Incident Report Samples
-

Workplace Incident Report
download now -

Police Incident Report
download now -

Incident Report for Security Guard
download now -

Hospital Incident Report
download now -

Incident Report
download now -

Incident Report Confidential Information
download now -
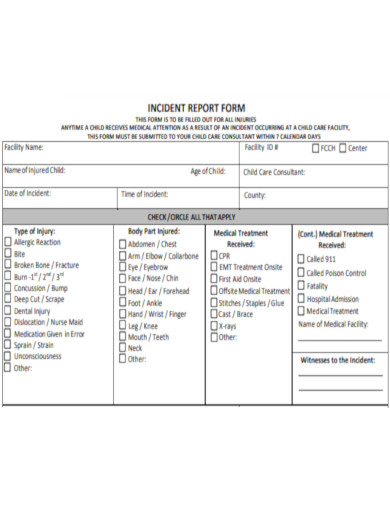
Incident Report Form
download now -
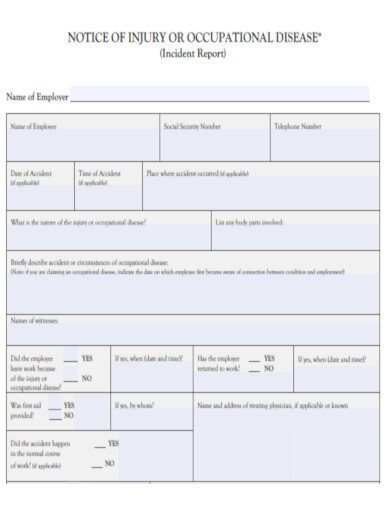
Notice of Injury Incident Report
download now -

General Incident Report
download now -
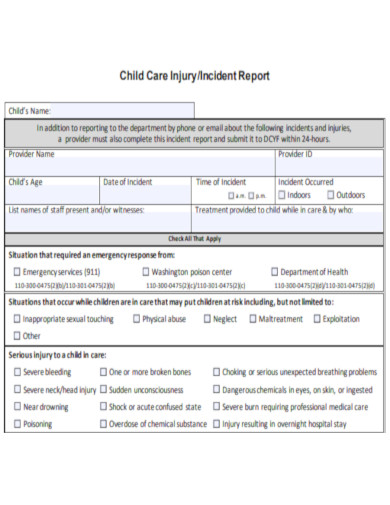
Child Care Injury Incident Report
download now -
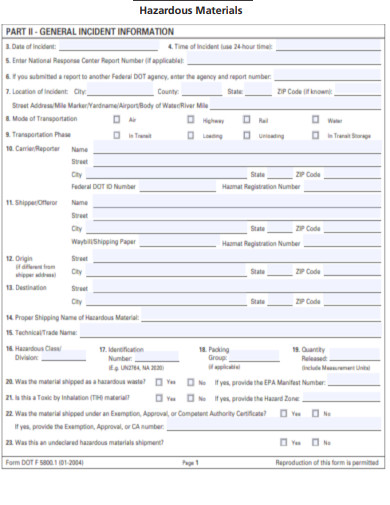
Hazardous Materials Incident Report
download now -
Incident Reporting Tool
download now -

Simple Incident Report Form
download now -

What is an Incident Report
download now -
Misconduct Incident Report
download now -

Basic Incident Report
download now -

Customer Service Incident Report
download now -

Facility Incident Report Form
download now -
Standard Incident Report
download now -
Unusual Incident Report
download now -

Audits and Investigation Incident Report
download now -
Professional Incident Report Form
download now -

Program Participant Incident Report
download now -

Fire Incident Report
download now -
Medicaid Incident Report
download now -
Animal Incident Report
download now -
Medication Incident Report
download now -
Vaccine Storage Handling Incident Report
download now -

Physician Office Adverse Incident Report
download now -
Incident Tracking Report
download now -
Incident Report Example
download now -

Adult Foster Home Incident Report
download now -

Editable Incident Report
download now -

Adverse Incident Report
download now -

Completing Incident Reports
download now -
Critical Incident Report
download now -

Free Incident Report
download now -

On the Job Injury Incident Report
download now -
Significant Incident Report
download now -

Global Learning Incident Report
download now -
Employee Incident Report
download now -

Work Zone Crash Incident Report
download now -
Medical Incident Report
download now -

Insurance Program Incident Report
download now -

Instructions for Completing the Incident Report Form
download now -
Volunteer Incident Report
download now -

Track & Field Incident Report
download now -

Biosafety Incident Report Form
download now -
Accident Incident Report
download now -

Serious Injury Incident Report
download now -

Printable Incident Report
download now -

Instructions Incident Report
download now -

Community Rowing Incident Report
download now -

Security Incident Report
download now -

Risk Management Incident Report
download now -
Operator Boating Incident Report
download now -
Contractor Incident Report System
download now
FREE Incident Report s to Download
Incident Report Format
Incident Report Samples
What is an Incident Report?
Benefits of Incident Reports at Work
Types of Incident Reports
How to Create an Incident Report
FAQs
What is a formal report format?
What is report writing?
What is the format of the report?
What is incident analysis?
How do incident reports help improve workplace safety?
What are the legal implications of not filing an incident report?
What are the key challenges in creating effective incident reports?

Download Incident Report Bundle
Incident Report Format
1. Incident Details
- Date of Incident: [Insert Date]
- Time of Incident: [Insert Time]
- Location of Incident: [Insert Location]
- Type of Incident: [e.g., Accident, Theft, Damage, Injury, etc.]
2. Reporter Information
- Name of Reporter: [Full Name]
- Position/Role: [Position or Role]
- Contact Information: [Phone Number/Email]
3. Individuals Involved
- Name(s): [List names of individuals involved, including witnesses]
- Role(s): [Indicate whether they are employees, visitors, witnesses, etc.]
- Contact Information: [Provide contact details for each individual]
4. Incident Description
- What Happened: [Provide a detailed description of the incident]
- Sequence of Events: [Step-by-step account of what led to the incident]
- Immediate Actions Taken: [Describe any actions taken to address the situation, such as first aid, securing the area, contacting authorities, etc.]
5. Damage/Impact
- Injuries (if any): [Describe the injuries sustained, if applicable]
- Property Damage (if any): [Detail any property affected]
- Other Impacts: [List any other consequences of the incident]
6. Witness Statements
- Witness Name: [Full Name]
- Contact Information: [Phone Number/Email]
- Statement: [Include a brief statement from the witness regarding what they saw or heard]
7. Evidence Collected
- Photographs/Videos: [Indicate if any visual evidence was collected]
- Documents/Reports: [Mention if any related documents were obtained]
8. Follow-Up Actions
- Planned Actions: [Describe steps to prevent similar incidents in the future]
- Reporting to Authorities: [Mention if law enforcement or other authorities were contacted]
- Other Notes: [Any other relevant information]
9. Reporter’s Signature
- Name: [Full Name]
- Signature: [Signature]
- Date: [Insert Date]
10. Supervisor’s Review (if applicable)
- Name: [Full Name]
- Position: [Position/Role]
- Signature: [Signature]
- Date: [Insert Date]
What is an Incident Report?
An incident report is a document used to document illnesses, injuries, near-misses, and accidents in the workplace. No matter the harm’s minor, an incident report must be filed immediately after its occurrence. Any illness or injury affecting a worker’s workability must be documented. What is legally necessary to be comprised in an incident report will differ based on the federal or provincial laws that apply to your business. Over eighty percent of industrial accidents worldwide are attributable, in whole or in part, to human mistakes. You can also see more on Incident Analysis Report.
Benefits of Incident Reports at Work

As a business or organization, having a protocol for incident reporting and a culture of open communication that encourages incident reporting is essential for maintaining workplace safety. You can also see more on Audit Incident Report. Here are five reasons why reporting workplace occurrences is crucial and how doing so may benefit employees and employers.
Types of Incident Reports
Incident reports come in various forms, each tailored to specific scenarios or environments. Here’s a detailed explanation of the common types of incident reports:
1. Workplace Incident Reports: Document workplace accidents, injuries, or hazardous conditions to ensure safety and legal compliance.
2. Security Incident Reports: Record breaches, thefts, or suspicious activities to enhance security and protect assets. You can also see more on Incident Violation Report.
3. Customer Incident Reports: Address incidents involving customers, such as injuries or disputes, to maintain trust and legal protection.
4. Environmental Incident Reports: Log environmental hazards like spills or emissions to minimize damage and ensure compliance.
5. Near Miss Reports: Capture incidents with potential harm to identify risks and prevent future occurrences. You can also see more on Medical Incident Report.
6. Property Damage Reports: Document damage to property or equipment for assessment and insurance claims.
7. Health and Safety Incident Reports: Record medical emergencies or safety violations to protect health and ensure regulations are met.
8. IT Incident Reports: Address issues like data breaches or system failures to safeguard IT systems and resolve problems.
9. Transportation Incident Reports: Track vehicle accidents or cargo damage in logistics to ensure safety and mitigate risks.
10. Educational Incident Reports: Log incidents in schools, such as bullying or injuries, to maintain a safe learning environment. You can also see more on Security Incident Report.
How to Create an Incident Report
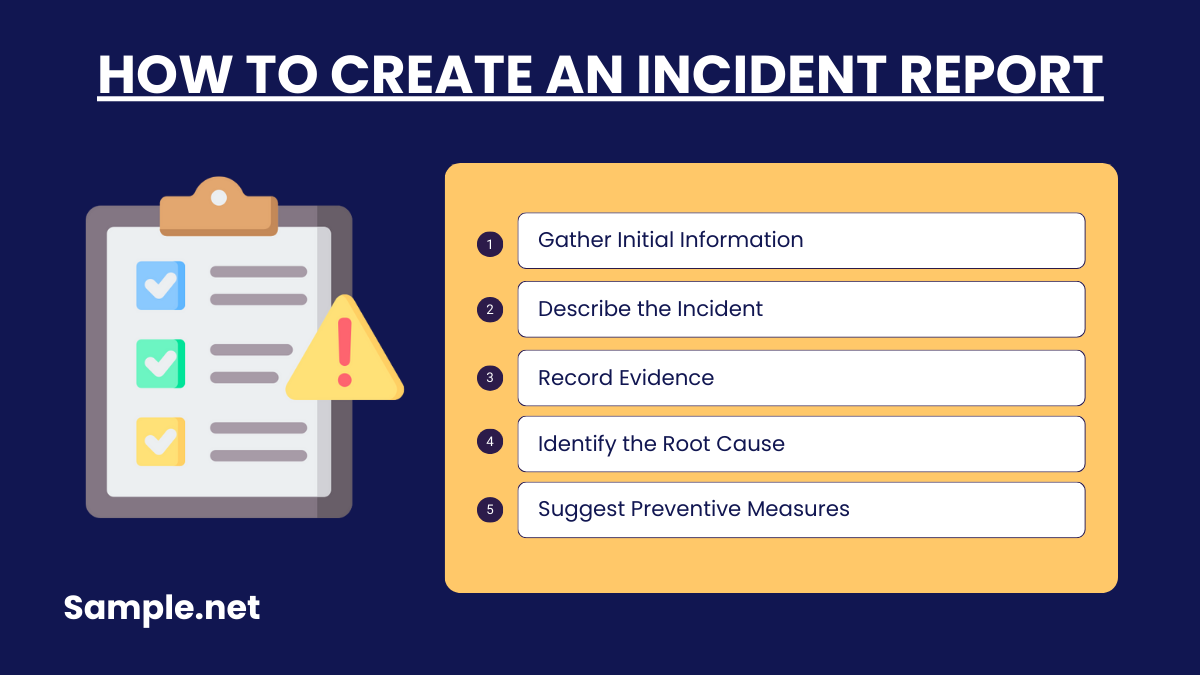
Step 1: Gather Initial Information
Begin by collecting the basics: the date, time, and location of the incident. Note down the names of everyone involved and any witnesses. Accuracy is crucial at this stage to ensure the report’s reliability.
Step 2: Describe the Incident
Provide a detailed account of what happened. Include the sequence of events, actions taken by the individuals involved, and any contributing factors. Use clear and objective language to avoid misinterpretation. You can also see more on Construction Incident Report.
Step 3: Record Evidence
Attach supporting materials, such as photographs, videos, or witness statements. These provide a visual and contextual understanding of the incident and strengthen the report’s credibility.
Step 4: Identify the Root Cause
Analyze the incident to determine its root cause. Consider environmental, human, or system-related factors. This analysis helps in proposing actionable solutions. You can also see more on Laboratory Incident Report.
Step 5: Suggest Preventive Measures
End the report with recommendations for preventing similar incidents in the future. This could include changes to procedures, training sessions, or the introduction of new safety measures.
Incident reports play a vital role in documenting and addressing unplanned events. They promote transparency and help organizations analyze causes and outcomes effectively. By addressing incidents thoroughly, organizations can identify root causes, implement preventive measures, and ensure a safer and more efficient environment for all involved, fostering continuous improvement. You can also see more on School Incident Report.
FAQs
What is a formal report format?
Formal reports are divided into three divisions, each having a distinct function. The report’s front section will include a cover letter and a summary of the information. In addition, the data will have a title page, a table of contents, and an abstract or summary.
What is report writing?
Report writing is a formal style of report that examines a subject in depth. A report’s tone is always proper. The intended audience is always considered in this section. For instance, writing an essay on a school event, writing a report on a business case, etc. The introduction and conclusion should each comprise roughly 10% of the total word count.
What is the format of the report?
A concise title for the report. Table of Contents: A page detailing the report’s contents. You must wait until you’ve completed the entire report to create this section, which provides an overview of the document. Introduce the subject of your report and what the reader will find within its pages.
What is incident analysis?
Incident analysis is a method for determining what transpired during an outage, such as which system components were involved and resolved. There are numerous approaches to conducting incident analysis. You can also see more on Job Incident Report.
How do incident reports help improve workplace safety?
Incident reports identify patterns and root causes of accidents, guiding organizations to enhance safety measures. By addressing these issues, future incidents can be minimized, creating a safer work environment.
What are the legal implications of not filing an incident report?
Failure to file an incident report can lead to legal issues, including non-compliance fines, loss of insurance claims, or weakened defense in lawsuits due to lack of documentation.
What are the key challenges in creating effective incident reports?
Common challenges include ensuring accuracy, avoiding bias, maintaining objectivity, and providing actionable insights. Proper training and clear guidelines can mitigate these challenges. You can also see more on Teacher Incident Report.
