Fast Food Business Plan Samples
-

Bank Internal Audit Report
download now -

Logistics Internal Audit Report
download now -

Church Internal Audit Report
download now -

Company Internal Audit Report
download now -

Simple Internal Audit Report Template
download now -

Internal Audit Report Template
download now -
Finance Internal Audit Report Template
download now -

Sample Internal Audit Report Template
download now -

HR Internal Audit Report Template
download now -
Food Safety Internal Audit Report Template
download now -

Internal Quality Audit Report Template
download now -

Internal Process Audit Report Template
download now -

General Internal Audit Report Template
download now -

Internal Audit Report Template
download now -
Internal Audit Quarterly Report
download now -
Internal Audit Division Report
download now -

Internal Audit Report Example
download now -

Internal Audit Annual Report
download now -

Standard Internal Audit Report
download now -

Internal Audit Report in PDF
download now -

Printable Internal Audit Report
download now -
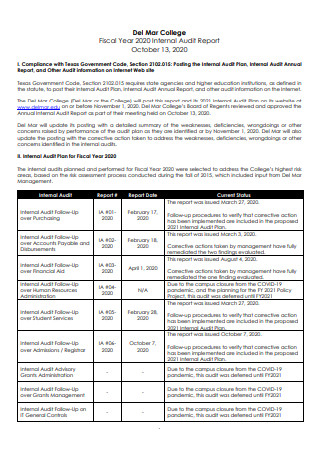
Fiscal Year Internal Audit Report
download now -

Simple Internal Audit Report
download now -

Internal Audit Report Letter
download now -

Basic Internal Audit Report
download now -

Internal Audit Activities Report
download now -

Expenditure Internal Audit Report
download now -

Internal Audit Creditor Report
download now -

Formal Internal Audit Report
download now -

Internal Audit and Compliance Report
download now -
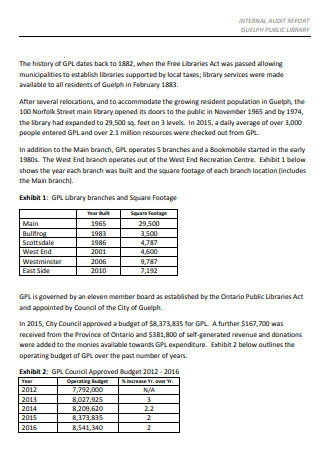
Public Library Internal Audit Report
download now -

Internal Audit Services Report
download now -
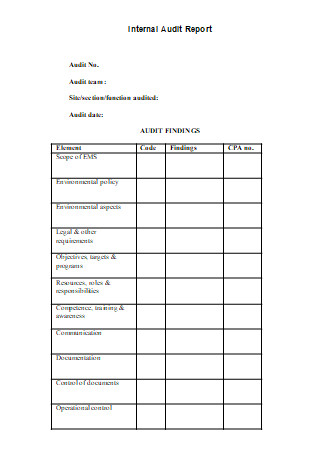
Draft Internal Audit Report
download now -
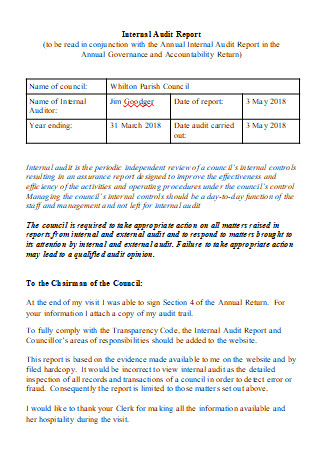
Internal Audit Report in DOC
download now -
Internal Audit Report Form
download now
FREE Internal Audit Report s to Download
Internal Audit Report Format
Fast Food Business Plan Samples
What is an Internal Audit Report?
Components of an Internal Audit Report
How to Create an Internal Audit Report
FAQs
How do you report internal audit findings?
What is the importance of creating an internal audit report?
What are the challenges of internal auditing?
What are the key benefits of an Internal Audit Report?
How does an Internal Audit Report help in risk management?
What role does an Internal Audit Report play in improving governance?

Download Internal Audit Report Bundle
Internal Audit Report Format
Title Page
- Title: Internal Audit Report
- Organization Name:
- Audit Area/Process Name:
- Date of Report:
- Prepared By: (Name of Auditor(s))
- Department:
Table of Contents (Optional for lengthy reports)
- Executive Summary
- Introduction
- Objectives and Scope
- Methodology
- Findings and Observations
- Recommendations
- Conclusion
- Action Plan
- Appendices
1. Executive Summary
- Brief overview of the audit purpose.
- Key findings (e.g., significant risks, process inefficiencies).
- Summary of critical recommendations.
- Overall audit opinion (e.g., Satisfactory, Needs Improvement, Unsatisfactory).
2. Introduction
- Purpose of the Audit: Why the audit was conducted.
- Audit Area/Scope: Departments, processes, or areas included.
- Audit Period: Timeframe of the audited processes.
- Audit Authority: Reference to internal policies, regulations, or laws authorizing the audit.
3. Objectives and Scope
- Objectives: Outline the specific goals of the audit. Examples:
- To ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- To assess operational efficiency.
- Scope: Define the boundaries (e.g., timeframe, processes, systems, or departments included).
4. Methodology
- Techniques Used: Describe the techniques applied to gather and analyze data (e.g., document review, interviews, walkthroughs, sampling).
- Criteria: Standards or benchmarks used to evaluate findings.
5. Findings and Observations
Format for Each Finding:
- Observation: Description of the issue or risk identified.
- Implications: Potential risks or impact of the issue (financial, operational, compliance-related, etc.).
- Root Cause: Analysis of why the issue occurred.
- Supporting Evidence: Details of data or documents reviewed to support the finding.
- Severity Rating: Critical/High/Medium/Low (optional but recommended).
6. Recommendations
- Actionable Steps: Provide specific, realistic, and measurable recommendations to address each finding.
- Priority Level: High, Medium, or Low.
- Responsible Party: Suggest which department or role should implement the recommendation.
7. Conclusion
- Summary: Recap the audit process and highlight overall results.
- Assurance Statement: Provide assurance on the audit’s integrity and objectivity.
- Acknowledgment: Optional recognition of cooperation from the audited team.
8. Action Plan
- Implementation Timeline: Suggest deadlines for implementing recommendations.
- Management’s Response: Include comments or commitments from management.
- Follow-Up: Details on when and how the implementation will be reviewed.
9. Appendices (Optional)
- Glossary of terms.
- Supporting documents or charts.
- Detailed risk matrices, if applicable
What is an Internal Audit Report?
An internal audit report is a document that contains the official results of internal auditing. The internal auditor utilizes this report to present the scope of the audit, outlining the positives, negatives, and significant conclusions. The information is what management needs to determine the smooth transactions of a company’s daily operations or implement necessary improvements to increase efficiency and performance plans. An audit report must be under intense scrutiny and preparation. The content must be clear, concise, understandable, impartial, and objective to guarantee that results are accurate and valuable to the organization. The report’s content must follow the standards for the business to utilize the information as a guide to set the company’s direction to follow necessary actions.
Components of an Internal Audit Report

Internal audit reports are necessary for organizations as it details any identified deficiencies and recommendations by internal auditors. There are no set standards for the format of an internal audit report. However, compiled below are the vital components you can find in one.
How to Create an Internal Audit Report

1. Define the Audit Scope and Objectives
Clearly outline the purpose of the audit, including the specific area, process, or function to be examined. Identify the audit’s objectives, such as evaluating financial records, reviewing operational processes, or ensuring compliance. Establishing a defined scope ensures focus and clarity throughout the audit process.
2. Conduct Thorough Data Collection
Gather relevant data, documents, and information related to the audit. This may include reviewing financial statements, operational records, or policy documents. Observing processes and interviewing key personnel helps provide a comprehensive understanding of the area under review. You can also see more on Audit Incident Reports.
3. Analyze and Identify Findings
Assess the data collected during the audit to identify strengths, weaknesses, and potential risks. Highlight areas where internal controls are effective and pinpoint gaps that need improvement. Use analytical tools or methods to present findings accurately and systematically.
4. Develop Recommendations and Action Plans
Based on the findings, provide detailed recommendations to address identified issues. Ensure that recommendations are practical, actionable, and aligned with organizational goals. Include timelines and responsible parties for implementing these recommendations.
5. Draft, Review, and Present the Report
Prepare a clear and concise report summarizing the audit’s objectives, scope, findings, and recommendations. Review the draft to ensure accuracy and completeness before presenting it to stakeholders. Use visuals like charts or graphs to enhance the report’s readability and impact. You can also see more on Non Profit Audit Report.
FAQs
How do you report internal audit findings?
Audit findings are effective when stakeholders understand the issues, risks, and impact on daily operations, and provide practical solutions. To improve audit communication with your target reader, have discussions with the auditee. It is also critical to report information based on facts. Remember to utilize precision and provide clarity to your audience reading the report. Sharing background information about the objective of the report and maintaining a constructive tone demonstrates effectiveness in gaining your reader’s attention. It is also fitting to review the document and be timely in the significance of corrective actions.
What is the importance of creating an internal audit report?
The internal auditor helps executive management and boards to demonstrate they are managing the company effectively through reporting the evaluation and countermeasures of perceived risks. The mission statement of internal auditors centers on their responsibility to enhance and protect organizational value by presenting assurance, advice, and insight.
What are the challenges of internal auditing?
Internal auditors suffer from challenges in the public sector, and these challenges are also prevalent in the private industry. The challenges are as follows:
- Lack of audit staff
- Internal audit functions do not gain sufficient support from management
- Lack of cooperation from other auditors
- Lack of training and independence
- Lack of competency and knowledge on auditing techniques
- Management does not consider recommendations and countermeasures
- Lack of experienced staff
- Low grading positions of internal auditors
- Negative perceptions from auditees
- Limited or lack of resources
What are the key benefits of an Internal Audit Report?
An Internal Audit Report identifies operational inefficiencies, assesses internal controls, and ensures compliance. It helps organizations mitigate risks, improve workflows, and build trust with stakeholders. Additionally, the report serves as a valuable tool for decision-making by providing detailed insights into the organization’s processes and risks.
How does an Internal Audit Report help in risk management?
By identifying and analyzing potential risks, the report enables organizations to take preventive actions. It highlights gaps in processes or controls that could lead to financial loss, operational disruption, or compliance issues. This proactive approach minimizes the likelihood of adverse events.
What role does an Internal Audit Report play in improving governance?
It enhances governance by promoting transparency, accountability, and informed decision-making. The report ensures that internal controls are effective, policies are followed, and risks are mitigated. This strengthens trust with stakeholders and aligns the organization with its strategic objectives. You can also see more on Construction Audit Report.
