20+ SAMPLE Incident Analysis Reports in PDF
-
Critical Incident Reporting and Learning
download now -

Analysis Review Report Template
download now -

Incident Analysis Report Template
download now -

Incident Reporting Review
download now -

Annual Trend Analysis
download now -

Incident Reporting Policy
download now -
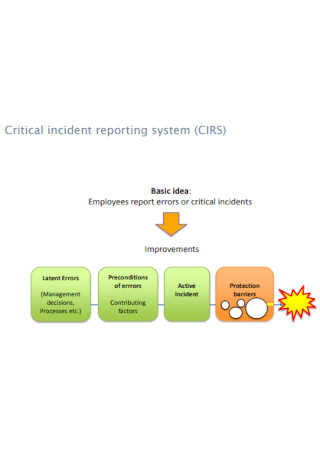
Analysis of Critical Incident Reports
download now -

Incident Analysis Report Sample
download now -

Sample Incident Investigation Report
download now -
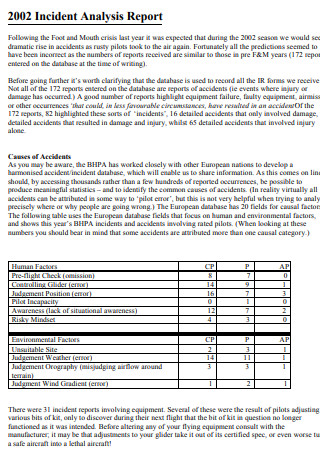
Incident Analysis Report Format
download now -

Medication Incident Reporting and Analysis
download now -

Incident Reporting & Policy and Procedure
download now -
Provider Incident Report Template
download now -

Incident Reporting & Automation
download now -

Analysis of Critical Incident Report
download now -
Printable Incident Analysis Report
download now -
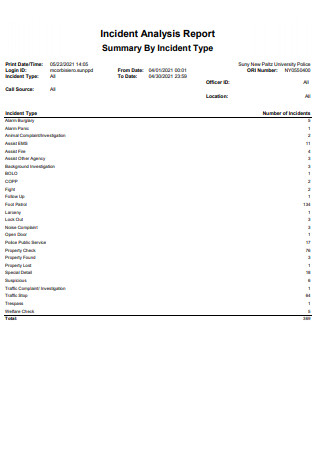
Simple Incident Analysis Report
download now -

Accident/Incident Reporting and Investigation
download now -

Incident Management Trend Analysis
download now -

Critical Incident Analysis Report
download now -
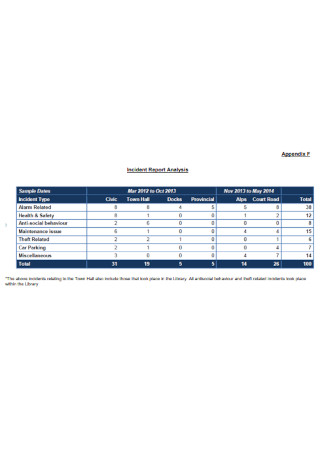
Incident Report Analysis Review
download now
FREE Incident Analysis Report s to Download
20+ SAMPLE Incident Analysis Reports in PDF
What Is an Incident Analysis Report?
Why Incident Reporting is Necessary
How to Write an Incident Analysis Report
Tips for Incident Analysis
FAQs
What is the difference between an accident and an incident?
When should an event be reported?
What should happen once you have completed an incident report?
What Is an Incident Analysis Report?
What happened, how and why it happened, what can be done to decrease the risk of recurrence and make care safer, and what was learned are all part of the incident analysis process. It’s part of the incident analysis report system, which encompasses all of the actions and processes that surround a company’s safety occurrence.
An incident analysis report gives a clear picture of where a company can improve. Every report’s documentation will allow data to be assembled, revealing which procedures need to be altered, enhanced, or deleted. The information obtained from a Data Analysis Report will aid management in enacting new rules and laws to keep employees safe.
Why Incident Reporting is Necessary
Incidents cannot be avoided in any given place even if the workplace employees and supervisors try their best to create a safe environment, some may still occur. This is why reporting incidents is critical in coming up with solutions to address the incident as well as act as a survey on what the best option could be followed. There are available Incident Report Forms for you to use if your company does not have one yet.
How to Write an Incident Analysis Report
Investigate workplace events to determine what caused them and how to avoid them in the future. You want to act fast on an immediate solution as soon as possible when catastrophe hits. Putting a band-aid on an issue, on the other hand, puts your company in danger of future occurrences, which might be even worse. Conducting a comprehensive incident analysis allows you to figure out why something happened, eliminate the main causes, and prevent future occurrences. Follow these steps to help you get started and view the available incident analysis report format for the reference.
Step 1: Gather the Whole Story
The initial stage in an incident examination is to collect as many facts as possible as fast as possible. Gather evidence by obtaining physical evidence, pictures, and videos from the scene of the event (if feasible), questioning the subject and victim (if appropriate), and interviewing witnesses, as well as analyzing documents such as emails, training records, computer history, policies, and procedures.
After obtaining information, create a chronology of events around the occurrence using the facts. What occurred prior to, during, and shortly following the incident? A precise timeline will assist you in determining the cause of the event as well as any issues with how it was handled. Above all, avoid blaming, judging, or making assumptions. At best, this will limit your inquiry; at worst, it will result in a wrongful termination case.
Step 2: Conduct a Root Cause Analysis
You may then begin a root cause analysis using the chronology of events. The process of determining the underlying causes of an occurrence is known as root cause analysis. A root cause is a fundamental flaw in an existing system or process inside your company that would have prevented the incident from occurring if it hadn’t been present.
Identify contributing variables to each key timeline event to conduct a root cause analysis. These are the incident’s secondary causes. Then inquire as to why each contributing element arose in the first place. Continue to question “why?” until you discover a flaw in one of your rules or practices.
Analyze the incident’s core causes as a group for the best outcomes. Include personnel from all levels and departments if at all feasible. You’ll hear from more people with different perspectives, and you could discover an issue you weren’t aware of.
Step 3: Distinguish Patterns
Many occurrences are not one-of-a-kind. If the conditions are right for an occurrence to happen once, chances are it will happen again.
Examine past case data as part of your incident examination. Is there a pattern to a specific sort of incident? Is there a tendency for one office or location to have more overall occurrences or incidents of a certain type? Do there seem to be more instances at various periods of the year? Is one individual responsible for a large number of incidents?
Use case management software with a data analysis tool to produce reports that indicate areas of risk in your business to make this process faster, easier, and more accurate.
Step 4: Come up with Correct and Prevent Actions
After you’ve discovered the trends and the main cause of the incident, come up with ideas for how to fix the current problems and avoid future occurrences.
Determine the remedial steps you’ll need to conduct following the event first. These steps eradicate the incident’s fundamental cause, ensuring that it does not happen again. Updating rules, altering training content and frequency, and replacing or recalibrating equipment are all examples of corrective action and installing or beefing up security measures including cameras, locks, and cybersecurity.
Decide what preventative steps you need to take as the final phase of your incident examination. Rather than reacting to an occurrence, a preventative measure tackles issues before they occur. These should be based on the patterns you discovered, as well as what you learned from the occurrence itself. Creating emergency plans, adopting new forms of staff training, conducting internal audits, reviewing policies and procedures yearly, and performing routine maintenance on equipment and data systems are all examples of preventative action.
After each event, your firm will be able to gain a clear view of its risks and possibilities for improvement by conducting an analysis. This can help you develop an efficient preventive program over time, reducing the number of incidents and accidents while also increasing safety and security throughout your company.
Tips for Incident Analysis
Analyzing information that you collected from an incident is just as important as writing the report post-incident as well. Any incident data collection and analysis proves to be helpful in obtaining information that could be vital for any given circumstance. Coming up with a Data Analysis Plan can help your company remain updated with the information you received and knowing how to go handle the data you have collected.
FAQs
What is the difference between an accident and an incident?
In general, an accident is an unintended, undesirable occurrence that occurred at random and could not be avoided. An unexpected, undesirable occurrence is also referred to as an incident, although the phrase is used differently because it might have been avoided. Regardless, either situation would be needed to create a Risk Management Action Plan to better provide a solution for them.
When should an event be reported?
All accidents, near misses, and injuries must be recorded as soon as possible. Fast incident reporting using mobile incident applications enables more accurate event information, better examinations, and quicker remedial measures. No employee should have to wonder if their situation is serious enough to warrant a complaint. Work Investigation Report may be necessary to properly examine the reports that each workplace receives.
What should happen once you have completed an incident report?
Any incident report should be treated carefully when it is submitted. The employee who filed the incident report should never face retaliation. Following the company’s incident report procedure, the employee who filled out the report should be questioned to confirm that all information has been gathered and that the occurrence has been properly comprehended. An incident examination, documentation of medical treatment provided, remedial measures taken, and preventative actions taken should all be part of the incident report follow-up procedure. Every report should be kept in a safe area, such as the incident and examination software used by the company. It’s also a good idea to discuss the threat at your next corporate safety meeting to come up with Risk Management Plan.
The data collected from incident reports may not be utilized to its full potential if it isn’t thoroughly given an analysis. This is why an incident analysis report serves its purpose in enhancing the solutions that may be brought up to solve incidents or at least minimize them in any given situation, be it in the workplace or in a public place. Everyone wants to work and function in a safe environment, after all.
