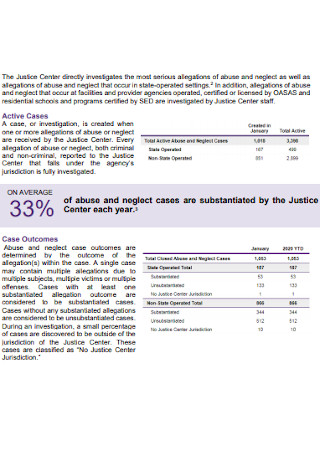
Monthly Data Report
download now -
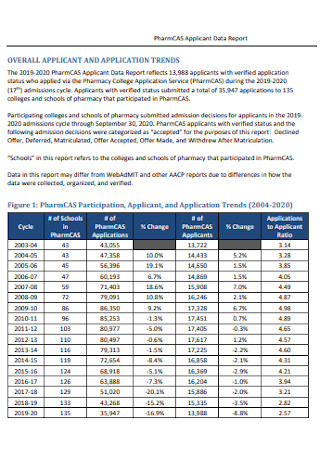
Pharmacas Applicant Data Report
download now -

Timesheet Data Report
download now -
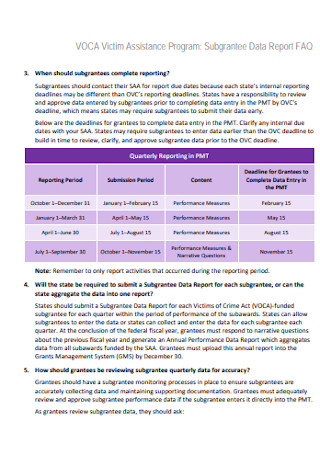
Subgrantee Data Report
download now -

Correspondent Banking Data Report
download now -

Construction Data Report
download now -
Standard Data Report
download now -
Softwae Resources Data Report
download now
FREE Data Report s to Download
48+ Sample Data Reports
What Is a Data Report?
Why Is Data Reporting Important?
Basic Components of a Data Report
Types of Data Report
How to Write a Data Report
FAQs
What characteristics distinguish an excellent data report?
What is the format of a report?
What is the definition of a media report?
If you use business intelligence correctly, you will not only be able to connect the dots in your data, but you will also be able to gain control of your data across the organization and boost your bottom line. Here, we’ll look at what a data report is, organize report data, and some of the most remarkable data report examples available, all generated with modern software.
What Is a Data Report?
A data report is a tool for evaluating past, current, and future business information while keeping track of a company’s overall performance. It is a decision-making tool that combines multiple business data and is typically utilized on an operational and strategic level. As previously stated, these reports had features such as static data presentation, manually written or calculated calculations. Still, with the introduction of modern processes such as dashboard reporting, they have evolved into an invaluable resource for successfully managing your sales processes, marketing data, even robust manufacturing analytics, and numerous other business processes required to stay ahead of the competition. Data reporting is the process of gathering and structuring raw data and converting it into a usable format to assess your organization’s continuous performance.
Basic queries about the state of your firm can be answered with data reports. Static data reports often employ the same structure over time and collect data from a single source. A data report is just a compilation of facts and figures that has been documented. Take, for example, the population census. This is a technical document that conveys essential information on a country’s population and demographics. It can be presented as text or as a visual representation, such as a graph or chart. However, it is static data that can be utilized to evaluate present conditions. According to statistics, 73% of journalists and data reporters who respond to the survey have encountered online violence in their work, including threats of physical and sexual violence and cybersecurity attacks. Financial Data such as revenues, accounts receivables, and net profits are frequently summarized in a company’s data reporting. This keeps track of the company’s financial health or a specific aspect of your finances, such as sales, in real-time. To provide an accurate picture of the overall sales pipeline, a sales director can report KPIs by location, funnel stage, and closing rate.
Why Is Data Reporting Important?
Data provides a metric by which we can track our development in many aspects of our lives. It guides our professional decisions as well as our daily activities. A data report will show us where we should invest the most time and money and where we need to organize or pay more attention. Every industry relies heavily on accurate data reporting. By offering more effective and efficient patient care, business intelligence in healthcare can help physicians save lives. Data reports can be utilized in education to investigate how attendance sheets link to seasonal weather patterns or how acceptance rates intersect with neighborhood regions. The most competent business analysts master specific competencies. A good business analyst should be able to prioritize the most critical data. There is no space for errors in data reports. Therefore they must be exceedingly thorough and detail-oriented. The capacity to organize and aggregate enormous amounts of data is another helpful talent. Finally, all data reporters must manage their data and display it in an easy-to-read style.
Basic Components of a Data Report
We’ve looked at the definition of data reports; now it’s time to look at the essential reports and data fundamentals, which are the foundations of business intelligence success.
Types of Data Report
A report can be classified into one of several types based on particular features. Why are they divided into types? Well, depending on the report’s objective, it’s always best to know which kind is better in that situation. Informal reports, for example, may not be appropriate in formal office settings. In that instance, even if your report is accurate and excellent, the organization, format, or language may work against you. Things like that shouldn’t get in the way of you getting your point across. So, for these and other reasons, let’s look at the different types of available reports to know how to use them.
1. Functional Report
Marketing reports, financial reports, analytical reports, and various other reports that perform a specific role are examples of these types of reports. Almost all reports may be classified into one of these groups. We can also integrate a single report for many kinds of reports.
2. Proposal Report
These reports are similar to analytical/problem-solving reports in that they are an extension of them. A proposal is a document that describes how one company can help solve a problem that they are facing. In a business, it is almost always necessary to prepare a report. Typically, the end aim is quite solution-oriented. Proposal reports are what we term these kinds of statements.
3. Informational and Analytical Report
Informational reports convey objective data from one organization to another and possibly to a broader system. Analytical reports (scientific research, feasibility studies, and personnel evaluations) document efforts to resolve real-world issues. These analytical studies frequently include recommendations at the conclusion.
4. Formal and Informal Report
Formal reports have a strict framework. They emphasize objectivity and structure, contain more detail, and require the writer to write in a style that avoids personal pronouns. Informal reports are usually brief communications written in a free-flowing, conversational tone. Internal reports/memorandums are often referred to as informal reports.
5. Periodic Report
Periodic reports are sent out at predetermined intervals. Their primary tendency is upward, and they act as management control in most circumstances. Some, such as yearly reports, are not vertical but are required by the government to be produced regularly. We have annual, quarterly, and half-yearly reports for this reason. If they happen so frequently, it only makes sense to pre-structure the reports and put in the data each period. That’s also what happens in the vast majority of cases.
6. Long and Short Report
As the name implies, these reports are incredibly straightforward. A two-page report, sometimes known as a memorandum, is short, whereas a thirty-page report is exceptionally long. But what distinguishes a clear distinction between short and long reports? More comprehensive reports, on the other hand, are frequently prepared in a formal tone.
7. Internal and External Report
An internal report stays within a specific organization or group of people, as the name implies. Internal reports are for use within the organization in office environments. We generate external reports for distribution outside the organization, such as news articles about firms’ occurrence or yearly reports. These are referred to as public reports.
How to Write a Data Report
We’ve covered the fundamentals; now it’s time to look at how to create data reports in practice. This is where our tips for documenting data in business reports come in handy. Each report type has its own set of rules and best practices. We will mention the most common ones below. Still, our primary focus will be on business data reports, which will ultimately provide you with a roadmap for increasing the productivity of your reports.
Step 1: Find out who your target market is.
Knowing who you’re conversing with will help you decide what data to present, what recommendations to make, and how to convey it. Upper, middle, or line management, other departments within the company, coworkers, the client, future clients, the government, or a company in the same industry may be among your target audiences. Knowing who you’re writing for can assist you in deciding what kind of material to include in your report. When a report is intended for internal use, branding elements such as colors, font, and logo are less critical. If you’re giving a one-time live presentation, printing formatting isn’t necessary. Determine whether your audience requires persuasion of knowledge ahead of time. If you’re speaking to the C-suite or the board, you might want to focus on high-level information with explicit callouts and action items. You may wish to provide more granular data and tools to interact with the data if the report is more exploratory.
Step 2: Make a thorough plan.
Plan your reporting strategy before you begin your analysis. What information does management need to make sound decisions? What data and information do your investors require? Consider the scope of the data you’ll require and how you intend to use it. Utilize as many data sources as possible. However, don’t go data-crazy and become bogged down in useless data. Of course, you must be adaptable and change the plan as needed, but a solid plan is essential. Maintaining a goal-oriented mindset will allow you to focus your efforts, save time in the long run, and improve the quality of your business reporting.
Step 3: Be Objective
An excellent business data report is impartial and neutral in describing the past, present, or potential future scenario. The term “objective” refers to a report that presents facts rather than opinions. Keep your views to a bare minimum. In addition, employing the passive voice in a report helps to keep it formal and objective. You’re effectively going away from your goal of obtaining real insights that will provide you a competitive edge if you’re too subjective or prejudiced with any data report style. Collect data from reputable sources, document your insights with precise accuracy, and you’ll be able to connect with objective insights that will propel your company forward.
Step 4: Be visually appealing.
A variety of data visualization techniques have shown to be quite effective. Decision-makers can more easily grasp challenging ideas or recognize new trends when analytics are presented visually. Humans are better at perceiving and digesting data when it is presented visually. When possible, data visuals should be used instead of text in reports. Ensure that you select the most appropriate data visualization for your data story and that you adhere to BI dashboard best practices. Anyone can generate relevant images and share them with their employees, customers, and other shareholders using the correct data reporting technology. All of this may be done without the use of a data scientist. Also, no matter how your report is shared or disseminated, make sure it retains its aesthetic appeal.
Step 5: Have a content that is well-written.
While images should take precedence, some data report kinds require text as well. Make sure your papers are written in a clear and even tone. Use language that is concise, energetic, and engaging. Instead of extensive paragraphs, use bullet points. For your visualizations, use headers, legends, and supplemental text. You should also proofread everything! Our guide to digital dashboard creation and best practices includes practical ideas that will help you format your reports for success so that you can make the most of your data analysis presentation and content.
FAQs
What characteristics distinguish an excellent data report?
An excellent business data report is impartial and neutral in describing the past, present, or potential future scenario. The term “objective” refers to a report that presents facts rather than opinions. Keep your views to a bare minimum.
What is the format of a report?
A report is essentially a brief, sharp, and concise document created for a specific purpose and audience. It usually lays out and analyzes a scenario or problem, with ideas for future action frequently included. It is a factual paper that must be well-structured and clear.
What is the definition of a media report?
Reports in the media promote your ideas and products in front of people, increasing brand awareness and driving sales agreements, but they only work if you can pique the reader’s interest right away. When producing a media report, your main goal is to persuade your reader to keep reading.
Now that you’ve mastered writing a data report, it’s time to control the power of modern business intelligence (BI) solutions and data analytics. When done correctly, task reports, analytics, and intelligent information processing can positively affect an organization. Fortunately, the tedious task of manually creating daily or weekly reports is no longer necessary. With the right plan and appropriate business reporting software, you can quickly analyze your data and create visually appealing and impressive data and project reports. We live in the information age – an era in which anything is possible. By embracing data-centric reports and laying the proper groundwork, you can accelerate your organization’s success. You have to follow these critical steps and recommendations, and you will have a prosperous commercial future.
