Project Report Samples
-

Industrial Project Report
download now -

Bakery Project Report
download now -

College Project Report
download now -

Agriculture Project Report
download now -

Business Project Report Template
download now -

Construction Project Report Template
download now -

Real Estate Project Report Template
download now -

Project Report For New Business Template
download now -
Operational Plan For Project Report Template
download now -

Manufacturing Project Report Template
download now -
Project Weekly Status Report Template
download now -

Weekly Project Report Template
download now -

Project Report Template for Investors
download now -

Monthly Project Report Template
download now -

Sample Project Report For Investors Template
download now -

Project Report Gantt Chart Template
download now -

Free University Project Report Template
download now -

School Project Report Template
download now -

Project Report Template
download now -

Free Advertising Agency Project Report Template
download now -

Project Summary Report Template
download now -

Simple Project Expense Report Template
download now -

Project Analysis Report Template
download now -

Project Progress Report Template
download now -

Basic Project Summary Report Template
download now -

New Business Project Report Template
download now -

Petty Project Report Template
download now -

Project Report
download now -

Project Report Toolkit
download now -

Sample Project Report Guide
download now -

Detailed Project Report
download now -

Format for Internship Project Report
download now -

School Project Report
download now -

Formal Acknowledgement Project Report
download now -

Business Project Report
download now -
Education Project Bank Loan Report
download now -

Final Project Report Sample
download now -

Software Engineering Project Report
download now -
Preliminary Project Report Sample
download now -

Preparation of Project Report Executive Summary
download now -

Construction Project Information Report
download now -

Front Page Project Report
download now -

Writing Group Project Report
download now -

Major Project Report in PDF
download now -

Model Detailed Project Report
download now -

Simple Certificate Project Report
download now -

Project Report Progress
download now -

Good Project Report Cover
download now -

Basic Project Report First page
download now -

Introduction Monthly Status Report
download now -

Abstract Project Status Report
download now -

Solar Project Status Report
download now -
IT Project Status Report
download now -

Intermediate Project Report
download now -

Declaration of Major Project Report
download now -
Cumulative Project Status Report
download now -

Monthly Project Status Report
download now -
Sample Project Report Form
download now -

Project Report for Social Study
download now -

Metro Project Report Sample
download now -

Project Report Model
download now -

Simple Project Report Template
download now -

Team Project Report Sample
download now -

Project Final Report Outline
download now -

Project Final Report
download now -
Project Report Framework
download now -

Students Project Report Format
download now -

Project Development Report
download now -
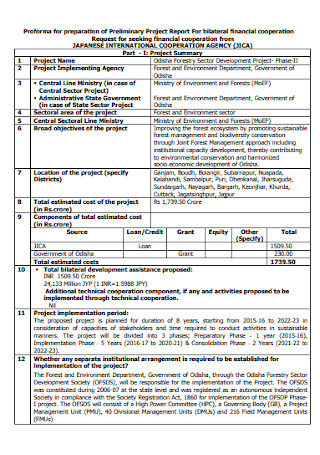
Preliminary Project Financial Report
download now -

Digital Project Report Template
download now -

Final Project Report Sample
download now -
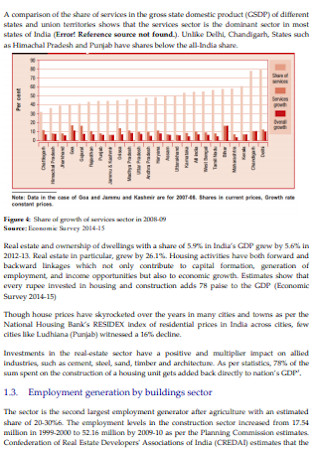
Building Project Report
download now -

Simple Project Report
download now -

B.Tech Project Report
download now -

Standard Project Report
download now -

Project Management Status Report
download now -

Sample Monthly Project Status Report
download now -

Staff Project Status Report
download now
FREE Project Report s to Download
Project Report Format
1. Title Page
2. Declaration (Optional)
3. Certificate (Optional)
4. Acknowledgement
5. Abstract/Executive Summary
6. Table of Contents
7. List of Figures, Tables, and Abbreviations
8. Introduction
9. Literature Review
10. Methodology
11. Project Plan
12. Implementation/Development
13. Results and Analysis
14. Discussion
15. Conclusion
16. Recommendations (Optional)
17. References/Bibliography
18. Appendices
19. Glossary (Optional)
20. Annexure (Optional)
Project Report Samples
What is a Project Report?
Purposes of a Project Report
How Do You Write a Project Report?
FAQs
What are the things I should include in my project report?
How to keep a project status report effective?
Why is a report form relevant?
What are the key mistakes to avoid when writing a project report?
How do you create a visually appealing project report?
What is the difference between a feasibility report and a project report?

Download Project Report Bundle
Project Report Format
1. Title Page
- Project Title (Bold, Centered, Large Font)
- Name of the Organization/Institution
- Team Members (Names, Roles, and Designations)
- Supervisor/Guide (Name, Designation)
- Submission Date (DD/MM/YYYY)
- Project Duration (Start Date – End Date)
- Logo (If applicable)
2. Declaration (Optional)
- A statement declaring that the project report is original and has not been submitted elsewhere.
- Signatures of the project members and date.
3. Certificate (Optional)
- Certificate from the institution or guide certifying the successful completion of the project.
4. Acknowledgement
- A section to thank individuals, guides, team members, and other contributors who supported the project.
5. Abstract/Executive Summary
- A brief overview of the entire project, including:
- Objective (1-2 sentences)
- Methods Used (1-2 sentences)
- Key Results/Findings (2-3 sentences)
- Conclusion (1-2 sentences)
- This section should not exceed 1 page.
6. Table of Contents
- List of all sections, subsections, and appendices with page numbers.
- Use proper hierarchical numbering (e.g., 1.1, 1.2.1, etc.).
7. List of Figures, Tables, and Abbreviations
- List of Figures: Title, figure number, and page number for all images, diagrams, and illustrations.
- List of Tables: Title, table number, and page number for all tables.
- Abbreviations: List of all the abbreviations and their full forms.
8. Introduction
- Background: Context or background of the project.
- Problem Statement: The problem that the project aims to solve.
- Objectives: Clear objectives or goals of the project.
- Scope: The scope and limitations of the project.
- Significance: Importance or impact of the project.
9. Literature Review
- A review of related studies, previous work, or similar projects.
- Identify gaps in existing work and explain how your project addresses them.
- Cite references in the appropriate format (APA, MLA, etc.).
10. Methodology
- Approach: The approach used to achieve the project objectives.
- Research Design: Details of research methods, techniques, or frameworks applied.
- Data Collection: Sources of data (primary or secondary) and methods used to collect it.
- Tools and Technologies Used: Software, hardware, or platforms utilized in the project.
- Data Analysis: The methods used to analyze and process the data.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): A breakdown of the project tasks and schedule.
11. Project Plan
- Timeline: Use Gantt charts, milestones, and deadlines.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Define who is responsible for each task.
- Risk Management: Identify possible risks and how they will be mitigated.
- Resource Allocation: Allocation of resources such as time, money, and human resources.
12. Implementation/Development
- System Design: Details of system architecture, flowcharts, or UML diagrams.
- Technical Specifications: Software/hardware requirements, configurations, etc.
- Development Stages: Key stages of development and their descriptions.
- Testing and Debugging: Explain how the system was tested and issues resolved.
- Challenges Faced: Issues or obstacles faced during implementation and how they were overcome.
13. Results and Analysis
- Data Presentation: Present data using charts, graphs, and tables.
- Findings: Key observations and discoveries from the project.
- Comparisons: Compare expected vs. actual results.
- Significance of Results: Discuss the significance of your findings.
14. Discussion
- Interpretation: Explanation of the results and their meaning.
- Relation to Objectives: Show how the results align with the initial objectives.
- Implications: Real-world implications of the project findings.
- Limitations: Acknowledge any limitations in the project.
- Future Work: Opportunities for future development, improvement, or extensions.
15. Conclusion
- Summarize the key aspects of the project.
- Restate the problem, approach, and results.
- Highlight the key achievements and contributions of the project.
- End with closing remarks on future possibilities.
16. Recommendations (Optional)
- Suggest recommendations for stakeholders, users, or developers.
- Provide insights for improvement or future work.
17. References/Bibliography
- List all the sources (books, journals, websites) cited in the project report.
- Follow an appropriate citation format (APA, MLA, etc.).
18. Appendices
- Raw Data: Raw survey data, results, or large tables.
- Additional Information: Any supporting material or detailed explanations that do not fit in the main body.
- Questionnaires/Forms: Sample forms, surveys, or interviews conducted as part of the project.
19. Glossary (Optional)
- Definitions of technical terms, industry jargon, or key concepts used in the report.
20. Annexure (Optional)
- Additional supporting materials such as certificates, legal documents, or project approvals.
What is a Project Report?
A project report is a structured document that outlines all essential details of a project, including its objectives, scope, progress, milestones, challenges, and results. It serves as a communication bridge between the project team and stakeholders. Typically used in business, academic, and engineering fields, a project report tracks project development, facilitates decision-making, and ensures accountability. It can be prepared at various project stages, such as initiation, progress, and closure, offering a clear overview of the project’s status. You can also see more on Project Implementation Report.
Purposes of a Project Report

1. Progress Tracking:
A project report helps track the progress of a project from start to finish. It highlights key milestones, completion rates, and ongoing activities, enabling project managers and stakeholders to assess whether the project is on schedule.
2. Stakeholder Communication:
Project reports serve as a communication bridge between the project team and stakeholders. They provide transparent updates on project developments, ensuring that stakeholders remain informed about the current status, risks, and changes. You can also see more on Group Project Report.
3. Risk Identification and Mitigation:
Project reports help identify potential risks and issues before they escalate. By highlighting existing and emerging challenges, project teams can take corrective actions, thereby mitigating risks and reducing the likelihood of project delays or failures.
4. Performance Analysis and Accountability:
Project reports assess the performance of the project team and its progress toward achieving objectives. This accountability encourages teams to stay focused and aligned with project goals, leading to improved performance and efficiency.
5. Informed Decision-Making:
Decision-makers and stakeholders rely on project reports to make strategic decisions. By presenting clear, data-driven insights, the report enables stakeholders to make timely, well-informed choices regarding budget adjustments, scope changes, or project continuation. You can also see more on Construction Project Report.
How Do You Write a Project Report?
Step 1: Define the Objective
The first step in creating a project report is to define its objective. Identify the purpose of the report, whether it is to provide a progress update, assess feasibility, or present the final outcomes. Clearly specify the intended audience, such as stakeholders, managers, or team members, and outline the key takeaways you want to communicate. This helps in setting the direction and scope of the report. Include an introduction that briefly explains the project, its goals, and the reporting period it covers.
Step 2: Gather Data and Information
Once the objective is clear, start gathering relevant data and information about the project. This data may include project timelines, tasks completed, milestones achieved, resources used, risks encountered, and financial details. Use tools like project management software, meeting notes, and performance dashboards to collect accurate and up-to-date information. Data visualization tools like charts, graphs, and infographics can make the report more understandable and impactful for stakeholders. You can also see more on Status Reports.
Step 3: Organize the Structure of the Report
Organize the report into a logical and easy-to-read structure. Common sections in a project report include:
- Title Page: Project title, team name, and date of submission.
- Table of Contents: A list of sections and page numbers for easy navigation.
- Executive Summary: A high-level overview of the report’s key points.
- Project Objectives: The goals and scope of the project.
- Progress and Milestones: Details of tasks completed, tasks pending, and current status.
- Challenges and Risks: List of risks encountered and how they were managed.
- Financial Analysis: Breakdown of costs, expenses, and return on investment (if applicable).
- Conclusions and Recommendations: Final thoughts and suggestions for future steps.
This structure provides a roadmap for the report, allowing readers to navigate the content with ease. You can also see more on Monthly Project Status Report.
Step 4: Write and Design the Report
Begin writing the content of the report, starting with the executive summary, which offers a concise snapshot of the entire report. Write each section clearly and concisely, ensuring it aligns with the objectives defined in Step 1. Use simple, professional language that is understandable to the target audience. Avoid excessive technical jargon, especially for stakeholders who may not be familiar with industry terms. Include visual elements like tables, graphs, and infographics to present complex information in a simple, engaging format.
Step 5: Review, Revise, and Finalize
After writing the report, review it thoroughly for grammatical errors, inaccuracies, and formatting issues. Ensure the data is correct, the visuals are clear, and the language is concise. Request feedback from project team members or supervisors to identify areas for improvement. Make revisions where necessary and finalize the layout to create a polished, professional document. Export the report as a PDF or print a hard copy, depending on the recipient’s preference. Finally, distribute it to stakeholders, clients, or team members to ensure transparency and facilitate better decision-making. You can also see more on Progress Report.
FAQs
What are the things I should include in my project report?
Your project report should contain facts related to a project including the following:
- Summary/Overall Health of the Project
- Facts on the Project Progress
- Target vs. Actual Accomplishments
- Analysis
- Actions Taken
- Risks and Issues
- Resources
- Budget
- Schedule
How to keep a project status report effective?
- Submit the report on time.
- Give complete and accurate information.
- Do not cover up bad news or adverse reports.
- Be proud of the team working on the project and their accomplishments.
- Anticipate questions from other people.
- Be familiar with the culture of the organization and respect the information hierarchy they follow.
- Craft the report without overloading it with too much information.
Why is a report form relevant?
In order to properly record the number of people who are infected by the coronavirus, authorities use report forms. When this is done properly, authorities will know how to fight back and curb Covid-19 cases globally. According to a report by Statista, there are 120,695,785 cases of coronavirus worldwide as of March 16, 2021. This number is increasing as of the moment of writing. This is only one of the many importance of report forms.
What are the key mistakes to avoid when writing a project report?
Key mistakes to avoid include poor organization, using technical jargon, inaccurate data, and lack of visual aids. Missing deadlines or omitting key stakeholders from the review process can also compromise the report’s quality. It is essential to review and proofread the document to maintain clarity and professionalism.
How do you create a visually appealing project report?
To make a project report visually appealing, use a professional template with clear headings, bullet points, and sections. Incorporate charts, graphs, and infographics to present data effectively. Use consistent font styles, colors, and page layout for a polished appearance. Ensure the design maintains clarity and readability while avoiding over-cluttered visuals. You can also see more on Process Report.
What is the difference between a feasibility report and a project report?
A feasibility report evaluates whether a project is viable before it begins, focusing on profitability, risks, and sustainability. In contrast, a project report tracks progress and provides a detailed assessment of the project once it is in progress. The feasibility report influences the decision to start the project, while the project report ensures transparency throughout its execution.
