Recommendation Report Samples
-

Financial Recommendation Report
download now -

Accounting Recommendation Report
download now -

Award Recommendation Report
download now -

Client Recommendation Report
download now -

Recommendation Report Template
download now -

Consulting Recommendations Report Template
download now -

Sample Recommendation Report
download now -

Simple Recommendation Report
download now -

Committee Recommendation Report
download now -

Business Recommendation Report
download now -

Technical Writing Recommendation Report
download now -

Recommendation Report Proposal
download now -

Student Recommendation Report
download now -

Basic Recommendation Report
download now -
Sample Recommendation Memo Report
download now -
Audit Recommendation Status Report
download now -

Recommendation Report Executive Summary
download now -
Feasibility Recommendation Report
download now -

Sample Marketing Recommendation Report
download now -

APA Recommendation Report
download now -
Introduction Recommendation Report
download now -

Sample Recommendation Report Outline
download now -

Engineering Recommendation Report
download now -

Recommendation Report Abstract
download now -

Sample Recommendation Product Report
download now -

Recommendation Assignment Report
download now -
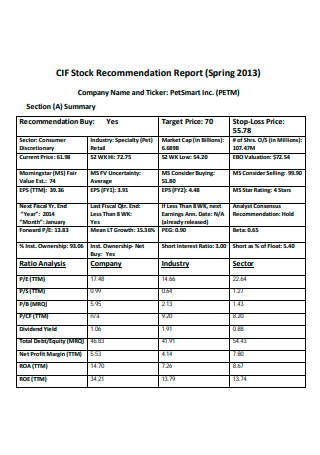
Problem Recommendation Report
download now -
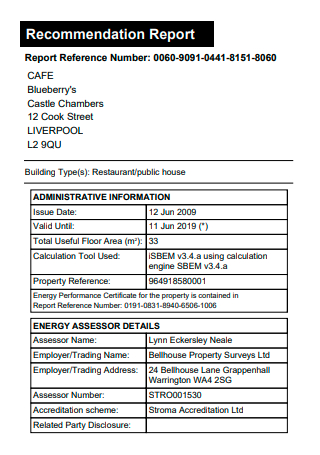
Internship Recommendation Report
download now -

Sample Technology Recommendation Report
download now -

Restaurant Recommendation Report
download now -

Climate Action Recommendation Report
download now -

Recommendation Management Report
download now -
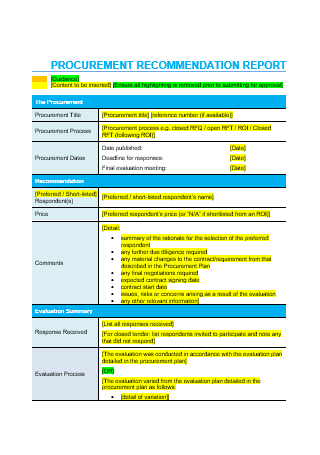
Sample Procurement Recommendation Report
download now -

Construction Recommendation Report
download now -

Appointment Recommendation Report
download now
FREE Recommendation Report s to Download
Recommendation Report Format
Recommendation Report Samples
a Recommendation Report?
Purposes of a Recommendation Report
How To Write a Recommendation Report
FAQs
What is the purpose of a recommendation after a report?
How is a reference report defined?
What is a report’s appendix?
What is the difference between a recommendation report and a feasibility report?
How should alternatives be compared in a recommendation report?
What role does research play in recommendation reports?

Download Recommendation Report Bundle
Recommendation Report Format
[Title of the Report]
[Your Name / Your Company Name]
[Date]
1. Executive Summary
Provide a brief overview of the report. Summarize the purpose, key findings, and your recommendation in 1-2 paragraphs.
2. Introduction
- Purpose: Explain why the report was created.
- Background: Provide context or background information relevant to the recommendation.
- Scope: Outline the boundaries of the analysis or recommendation.
3. Problem Statement
Clearly define the problem or opportunity the report addresses.
4. Analysis and Evaluation
Provide detailed information on your research, analysis, or evaluation process. Use subheadings for clarity.
- Methodology: Outline the approach you used to analyze the situation.
- Findings: Present key data, observations, or research results.
- Options Considered: Summarize the alternatives you evaluated, including pros and cons.
5. Criteria for Recommendation
Explain the criteria used to evaluate the options and justify your choice.
6. Recommendation
- Clearly state your recommendation.
- Explain how it meets the criteria and why it’s the best option.
7. Implementation Plan
Outline actionable steps to implement your recommendation. Include:
- Timeline
- Resources required
- Potential challenges and how to address them
8. Conclusion
Reiterate the recommendation and summarize the expected benefits.
9. Appendices (if applicable)
Include supporting documents, charts, or detailed data that back your analysis but are too detailed for the main report.
10. References (if applicable)
List all sources, research, and data you used in the report.
What is a Recommendation Report?
A recommendation report is a structured document designed to present findings, compare alternatives, and propose actionable suggestions. These reports are typically used in business, academic, or professional settings where decision-making needs data-driven support. The goal is to clearly communicate the best course of action to address a specific problem or opportunity, backed by detailed analysis and research. You can also see more on Status Reports.
Purposes of a Recommendation Report
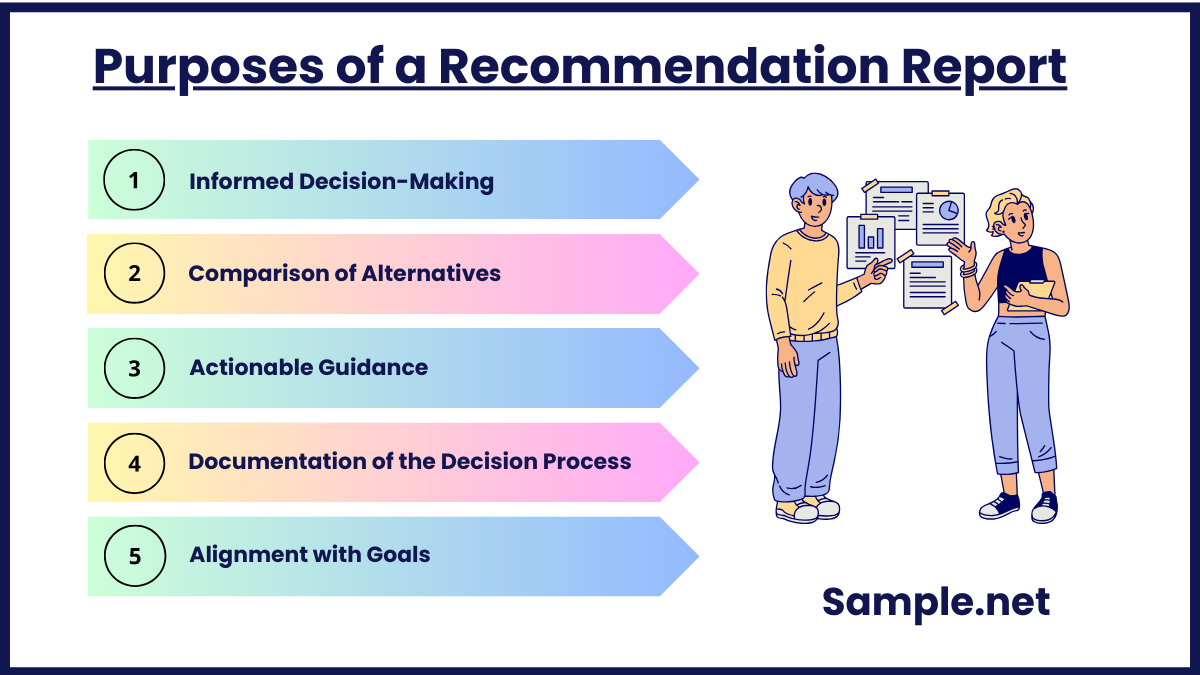
A recommendation report serves several essential purposes that make it a valuable document in decision-making and problem-solving. These include:
1. Informed Decision-Making
The primary purpose of a recommendation report is to provide stakeholders with clear, evidence-based information to make informed decisions. By analyzing data and evaluating options, the report format ensures decisions are grounded in logic and factual evidence.
2. Comparison of Alternatives
When multiple solutions or courses of action are available, a recommendation report systematically compares the alternatives. This helps stakeholders understand the pros and cons of each option, facilitating a well-reasoned choice.
3. Actionable Guidance
Recommendation reports go beyond mere analysis to provide specific, actionable suggestions. This clarity enables organizations or individuals to implement changes or strategies effectively. You can also see more on Visit Report.
4. Documentation of the Decision Process
These reports serve as a record of the decision-making process, documenting the rationale behind the chosen solution. This transparency is crucial for accountability and future reference.
5. Alignment with Goals
By focusing on the objectives and challenges at hand, recommendation reports ensure the proposed solutions align with organizational goals, policies, and resources, thereby driving strategic success. You can also see more on Process Report.
How To Write a Recommendation Report
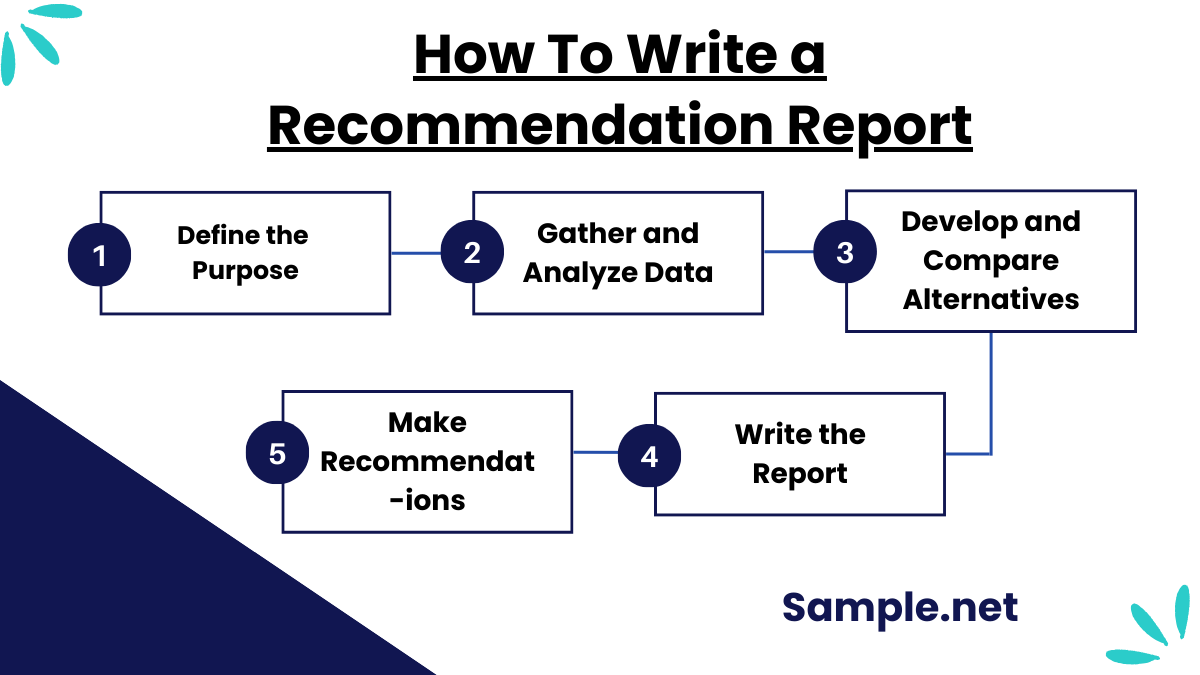
Typically, writing a recommendation report includes explaining a situation, analyzing various solutions, and recommending a remedy to a problem. The final report should include conclusions and recommendations that are detailed, precise, and evidence-based. Whether you’re writing a project, performance, or risk assessment, articulating the facts helps people make an informed conclusion based on your research.
Step 1: Define the Purpose
Start by identifying the problem or decision at hand. Clearly outline the scope and objectives of the report. This step ensures that the report remains focused on its purpose, addressing key issues and questions that need resolution.
Step 2: Gather and Analyze Data
Conduct thorough research to collect relevant data. Use credible sources like market research, case studies, and expert opinions. Analyze the data to identify patterns, insights, and viable options. You can also see more on Analytical Reports.
Step 3: Develop and Compare Alternatives
Identify potential solutions or courses of action. Evaluate each option against criteria such as cost, feasibility, and benefits. Highlight the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Step 4: Make Recommendations
Based on your analysis, select the best solution. Justify your recommendation with evidence and a clear rationale. Ensure the recommendation aligns with the objectives outlined in Step 1.
Step 5: Write the Report
Organize the report into a structured format, including an introduction, methodology, analysis, recommendations, and conclusion. Use clear language and visuals, such as charts or tables, to enhance understanding. You can also see more on Report Forms.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a recommendation after a report?
Although they serve distinct objectives, recommendations are frequently provided after a report. Whereas a conclusion allows you to summarize or examine the report’s essential points, recommendations indicate actions that should be made in response to the report’s findings.
How is a reference report defined?
A reference informs readers about the source in sufficient detail to understand its source, and typically, references are given after the lab report.
What is a report’s appendix?
Appendices contain too comprehensive information for the main report, such as lengthy mathematical derivations or calculations, detailed technical drawings, or raw data tables. The content should be summarized and referred to appropriately throughout the report’s body.
What is the difference between a recommendation report and a feasibility report?
A feasibility report examines whether a specific idea or project is practical, focusing on its viability. A recommendation report, however, evaluates multiple options and suggests the best course of action. While a feasibility report determines “if” something is possible, a recommendation report advises “what” should be done based on sample analysis.
How should alternatives be compared in a recommendation report?
Alternatives should be compared using criteria such as cost, feasibility, benefits, risks, and alignment with organizational goals. Use a consistent framework or matrix to evaluate each option. For example, a scoring system can help quantify the advantages and drawbacks of each solution, ensuring an objective comparison.
What role does research play in recommendation reports?
Research is the backbone of any recommendation report. It ensures the findings and recommendations are accurate, credible, and relevant. Without thorough research, the report lacks the necessary evidence to persuade decision-makers or justify the proposed actions. You can also see more on Research Analysis Report.
